
Electromagnetic Simulation Using the FDTD Method with Python
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Electromagnetic Simulation Using the FDTD Method with Python
About this book
Provides an introduction to the Finite Difference Time Domain method and shows how Python code can be used to implement various simulations
This book allows engineering students and practicing engineers to learn the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method and properly apply it toward their electromagnetic simulation projects. Each chapter contains a concise explanation of an essential concept and instruction on its implementation into computer code. Included projects increase in complexity, ranging from simulations in free space to propagation in dispersive media. This third edition utilizes the Python programming language, which is becoming the preferred computer language for the engineering and scientific community.
Electromagnetic Simulation Using the FDTD Method with Python, Third Edition is written with the goal of enabling readers to learn the FDTD method in a manageable amount of time. Some basic applications of signal processing theory are explained to enhance the effectiveness of FDTD simulation. Topics covered in include one-dimensional simulation with the FDTD method, two-dimensional simulation, and three-dimensional simulation. The book also covers advanced Python features and deep regional hyperthermia treatment planning.
Electromagnetic Simulation Using the FDTD Method with Python:
- Guides the reader from basic programs to complex, three-dimensional programs in a tutorial fashion
- Includes a rewritten fifth chapter that illustrates the most interesting applications in FDTD and the advanced graphics techniques of Python
- Covers peripheral topics pertinent to time-domain simulation, such as Z-transforms and the discrete Fourier transform
- Provides Python simulation programs on an accompanying website
An ideal book for senior undergraduate engineering students studying FDTD, Electromagnetic Simulation Using the FDTD Method with Python will also benefit scientists and engineers interested in the subject.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
ONE‐DIMENSIONAL SIMULATION WITH THE FDTD METHOD
1.1 ONE‐DIMENSIONAL FREE‐SPACE SIMULATION
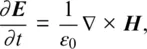
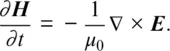
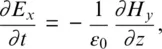
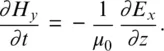
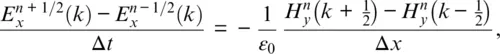
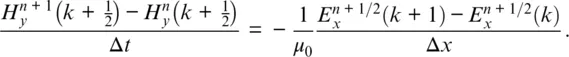
Table of contents
- COVER
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
- ABOUT THE AUTHORS
- PREFACE
- GUIDE TO THE BOOK
- 1 ONE‐DIMENSIONAL SIMULATION WITH THE FDTD METHOD
- 2 MORE ON ONE‐DIMENSIONAL SIMULATION
- 3 TWO‐DIMENSIONAL SIMULATION
- 4 THREE‐DIMENSIONAL SIMULATION
- 5 ADVANCED PYTHON FEATURES
- 6 DEEP REGIONAL HYPERTHERMIA TREATMENT PLANNING
- APPENDIX A: THE Z TRANSFORMTHE Z TRANSFORM
- APPENDIX B: ANALYTIC SOLUTION TO CALCULATING THE ELECTRIC FIELDANALYTIC SOLUTION TO CALCULATING THE ELECTRIC FIELD
- INDEX
- END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app