
- 432 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Organozinc Reagents in Organic Synthesis
About this book
Organozinc reagents are used extensively in organic synthesis to find useful pathways to organic products. Illustrated and tabulated with over 950 equations, schemes, tables, and figures, Organozinc Reagents in Organic Synthesis provides an overall picture of the chemistry of organozinc compounds. Written by a professor of organic chemistry, the book familiarizes the reader with the reactions involving organozinc reagents that have general usefulness in synthesis. Emphasis is placed on preparation methods and reactivity of organozinc reagents. Reactions are summarized in equations and schemes, making it easy for you to see the characteristics of each type of reaction.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Organozinc Reagents in Organic Synthesis by Ender Erdik, Charles W. Rees in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Science History. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Structure and Reactivity of Organozinc Reagents
Organozinc reagents form one of the first classes in the main group of organometallic compounds. A number of methods are available for efficient and rapid preparation of organozinc reagents, and they react with various organic electrophiles in high yields. Organozinc reagents also show excellent functional group tolerance, and reactions of the functional group-bearing organozinc cuprates prepared by transmetallation of organozinc reagents prior to the reaction allow construction of polyfunctional molecules without the need to use protection-deprotection or functional group interconversion methodologies. Especially cross-coupling and conjugate-addition reactions of organozinc reagents can also be catalyzed by transition metal salts, and catalyzed reactions have advantages over the conventional ones for the control of the regio- and stereoselectivity. In addition, the use of electrophilic or nucleophilic chiral catalysts in the reactions of organozinc reagents with carbonyl substrates, which is one of the most fundamental operations in organic synthesis, leads to highly stereoselective additions. There has been an increasingly large amount of research devoted to organozinc chemistry in recent years.
1.1 HISTORICAL BACKGROUND AND LITERATURE OF ORGANOZINC CHEMISTRY
The ability of organozinc reagents to promote C-C bond formation with electrophiles has been recognized since the mid-1800s. The direct reaction of organic halides with zinc dates back to the work of Frankland1,2 in 1849. Frankland discovered that the reaction of methyl iodide and ethyl iodide with zinc in a sealed tube produced alkylzinc iodides, which upon heating, yielded dimethylzinc and diethylzinc (Equation 1.1).1 Frankland also observed that the formation of dimethylzinc was accelerated very much by the addition of dimethyl ether or diethyl ether, but he found the dimethylzinc to be inseparable from ether.3 Almost after one hundred years, it was established that a 1:1 complex of dimethylzinc and dimethyl ether is formed, and that it can be dissociated in the vapor phase.4 Frankland prepared dimethylzinc also by reacting dimethylmercury with zinc (Equation 1.2).5 The complex-forming ability of organozinc compounds was recognized in 1858 when Wanklyn reported the formation of triethylsodium zincate, Et3 ZnLi.6 The reactions of organozinc reagents with acyl halides,7 aldehydes and ketones,8,9 and esters10 were all described before 1880. Reactions of organozinc reagents with acyl halides for the synthesis of ketones were stimulated by the extensive work of Blaise11 during the period of 1900–1915. Reformatsky showed the in situ formation of ethyl 2-bromozincioacetate, i.e., Reformatsky reagent, BrZnC2COOEt in 1887.12,13 Almost 70 years later, its isolated preparation was successful.14 Reactions of Reformatsky reagent with various carbonyl substrates were reported by 1910.15
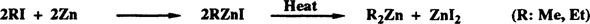 | (1.1) |
 | (1.2) |
At the beginning of the nineteenth century, organozinc reagents, except for Reformatsky reagents, were replaced by more reactive Grignard reagents, and have been considered as unreactive organometallics with limited applications in organic synthesis. However, in recent years, the high-yield preparation of organozinc reagents, their functional group tolerance, the high-yield reactions of organozinc cuprates and organozinc reagent/transition metal catalyst systems, and control of the stereoselectivity of their reactions using chiral transition catalysts, have rendered organozinc reagents again very useful as organometallic compounds in organic synthesis, and the use of organozinc reagents in organic synthesis is a research topic of current interest.
A very extensive survey of organozinc chemistry up to 1973 is given in Houben-Weyl.16 In Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry,17 a chapter is devoted to zinc and cadmium. In Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry II, Volume 3 is devoted to copper and zinc groups,18 and the use of organozinc and cadmium reagents in organic synthesis is covered in Volume 11.19 Comprehensive Organic Synthesis contains a chapter on the synthetic applications of organozinc, cadmium, and mercury compounds.20 Physical data and references for preparation of organozinc reagents up to 1985 are collected in a book.21 The literature of organozinc chemistry up to 196622 and the literature of organozinc coordination chemistry up to 196823 are covered in monographs. The Chemistry of Metal-Carbon Bond Series, Volume 3 by Patai,24 Organometallics in Organic Synthesis, by Negishi,25 Organometallic Reagents in Organic Synthesis by Bateson and Mitchell26 and Organometallic Reagents in Organic Synthesis by Schlosser27 contain useful references for organozinc chemistry.
A considerable number of reviews on the synthetic use of organozinc reagents have appeared. General reviews27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35 are considered here, and specific reviews will be given in related chapters. There is an extensive review covering the synthetic applications of organozincs up to 1973.28 The two important characteristic properties of organozinc chemistry (i.e., the use of functiona...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- The Author
- Table of Contents
- Abbreviations Used
- Chapter 1 Structure and Reactivity of Organozinc Reagents
- Chapter 2 Preparation of Organozinc Reagents
- Chapter 3 Addition of Organozinc Reagents to Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds
- Chapter 4 Addition of Organozinc Reagents to Carbonyl Groups
- Chapter 5 Addition of Organozinc Reagents to Carbon-Nitrogen Multiple Bonds
- Chapter 6 Conjugate Addition of Organozinc Reagents
- Chapter 7 Substitution at Carbon by Organozinc Reagents (Coupling Reactions of Organozinc Reagents)
- Chapter 8 Formation of C-H, C-Halogen, C-O, C-S, C-N, C-P, C-Si, C-Ge, C-Sn, and C-Pb Bonds via Organozinc Reagents, Organozinc-type Reactions in Aqueous Medium for the Formation of C-C Bonds
- References
- Author Index
- Subject Index