
Modern Information Processing
From Theory to Applications
- 478 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Modern Information Processing
From Theory to Applications
About this book
The volume "Modern Information Processing: From Theory to Applications, " edited by Bernadette Bouchon-Meunier, Giulianella Coletti and Ronald Yager, is a collection of carefully selected papers drawn from the program of IPMU'04, which was held in Perugia, Italy. The book represents the cultural policy of IPMU conference which is not focused on narrow range of methodologies, but on the contrary welcomes all the theories for the management of uncertainty and aggregation of information in intelligent systems, providing a medium for the exchange of ideas between theoreticians and practitioners in these and related areas.The book is composed by 7 sections: UNCERTAINTYPREFERENCESCLASSIFICATION AND DATA MININGAGGREGATION AND MULTI-CRITERIA DECISION MAKINGKNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION•The book contributes to enhancement of our ability to deal effectively with uncertainty in all of its manifestations. •The book can help to build brigs among theories and methods methods for the management of uncertainty. •The book addresses issues which have a position of centrality in our information-centric world. •The book presents interesting results devoted to representing knowledge: the goal is to capture the subtlety of human knowledge (richness) and to allow computer manipulation (formalization). •The book contributes to the goal: an efficient use of the information for a good decision strategy.APPLIED DOMAINS· The book contributes to enhancement of our ability to deal effectively with uncertainty in all of its manifestations.· The book can help to build brigs among theories and methods methods for the management of uncertainty.· The book addresses issues which have a position of centrality in our information-centric world.· The book presents interesting results devoted to representing knowledge: the goal is to capture the subtlety of human knowledge (richness) and to allow computer manipulation (formalization).· The book contributes to the goal: an efficient use of the information for a good decision strategy.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Entropies, Characterizations, Applications and Some History
Abstract
1 INTRODUCTION, ENTROPY
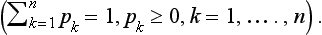
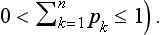
2 SHANNON ENTROPY
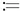
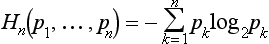
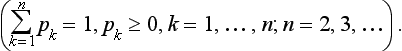
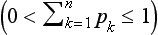
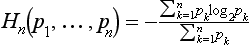
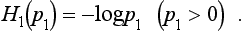
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Inside Front Cover
- Copyright
- Foreword
- Uncertainty
- Preferences
- Classification and Data Mining
- Aggregation and Multi-Criteria Decision Making
- Knowledge Representation
- Applied Domains
- Author Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app