
eBook - ePub
Exergy
Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development
- 472 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
This book deals with exergy and its applications to various energy systems and applications as a potential tool for design, analysis and optimization, and its role in minimizing and/or eliminating environmental impacts and providing sustainable development. In this regard, several key topics ranging from the basics of the thermodynamic concepts to advanced exergy analysis techniques in a wide range of applications are covered as outlined in the contents.- Comprehensive coverage of exergy and its applications- Connects exergy with three essential areas in terms of energy, environment and sustainable development- Presents the most up-to-date information in the area with recent developments- Provides a number of illustrative examples, practical applications, and case studies - Easy to follow style, starting from the basics to the advanced systems
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Exergy by Marc A Rosen,Ibrahim Dincer,Marc A. Rosen in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Environmental Science. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
THERMODYNAMIC FUNDAMENTALS
Publisher Summary
Thermodynamics plays a key role in the analysis of processes, systems, and devices in which energy transfers and energy transformations occur. Energy, entropy, and exergy concepts stem from thermodynamics and are applicable to all fields of science and engineering. This chapter focuses on the portion of the field of thermodynamics at the intersection of the energy, entropy, and exergy fields. It provides the necessary background for understanding these concepts, as well as basic principles, general definitions, and practical applications and implications. Illustrative examples are shown to highlight the important aspects of energy, entropy, and exergy. Energy management opportunities often exist to improve the effectiveness and efficiency with which energy is used. Most thermodynamic systems possess energy, entropy, and exergy, and thus appear at the intersection of these three fields. The basic phenomena like order and disorder as well as reversibility and irreversibility are also discussed. During the past several decades, exergy-related studies have received increasing attention from various disciplines ranging from mechanical and chemical engineering to environmental engineering and ecology. As a consequence, the international exergy community has expanded significantly in recent years.
1.1 Introduction
Energy, entropy and exergy concepts stem from thermodynamics and are applicable to all fields of science and engineering. This chapter provides the necessary background for understanding these concepts, as well as basic principles, general definitions and practical applications and implications. Illustrative examples are provided to highlight the important aspects of energy, entropy and exergy.
The scope of this chapter is partly illustrated in Fig. 1.1, where the domains of energy, entropy and exergy are shown. This chapter focuses on the portion of the field of thermodynamics at the intersection of the energy, entropy and exergy fields. Note that entropy and exergy are also used in other fields (such as statistics and information theory), and therefore they are not subsets of energy. Also, some forms of energy (such as shaft work) are entropy-free, and thus entropy subtends only part of the energy field. Likewise, exergy subtends only part of the energy field since some systems (such as air at atmospheric conditions) possess energy but no exergy. Most thermodynamic systems (such as steam in a power plant) possess energy, entropy and exergy, and thus appear at the intersection of these three fields.
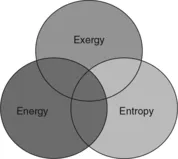
1.2 Energy
Energy comes in many forms. Thermodynamics plays a key role in the analysis of processes, systems and devices in which energy transfers and energy transformations occur. The implications of thermodynamics are far-reaching and applications span the range of the human enterprise. Throughout our technological history, our ability to harness energy and use it for society’s needs has improved. The industrial revolution was fueled by the discovery of how to exploit energy in a large scale and how to convert heat into work. Nature allows the conversion of work completely into heat, but heat cannot be entirely converted into work, and doing so requires a device (e.g., a cyclic engine). Engines attempt to optimize the conversion of heat to work.
1.2.1 Applications of energy
Most of our daily activities involve energy transfer and energy change. The human body is a familiar example of a biological system in which the chemical energy of food or body fat is transformed into other forms of energy such as heat and work. Engineering applications of energy processes are wide ranging and include power plants to generate electricity, engines to run automobiles and aircraft, refrigeration and air-conditioning systems, etc.
Many examples of such systems are discussed here. In a hydroelectric power system, the potential energy of water is converted into mechanical energy through the use of a hydraulic turbine. The mechanical energy is then converted into electric energy by an electric generator coupled to the shaft of the turbine. In a steam power generating plant, chemical or nuclear energy is converted into thermal energy in a boiler or a reactor. The energy is imparted to water, which vaporizes into steam. The energy of the steam is used to drive a steam turbine, and the resulting mechanical energy is used to drive a generator to produce electric power. The steam leaving the turbine is then condensed, and the condensate is pumped back to the boiler to complete the cycle. Breeder reactors use uranium-235 as a fuel source and can produce some more fuel in the process. A solar power plant uses solar concentrators (parabolic or flat mirrors) to heat a working fluid in a receiver located on a tower, where a heated fluid expands in a turbogenerator as in a conventional power plant. In a spark-ignition internal combustion engine, chemical energy of fuel is converted into mechanical work. An air–fuel mixture is compressed and combustion is initiated by a spark device. The expansion of the combustion gases pushes against a piston, which results in the rotation of a crankshaft. Gas turbine engines, commonly used for aircraft propulsion, convert the chemical energy of fuel into thermal energy that is used to run a gas turbine. The turbine is directly coupled to a compressor that supplies the air required for combustion. The exhaust g...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- PREFACE
- ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- ABOUT THE AUTHORS
- Chapter 1: THERMODYNAMIC FUNDAMENTALS
- Chapter 2: EXERGY AND ENERGY ANALYSES
- Chapter 3: EXERGY, ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
- Chapter 4: APPLICATIONS OF EXERGY IN INDUSTRY
- Chapter 5: EXERGY IN POLICY DEVELOPMENT AND EDUCATION
- Chapter 6: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF PSYCHROMETRIC PROCESSES
- Chapter 7: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- Chapter 8: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF DRYING PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS
- Chapter 9: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEMS
- Chapter 10: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS
- Chapter 11: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF STEAM POWER PLANTS
- Chapter 12: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF COGENERATION AND DISTRICT ENERGY SYSTEMS
- Chapter 13: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF CRYOGENIC SYSTEMS
- Chapter 14: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF CRUDE OIL DISTILLATION SYSTEMS
- Chapter 15: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF FUEL CELL SYSTEMS
- Chapter 16: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT FLIGHT SYSTEMS
- Chapter 17: EXERGEOCONOMIC ANALYSIS OF THERMAL SYSTEMS
- Chapter 18: EXERGY ANALYSIS OF COUNTRIES, REGIONS AND ECONOMIC SECTORS
- Chapter 19: EXERGETIC LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT
- Chapter 20: EXERGY AND INDUSTRIAL ECOLOGY
- Chapter 21: CLOSING REMARKS AND FUTURE EXPECTATIONS
- NOMENCLATURE
- REFERENCES
- Appendix A: GLOSSARY OF SELECTED TERMINOLOGY
- Appendix B: CONVERSION FACTORS
- Appendix C: THERMOPHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- INDEX