
- 304 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Mass Spectrometry for the Clinical Laboratory
About this book
Mass Spectrometry for the Clinical Laboratory is an accessible guide to mass spectrometry and the development, validation, and implementation of the most common assays seen in clinical labs. It provides readers with practical examples for assay development, and experimental design for validation to meet CLIA requirements, appropriate interference testing, measuring, validation of ion suppression/matrix effects, and quality control. These tools offer guidance on what type of instrumentation is optimal for each assay, what options are available, and the pros and cons of each. Readers will find a full set of tools that are either directly related to the assay they want to adopt or for an analogous assay they could use as an example.Written by expert users of the most common assays found in a clinical laboratory (clinical chemists, toxicologists, and clinical pathologists practicing mass spectrometry), the book lays out how experts in the field have chosen their mass spectrometers, purchased, installed, validated, and brought them on line for routine testing.The early chapters of the book covers what the practitioners have learned from years of experience, the challenges they have faced, and their recommendations on how to build and validate assays to avoid problems. These chapters also include recommendations for maintaining continuity of quality in testing. The later parts of the book focuses on specific types of assays (therapeutic drugs, Vitamin D, hormones, etc.). Each chapter in this section has been written by an expert practitioner of an assay that is currently running in his or her clinical lab.- Provides readers with the keys to choosing, installing, and validating a mass spectrometry platform- Offers tools to evaluate, validate, and troubleshoot the most common assays seen in clinical pathology labs- Explains validation, ion suppression, interference testing, and quality control design to the detail that is required for implementation in the lab
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Mass spectrometry in the clinical laboratory: determining the need and avoiding pitfalls
Abstract
Keywords
1. Clinical mass spectrometry
1.1. Basic mass spectrometry concepts
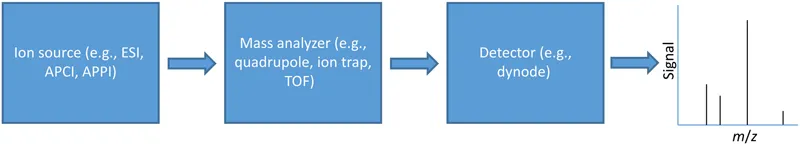
1.2. Common ion sources for clinical mass spectrometry
| Ionization Technique | Advantages | Limitations |
| ESI | • Sensitive ionization technique for polar analytes or ions generated in solution • Has broad applicability for relevant analytes in clinical MS • May yield multiply charged ions, which allows for analysis of larger molecules (i.e., >1000 Da) | • May be more sensitive to matrix effects compared to APCI |
| APCI | • Typically less sensitive to matrix effects than ESI • May provide better sensitivity for less polar analytes | • Typically only singly charged ions are formed, limiting the effective mass range, • May be unsuitable for thermally labile analytes • May yield less absolute signal relative to ESI |
| APPI | • Works well with nonpolar analytes • In some cases will ionize analytes that do not ionize by either ESI or APCI. | • Demonstrates limited applicability in clinical MS to date. |
1.2.1. Electrospray Ionization (ESI)
1.2.2. Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization (APCI)
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- List of Contributors
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Mass spectrometry in the clinical laboratory: determining the need and avoiding pitfalls
- Chapter 2: Application specific implementation of mass spectrometry platform in clinical laboratories
- Chapter 3: Sample preparation techniques for mass spectrometry in the clinical laboratory
- Chapter 4: Validation, quality control, and compliance practice for mass spectrometry assays in the clinical laboratory
- Chapter 5: Best practices for routine operation of clinical mass spectrometry assays
- Chapter 6: Toxicology: liquid chromatography mass spectrometry
- Chapter 7: Toxicology: GCMS
- Chapter 8: Therapeutic drug monitoring using mass spectrometry
- Chapter 9: Vitamin D metabolite quantitation by LC-MS/MS
- Chapter 10: Steroid hormones
- Chapter 11: Mass spectrometry in the clinical microbiology laboratory
- Chapter 12: High resolution accurate mass (HRAM) mass spectrometry
- Chapter 13: Evolving platforms for clinical mass spectrometry
- Index
