
- 400 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Multi-Level Methods in Lubrication
About this book
Efficient numerical solution of realistic and, therefore, complex equation systems occupies many researchers in many disciplines. For various reasons, but mainly in order to approximate reality, a very large number of unknowns are needed. Using classical techniques, the solution of such a system of equations would take too long, and so sometimes MultiLevel techniques are used to accelerate convergence. Over the last one and a half decades, the authors have studied the problem of Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication, governed by a complex integro-differential equation. Their work has resulted in a very efficient and stable solver. In this book they describe the different intermediate problems analyzed and solved, and how those ingredients finally come together in the EHL solver. A number of these intermediate problems, such as Hydrodynamic Lubrication and Dry Contact, are useful in their own right. In the Appendix the full codes of the Poisson problem, the Hydrodynamic Lubrication problem, the dry contact solver and the EHL solver are given. These codes are all written in 'C' language, based on the 'ANSI-C' version.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction
This book is about the steps necessary for the construction of an efficient and stable numerical solver for the ElastoHydrodynamic Lubrication problem. Therefore it is necessary to have a detailed understanding of the equations describing the ElastoHydrodynamic Lubrication problem with respect to their computational complexity and their stability. Thus this chapter is devoted to the analysis of the full set of equations describing the ElastoHydrodynamic Lubrication (abbreviated to EHL) problem. The problems related to the system of equations, the differential equation, the integral equation and the global equation will be highlighted. In particular the differential equation is very non linear and thus stability problems occur for certain sets of operating conditions.
This non linearity is caused by two different phenomena; coefficients in the Reynolds equation that depend on the pressure, and the cavitation condition. Furthermore, under some high load conditions the equation suffers from weak coupling in the y direction, in certain parts of the solution domain. Finally, it is shown that the differential equation suffers from slow convergence using classical solution techniques for large numbers of unknowns.
The integral part of the equations is characterised by a non-local character which will require a modification of the classical one point relaxation methods. Furthermore, when using fine grids with many points, the number of operations required to calculate this integral becomes very large, making a more advanced calculation necessary.
Finally, the global equation describing the load balance (or force equilibrium) also requires special attention before a stable and efficient solution algorithm can be obtained.
Since the system of equations describing the EHL problem is complicated, we will start our study on a much simpler equation, and gradually work towards the full EHL system, adding one difficulty at the time. After each step we will require that the algorithm performs with a similar efficiency as the one at the end of the previous step.
1.1 Justification
The regime of ElastoHydrodynamic Lubrication (EHL) is mainly found in lubricated non conforming contacts of machine elements. Common examples are: rolling element bearings (see Figure 1.1), gears, cams and tappets, etc.
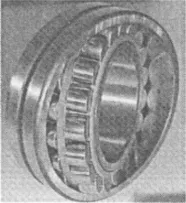
Figure 1.1 Example of ElastoHydrodynamically Lubricated contacts, the contacts between the rolling element and the inner and outer raceway in rolling element bearings.
As the contact area is limited and the forces are generally large, causing high pressures, elastic deformation of the contacting bodies takes place. As the contacting surfaces are generally moving with respect to one another, a lubricant (generally oil or grease) is used to limit friction and wear. The high pressure inside the contact compresses the oil and causes a dramatic increase in its viscosity, thus the lubricant properties like density and especially viscosity are far from constant.
These two characteristics of the EHL contact are essential for the physical comprehension as well as for the efficient numerical solution, and they play a central role in building an efficient solver. As such an EHL contact is characterised by:
• important elastic deformations, and
• important piezo viscous effects.
Apart from being governed by a complex system of equations, the EHL problem also requires a very detailed solution. One reason is physical: to optimize contact performance, a full EHL film completely separating the two surfaces is required. Such a film is very thin; its thickness is generally of the order of 0.1 to 1 μm. This means that the oil film thickness is smaller or even much smaller than the surface roughness of the two surfaces, and that this surface roughness will influence or even determine the way in which the contact will operate. In order to model the influence of surface roughness on EHL, a very fine grid with many points describing the roughness geometry will be needed, which results in the requirement for an efficient solver. Furthermore, the extreme non linearity of the system of equations requires a very stable solution method.
A second reason that requires a very fine grid is purely numerical: the highly loaded cases have very localised film thickness minima, and can only be computed on very fine grids. Otherwise, the precision in the film thickness calculated becomes very small, and in extreme cases it can result in locally negative...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Inside Front Cover
- Copyright page
- Dedication
- Foreword
- Notation
- Teaching
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Numerical Methods: Introduction
- Chapter 3: Multigrid
- Chapter 4: Hydrodynamic Lubrication
- Chapter 5: Dry Contact
- Chapter 6: ElastoHydrodynamic Lubrication
- Bibliography
- Appendix A: MultiLevel Routines
- Appendix B: Debugging Hints
- Appendix C: Systems of Equations for Line Relaxation
- Appendix D: Program Listing: MG1d.c
- Appendix E: Program Listing: MG2d.c
- Appendix F: Program Listing: HL2d.c
- Appendix G: Program Listing: DRY2d.c
- Appendix H: Program Listing: EHL2d.c
- Appendix I: Program Listing: Second Order
- Appendix J: Program Listing: Fourth Order
- Appendix K: Program Listing: Sixth Order
- Appendix L: Program Listing: Eighth Order
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Multi-Level Methods in Lubrication by C.H. Venner,A A Lubrecht in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Mechanical Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.