
eBook - ePub
Electrochemical Water Treatment Methods
Fundamentals, Methods and Full Scale Applications
- 310 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Electrochemical Water Treatment Methods
Fundamentals, Methods and Full Scale Applications
About this book
Electrochemical Methods for Water Treatment: Fundamentals, Methods and Full Scale Applications covers all traditional, emerging and combined methods currently available for the treatment of surface, drinkable water and industrial wastewater. Topics covered include an overview of pollutants and treatment methods, an extended introduction to electrochemical processes in water treatment, electrochemical oxidation (including electrodesinfection, electrochemical reduction, electrocoagulation, electroflotation, and electrodialysis. In addition, emerging and combined methods are presented, as is a discussion on the available equipment necessary to scale up the operation of all methods.
Electrochemical technologies have many common issues in terms of design, operation and performance. This book brings together a wealth of information on all different methods in a single source to provide broad insights and enable the connection between challenges and opportunities for different methods. The combination of technical information, design and case studies offered helps researchers better understand the challenges associated with scale up and implementation.
- Covers all electrochemical methods for water treatment
- Includes methods for the treatment of surface, drinking water and industrial wastewater
- Presents discussions on equipment in the context of scaling up the operation
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Electrochemical Water Treatment Methods by Mika Sillanpaa,Marina Shestakova,Mika Silanpää,Mika Sillanpää in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Environmental Management. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction
Mika Sillanpää, and Marina Shestakova Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland
Abstract
Less than 0.007% of freshwater from the total world water volume is easily accessible. The rapid growth of the population, the high level of industrialization, and intensification of agriculture are accompanied by pollution of the environment and water sources in particular. Traditional water treatment methods can no longer comply with tightening environmental standards. Electrochemical water treatment methods have a number of advantages over conventional methods such as compact reactor vessels, high pollutant removal efficiencies, no additional chemicals for process operation, broad area of applicability, insensitivity to toxic compound, and decreased formation or the total absence of secondary wastes generation. Electrochemical processes are accompanied by electrode reactions caused by the passage of electric current. The efficiency of electrochemical water treatments depends on the electrode material, nature and temperature of electrolyte solution, rate-limiting step of electrode reaction kinetics, etc. This chapter summarizes the information on water pollutants and electrochemical phenomena used in water treatment processes.
Keywords
Classification of electrochemical water treatment methods; Electrochemical water treatment principles; Fundamentals of electrochemistry; Pollutant classification; Water supply sources; Principles of electrolysis
Nomenclature
| Latin alphabet | ||
| Q | Electric charge | C |
| I | Current | A |
| t | Time | s |
| m | Mass of the substance liberated or deposited at an electrode | |
| M | Molar mass of a substance | g/mol |
| F | Faraday constant | 96485.33289(59) C/mol |
| NA | Avogadro's number | 6.022141·1023 mol−1 |
| e | Elementary charge of an electron | 1.6021766·10−19 C |
| z | Number of electrons participating in reaction | |
| E | Cell potential at a given temperature | V |
| E0 | Standard cell potential | V |
| R | Universal gas constant | 8.314472 (15) J/K mol |
| T | Temperature | K |
| Qr | Reaction quotient | |
| K | Electrochemical equivalent of a substance | |
| Vs | Solution volume | dm3 |
| ΔCOD | COD decay | g/dm |
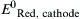 | Standard reduction potential for the reduction half reaction occurring at the cathode | V |
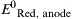 | Standard reduction potential for the oxidation half reaction occurring at the anode | V |
| ΔG | Change in the Gibbs energy | J/mol |
| W | Work by the galvanic cell for the chemical transformation of 1 mol of the reactant | J/mol |
| ΔH | Change in process enthalpy | J/mol |
| Table Continued | ||
| ΔS | Change in process entropy | J/K mol |
| γ | Activity coefficient | |
| a | Activity | mol/cm3 |
| ae/as | Ion activities in the near-electrode layer/the bulk solution, respectively | mol/cm3 |
| A | Electrode area | cm2 |
| j | Current density | A/cm2 |
| j0 | Ex... |
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Chapter 1. Introduction
- Chapter 2. Electrochemical Water Treatment Methods
- Chapter 3. Emerging and Combined Electrochemical Methods
- Chapter 4. Equipment for Electrochemical Water Treatment
- Appendices
- Index
