
- 366 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Fluid Transport: Pipes, part of the Industrial Equipment for Chemical Engineering set, provides a description and calculation of the essential equipment used for fluid transport. Gas-liquid flows are studied with regard to the nature of this type of flow, along with the pressure drop that they may trigger.
Many numerical examples are offered, and the calculation of a fluid transport line is detailed. The vacuum technique and the behavior of non-Newtonian liquids is thoroughly presented, and the author also provides the methods needed for understanding the equipment used in applied thermodynamics to encourage students and engineers to self build the programs they need. Chapters are complemented with appendices that provide additional information and associated references.
- Contains practical applications of ejectors and thermo-compressors
- Establishes pipe diameter thickness
- Includes studies in general and other types of valves
- Presents process parameters and the calculation of a control
- Provides a theoretical study of control valves and gas pipelines
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Fluid Transport by Jean-Paul Duroudier in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Fluid Mechanics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
Fluid Ejectors and Gas Ejectors
Abstract
Consider a convergent followed by a divergent. Between them is a neck with a constant cross-section, and the driving fluid goes through this convergent–divergent.
Keywords
Consumption; Driving fluid; Fluid Ejectors; Gas Ejectors; Global compression ratio; Nozzle; Stability; Suction fluid; Thermocompressors
1.1 General
1.1.1 Principle of an ejector
Consider a convergent followed by a divergent. Between them is a neck with a constant cross-section, and the driving fluid goes through this convergent–divergent.
Using the Bernoulli equation, we can describe the flow of an incompressible fluid:
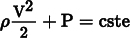
In other words, the more the velocity increases, the more the pressure diminishes.
At the neck, the speed is at its maximum and the pressure is at its minimum. Consequently, this location can be used for the arrival of suction fluid piping.
We will see that, for a simple fluid, the conservation of momentum should be emplo...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Dedication
- Copyright
- Preface
- 1: Fluid Ejectors and Gas Ejectors
- 2: Pipe Dimensions, Non-Newtonian Fluids, Liquid Hammer
- 3: Block or Stop Valves and Control Valves
- 4: Electric Motors: Performance and Choice of Pumps and Fans
- 5: Polymer Extruder Screw
- 6: Choice and Performance of Compressors
- 7: Free Gas Expansion
- 8: Safety Valves and Rupture Disks
- 9: Breathing, Inerting, Gas Losses and Circulation between Reservoirs, Tanks and Vats
- 10: Flow in Pipes: Rarified Gas, Non-Newtonian Liquids, Events, Gas–Liquid Flow
- Appendix: Characteristics of Various Gases
- Bibliography
- Index