
- 488 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Lipid Oxidation
About this book
In this second edition, Edwin Frankel has updated and extended his now well-known book Lipid oxidation which has come to be regarded as the standard work on the subject since the publication of the first edition seven years previously. His main objective is to develop the background necessary for a better understanding of what factors should be considered, and what methods and lipid systems should be employed, to achieve suitable evaluation and control of lipid oxidation in complex foods and biological systems.The oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids is one of the most fundamental reactions in lipid chemistry. When unsaturated lipids are exposed to air, the complex, volatile oxidation compounds that are formed cause rancidity. This decreases the quality of foods that contain natural lipid components as well as foods in which oils are used as ingredients. Furthermore, products of lipid oxidation have been implicated in many vital biological reactions, and evidence has accumulated to show that free radicals and reactive oxygen species participate in tissue injuries and in degenerative disease.Although there have been many significant advances in this challenging field, many important problems remain unsolved. This second edition of Lipid oxidation follows the example of the first edition in offering a summary of the many unsolved problems that need further research. The need to understand lipid oxidation is greater than ever with the increased interest in long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, the reformulation of oils to avoid hydrogenation and trans fatty acids, and the enormous attention given to natural phenolic antioxidants, including flavonoids and other phytochemicals.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Free radical oxidation
Publisher Summary
A Mechanism
1 Initiation
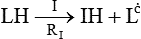
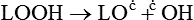
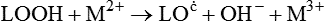
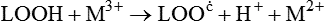
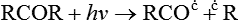
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Also in the Oily Press Lipid Library
- Copyright
- Preface
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Free radical oxidation
- Chapter 2: Hydroperoxide formation
- Chapter 3: Photooxidation of unsaturated fats
- Chapter 4: Hydroperoxide decomposition
- Chapter 5: Methods to determine extent of oxidation
- Chapter 6: Research methods for lipid oxidation
- Chapter 7: Stability methods
- Chapter 8: Control of oxidation
- Chapter 9: Antioxidants
- Chapter 10: Oxidation in multiphase systems
- Chapter 11: Foods
- Chapter 12: Frying fats
- Chapter 13: Biological systems
- Glossary
- Abbreviations
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app