- 464 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Reactivity of P-H Group of Phosphorus Based Compounds
About this book
Reactivity of P-H Group of Phosphorus Based Compounds bridges the gap between inorganic and organic phosphorus compounds, providing a basis to explore the myriad possibilities for synthesis of novel low and high molecular phosphorus-containing compounds. It covers well-documented reactions in detail, including: tautomerization, oxidation, reduction, alkylation, oxidation coupling, addition reaction to: carbon-carbon multiple bonds, Schiff base, isocyanates, nitriles, epoxides; addition to carbonyl group, Kabachnik- Fields reaction, cross-coupling reaction and more. In an accessible style complete with synthetic routes and figures, the resource then covers the reactivity of multiple P-H group members: phosphines, phosphine oxides, hypophosphorus acid, H-phosphinic acids and polys(alkylene H-phosphonate).This valuable coverage supports the advancement of research and applications in this area for scientists solving a scientific problem or starting a variety of new projects, such as a new reaction for the synthesis of biologically active compounds, new methods of polymer synthesis or a new methodology for polymer modification.- Describes the diverse reactivity of the phosphorus-hydrogen group, perhaps the most powerful in organic chemistry- Includes practical information for the synthesis of catalysts, biologically active substances, flame retardants, advance materials and polymer materials- Offers a visually-accessible guide to important reactions by an internationally recognized chemist
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Acidity and Tautomerization of P–H Group
Abstract

Keywords

1.1 Acidity
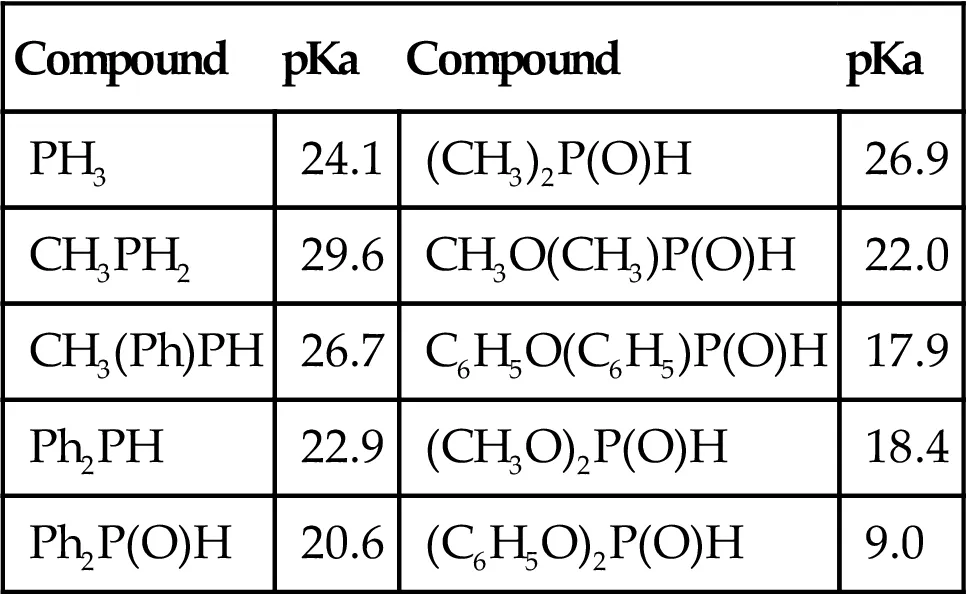
| Compound | pKa | Compound | pKa |
| PH3 | 24.1 | (CH3)2P(O)H | 26.9 |
| CH3PH2 | 29.6 | CH3O(CH3)P(O)H | 22.0 |
| CH3(Ph)PH | 26.7 | C6H5O(C6H5)P(O)H | 17.9 |
| Ph2PH | 22.9 | (CH3O)2P(O)H | 18.4 |
| Ph2P(O)H | 20.6 | (C6H5O)2P(O)H | 9.0 |
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- About the Author
- Preface
- Chapter 1. Acidity and Tautomerization of P–H Group
- Chapter 2. Reactivity of P–H Group of Phosphines
- Chapter 3. Reactivity of P–H Group of Phosphine Oxides
- Chapter 4. Reactivity of P–H Group of Hypophosphorous Acid and Its Derivatives
- Chapter 5. Reactivity of P–H Group of H-Phosphinic Acid and Its Derivatives
- Chapter 6. Reactivity of P–H Group of H-Phosphonic Acid and Its Derivatives
- Chapter 7. Reactivity of P–H Group of Poly(alkylene H-phosphonate)s
- Index