
- 304 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Advanced Welding Processes
About this book
Advanced welding processes provides an excellent introductory review of the range of welding technologies available to the structural and mechanical engineer. The book begins by discussing general topics such power sources, filler materials and gases used in advanced welding. A central group of chapters then assesses the main welding techniques: gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), high energy density processes and narrow-gap welding techniques. Two final chapters review process control, automation and robotics.Advanced welding processes is an invaluable guide to selecting the best welding technology for mechanical and structural engineers.
- An essential guide to selecting the best welding technology for mechanical and structural engineers
- Provides an excellent introductory review of welding technologies
- Topics include gas metal arc welding, laser welding and narrow gap welding methods
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
An introduction to welding processes
Publisher Summary
This chapter discusses some of the basic concepts that are needed to be considered and it highlights some of the features of traditional welding methods. Welding and joining are essential for the manufacture of a range of engineering components, which may vary from very large structures such as ships and bridges, to very complex structures such as aircraft engines or miniature components for micro-electronic applications. A large number of joining techniques are available and, in recent years, significant developments have taken place, particularly in the adhesive bonding and welding areas. A wide range of welding processes is available and their suitability for a given application is determined by the inherent features of the process.
1.1 Introduction
Welding and joining are essential for the manufacture of a range of engineering components, which may vary from very large structures such as ships and bridges, to very complex structures such as aircraft engines or miniature components for micro-electronic applications.
1.1.1 Joining processes
The basic joining processes may be subdivided into:
• mechanical joining;
• adhesive bonding;
• brazing and soldering;
• welding.
A large number of joining techniques are available and, in recent years, significant developments have taken place, particularly in the adhesive bonding and welding areas. Existing welding processes have been improved and new methods of joining have been introduced. The proliferation of techniques which have resulted makes process selection difficult and may limit their effective exploitation. The aim of this book is to provide an objective assessment of the most recent developments in welding process technology in an attempt to ensure that the most appropriate welding process is selected for a given application.
This chapter will introduce some of the basic concepts which need to be considered and highlight some of the features of traditional welding methods.
1.1.2 Classification of welding processes
Several alternative definitions are used to describe a weld, for example:
A union between two pieces of metal rendered plastic or liquid by heat or pressure or both. A filler metal with a melting temperature of the same order as that of the parent metal may or may not be used. [1]
or alternatively:
A localized coalescence of metals or non-metals produced either by heating the materials to the welding temperature, with or without the application of pressure, or by the application of pressure alone, with or without the use of a filler metal. [2]
Many different processes have been developed, but for simplicity these may be classified in two groups; namely ‘fusion’ and ‘pressure’ welding as shown in Fig. 1.1, which summarises some of the key processes. A more extensive list of processes is reproduced in Appendix 1. [1]
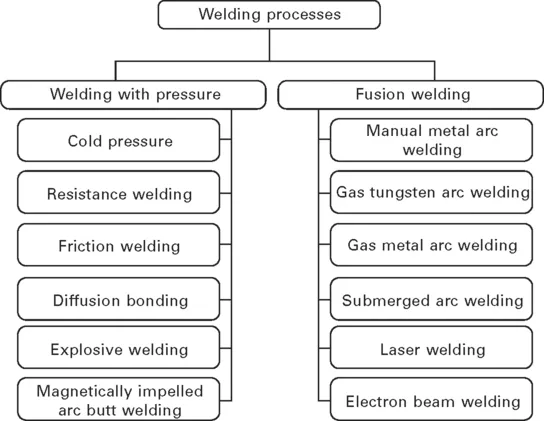
1.2 Conventional welding processes
A brief description of the most common processes, their applications and limitations is given below. The more advanced processes and their developments are dealt with in more detail in the remaining chapters.
An international standard ISO 4063 [3] identifies processes by a numeric code. The first digit of this code specifies the main process grouping whilst the second and third digit indicate sub-groups. The main groups and some examples of sub-groups are shown in Table 1.1 and where appropriate the classification code is given in {}brackets in Sections 1.2.1 and 1.2.2.
Table 1.1
Examples of numbering system from ISO 4063
| Main group | Secondary group | Sub-group |
| {1} Arc welding | {12} Submerged arc welding {13} Gas shielded metal arc welding {15} Plasma arc welding | {111} Manual metal arc welding {131} Metal inert gas welding {141} Tungsten inert gas welding |
| {2} Resistanc... |
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Inside Front Cover
- Copyright
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Chapter 1: An introduction to welding processes
- Chapter 2: Advanced process development trends
- Chapter 3: Welding power source technology
- Chapter 4: Filler materials for arc welding
- Chapter 5: Gases for advanced welding processes
- Chapter 6: Advanced gas tungsten arc welding
- Chapter 7: Gas metal arc welding
- Chapter 8: High-energy density processes
- Chapter 9: Narrow-gap welding techniques
- Chapter 10: Monitoring and control of welding processes
- Chapter 11: Welding automation and robotics
- Welding processes classification
- Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) electrode classification
- Burn-off characteristics
- American, Australian and European FCAW classification systems
- Flux-cored wire for surfacing and wear resistance
- Plasma keyhole welding parameters
- Plasma keyhole welding of titanium
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Advanced Welding Processes by J Norrish in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Industrial Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.