eBook - ePub
Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys
State of the Art, Challenges and Opportunities
- 94 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys
State of the Art, Challenges and Opportunities
About this book
Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys: State of the Art, Challenges and Opportunities provides alternative methods to the conventional approach for the fabrication of the majority of titanium components produced via the cast and wrought technique, a process which involves a considerable amount of expensive machining.
In contrast, the Additive Manufacturing (AM) approach allows very close to final part configuration to be directly fabricated minimizing machining cost, while achieving mechanical properties at least at cast and wrought levels. In addition, the book offers the benefit of significant savings through better material utilization for parts with high buy-to-fly ratios (ratio of initial stock mass to final part mass before and after manufacturing).
As titanium additive manufacturing has attracted considerable attention from both academicians and technologists, and has already led to many applications in aerospace and terrestrial systems, as well as in the medical industry, this book explores the unique shape making capabilities and attractive mechanical properties which make titanium an ideal material for the additive manufacturing industry.
- Includes coverage of the fundamentals of microstructural evolution in titanium alloys
- Introduces readers to the various Additive Manufacturing Technologies, such as Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) and Directed Energy Deposition (DED)
- Looks at the future of Titanium Additive Manufacturing
- Provides a complete review of the science, technology, and applications of Titanium Additive Manufacturing (AM)
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys by Bhaskar Dutta,Francis Froes in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Tecnología e ingeniería & Ingeniería minera. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
The Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys
Abstract
Titanium alloys are used extensively in both aerospace and terrestrial applications and in medical industry. This chapter gives a number of applications in these areas. This is followed by a detailed account of the cost of titanium components in which it is concluded that a major cost of these components is a result of the high cost of machining titanium, so that any way of reducing the machining by fabricating net or near-net shapes will reduce the cost of titanium parts. Major efforts have been directed to the use of powder metallurgy as one near-net approach, and this book is directed towards one powder metallurgy technique: additive manufacturing (AM). This chapter presents an overview of AM including a history of the evolution of this technique which dates back almost 100 years. The basic concept can be divided into a number of approaches of which four involve metal processing: directed energy deposition, powder bed fusion, sheet lamination, and binder jetting; and only the first three of these four have been used for processing titanium and its alloys.
Keywords
Titanium applications; titanium cost; titanium machining; titanium powder metallurgy; titanium additive manufacturing; titanium additive manufacturing history
Abbreviations and Glossary
3D three dimensional
AM additive manufacturing
CAD computer aided design
DED directed energy deposition
DMD direct metal deposition
DMLS direct metal laser sintering
EBM electron beam melting
GE General Electric Corporation
LENS laser engineered net shaping
PBF powder bed fusion
P/M powder metallurgy
SL stereolithography
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 Titanium Alloys and Their Importance
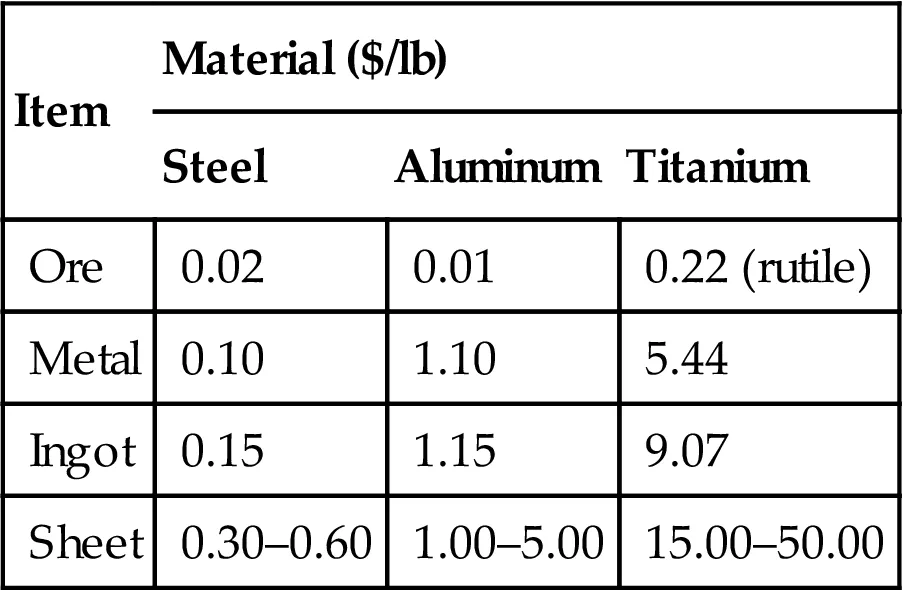
Titanium alloys are among the most important of the advanced materials that are key to improved performance in aerospace and terrestrial systems (Figs. 1.1–1.4) and is even finding applications in the cost conscience auto industry.1–5 These applications result from the excellent combinations of specific mechanical properties (properties normalized by density) and outstanding corrosion behavior6–11 exhibited by titanium alloys. However, negating its widespread use is the high cost of titanium alloys compared to competing materials (Table 1.1).



Table 1.1
Cost of Titanium: A Comparisona
| Item | Material ($/lb) | ||
| Steel | Aluminum | Titanium | |
| Ore | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.22 (rutile) |
| Metal | 0.10 | 1.10 | 5.44 |
| Ingot | 0.15 | 1.15 | 9.07 |
| Sheet | 0.30–0.60 | 1.00–5.00 | 15.00–50.00 |
a2015 Contract prices. The high cost of titanium compared to aluminum and steel is a result of (a) high extraction costs and (b) high processing costs. The latter relates to the relatively low processing temperatures used for titanium and the conditioning (surface regions contaminated at the processing temperatures, and surface cracks, both of which must be removed) required prior to further fabrication.
The high cost of titanium compared with the other metals shown in Table 1.1 has resulted in the yearly consumptions as shown in Table 1.2.
Table 1.2
Metal Consumption
| Structural Metals | Consumption/Year (103 Metric Tons) |
| Ti | 50 |
| Steel | 700,000 |
| Stainless steel | 13,000 |
| Al | 25,000 |
1.1.2 Challenges to Expanding the Scope of Titanium Alloys
In publications over the past few years1–29 the cost of fabricating various titanium precursors and mill products has been discussed (very recently the price of TiO2 has risen to US$2.00/lb and TiCl4 to US$0.55/lb). The cost of extraction is a small fraction of the total cost of a component fabricated by the cast and wrought (ingot metallurgy) approach (Fig. 1.5). To reach a final component, the mill products shown in the figure must be machined, often with very high buy-to-fly ratios (which can reach as high as 40:1). The generally accepted cost of machining a component is that it doubles the cost of the component (with the buy-to-fly ratio being another multiplier in cost per pound), as seen in Fig. 1.6. Fig. 1.7 illustrates how the machining of titanium has evolved, with rough machining showing a much greater improvement than the much more precise and more expensive final machining. Thus, while improvements in the machining of titanium have occurred, anything that can be done to produce a component which is closer to the final configuration will result in a cost reduction—hence the attraction of near-net shape components.

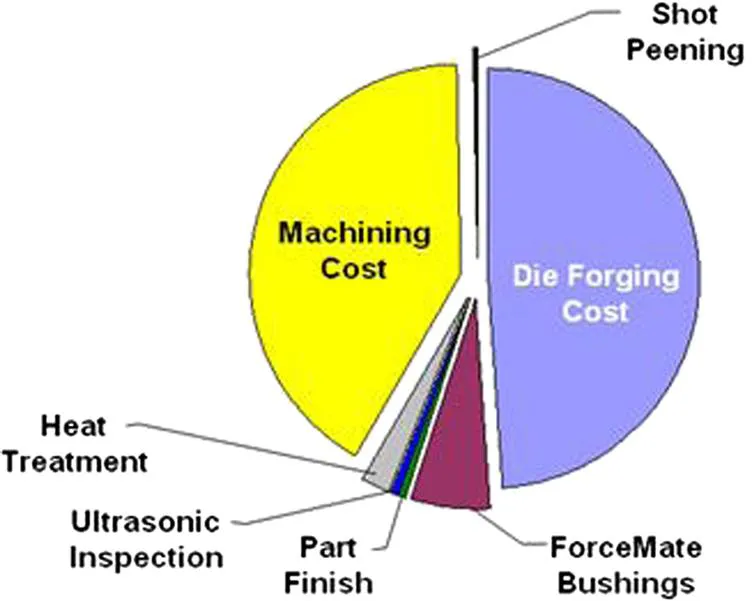

The high cost of conventional titanium components has led to numerous investigations of various potentially...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- About the Authors
- Preface
- Chapter 1. The Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys
- Chapter 2. Raw Materials for Additive Manufacturing of Titanium
- Chapter 3. Additive Manufacturing Technology
- Chapter 4. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
- Chapter 5. Comparison of Titanium AM Technologies
- Chapter 6. Markets, Applications, and Costs
- Chapter 7. Recent Developments and Projections for the Future of Titanium AM