
Presynaptic Receptors and Neuronal Transporters
Official Satellite Symposium to the IUPHAR 1990 Congress Held in Rouen, France, on 26–29 June 1990
- 372 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Presynaptic Receptors and Neuronal Transporters
Official Satellite Symposium to the IUPHAR 1990 Congress Held in Rouen, France, on 26–29 June 1990
About this book
Advances in the Biosciences, Volume 82: Presynaptic Receptors and Neuronal Transporters documents the proceedings of the Official Satellite Symposium to the IUPHAR 1990 Congress held in Rouen, France on June 26-29, 1990. The first part of this book deals with the extensive and still increasing list of presynaptic release-modulating auto and heteroreceptors, emphasizing the various subtypes of presynaptic receptors that are characterized by functional studies, both in vitro and in vivo, using a number of experimental approaches. The next chapters are devoted to the molecular pharmacology of presynaptic receptors, of which can interfere with G proteins and modify the activity of adenylate cyclase, guanylate cyclase, or protein kinase C. The purification and molecular biology of transporter systems, including cloning and sequencing of the neuronal sodium-ion coupled GABA transporter are also discussed. This compilation concludes with insights on the function of presynaptic receptors and neuronal transporters both in the periphery and in the CNS, as well as their ubiquitous locations and physiological roles. This publication is a good reference for students and individuals researching on the presynaptic autoreceptors and neurotransmitters.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Physiological and Pharmacological Relevance of Presynaptic Receptors in Neurotransmission
ABSTRACT
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Results
Discussion
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- ADVANCES IN THE BIOSCIENCES
- Copyright
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Physiological and Pharmacological Relevance of Presynaptic Receptors in Neurotransmission
- Chapter 2: Pre- and Postjunctional Muscarinic Receptors in the Guinea-pig Trachea
- Chapter 3: Presynaptic α-autoadrenoceptors on Peripheral Noradrenergic Neurones of Newborn Rabbits and Dogs
- Chapter 4: Cholinergic–Adrenergic Presynaptic Interactions in the Heart and Characterization of the Receptors Involved
- Chapter 5: Structural Requirements for DA2 (peripheral) Dopamine Receptor Agonist Activity
- Chapter 6: α2-adrenoceptor Modulation of Noradrenaline Release in Human and Rabbit Renal Arteries: Clonidine Acts as a Partial Agonist
- Chapter 7: Effect of α2-adrenoceptor Antagonists on Norepinephrine Release and Inhibition of Insulin Secretion During Pancreatic Nerve Stimulation. Interactions at Pre- and Postsynaptic Sites
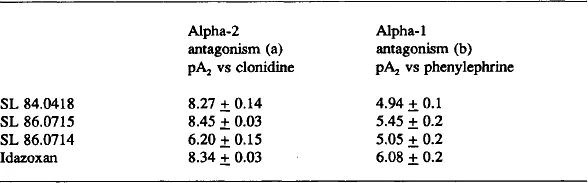
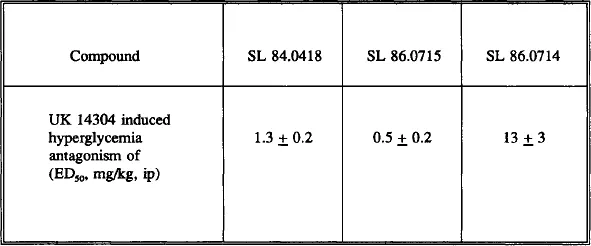
- Chapter 8: Antagonist Activity of SL 84.0418 and Idazoxan at Pre and Postsynaptic α2-adrenoceptors
- Chapter 9: Does the Distance Between Nerve Varicosities and Adrenoceptors Play Any Role in the Relative Contribution of ATP/Noradrenaline for Postjunctional Response?
- Chapter 10: In vivo Presynaptic Interaction Between 5-HT and Adrenergic Antagonists on Noradrenergic Neurotransmission
- Chapter 11: Activity of N-ethyl-nor-arecaidine Propargyl Ester and (R)-nipecotic Acid Ethyl Ester at Pre- and Postsynaptic Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes
- Chapter 12: Effects of Neuromuscular Blocking Agents on Neuronal Nicotine Receptors of Motor Nerves: Blockade of Nicotinic Autofacilitation and Backfiring
- Chapter 13: A Rapid in vitro Assay of the Histamine H3-receptor: Inhibition of Electrically Evoked Contractions of Guinea-pig Ileum Preparations
- Chapter 14: Factors Influencing the Function of Presynaptic α2-adrenoceptors in Rat Brain
- Chapter 15: Presynaptic Dopaminergic Autoreceptors as Targets for Drugs
- Chapter 16: DOPA Itself Facilitates Noradrenaline Release via Presynaptic β-adrenoceptors in Rat Hypothalamic Slices — DOPA is Probably a Neuroactive Substance
- Chapter 17: The Third Dopamine Receptor (D3) as an Autoreceptor
- Chapter 18: Terminal Dopaminergic Autoreceptors are of Minor Importance for the Sedation Produced by DA Receptor Agonists in Rats
- Chapter 19: Modulation of 5-HT Release by Presynaptic Inhibitory and Facilitatory 5-HT Receptors in Brain Slices
- Chapter 20: Modulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine and Noradrenaline Release in the Brain and Retina via Presynaptic Heteroreceptors: Some New Aspects
- Chapter 21: Autoreceptors and Heteroreceptors Evidenced by Histamine H3 Receptor Ligands
- Chapter 22: Somato-dendritic 5-HT1A Autoreceptors in the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus; Pharmacological and Functional Properties
- Chapter 23: Autoreceptor-mediated Control of Serotonin Release in the Rat Brain in vivo
- Chapter 24: Effects of α2-adrenoceptor Agonist and Antagonist on Spatial Memory in Rats
- Chapter 25: Modulation of the Ca2+-evoked Release of Dopamine from Synaptosomes
- Chapter 26: Evidence Against a Direct Link Between Serotonin Uptake Sites and Presynaptic Serotonin Autoreceptors
- Chapter 27: A Comparison of Presynaptic Serotonin Autoreceptors in Rabbit, Rat and Guinea-pig Brain Cortex
- Chapter 28: Serotonergic Modulation of the Release of [3H]GABA from Guinea-pig Hippocampal Synaptosomes
- Chapter 29: Pre- and Postsynaptic Location of 5-HT3 Receptors in the Rat Spinal Cord
- Chapter 30: Distribution of [3H]SCH 23390 Binding Sites in the Human Substantia Nigra
- Chapter 31: Presynaptic Regulation of Dopamine Release from Synaptosomes of the Rat Striatum is Controlled by Different Types of Glutamate Receptors
- Chapter 32: Microdialysis Studies of the Effects of Local Apomorphine Infusions on Dopamine Release in Rat Striatum
- Chapter 33: Dopaminergic Hetero-regulation of Striatal μ-Opiate Receptors: Further Evidence for Their Postsynaptic Location
- Chapter 34: Presynaptic Modulation of Striatal Dopamine Release by Enkephalins
- Chapter 35: Modulation of Dopamine and Acetylcholine Release in the Rabbit Caudate Nucleus by Opioids: Receptor Type and Interaction with Autoreceptors
- Chapter 36: Presynaptic Autoreceptors May Control the Release of Metenkephalin from the Rat Spinal Cord
- Chapter 37: Involvement of NMDA Receptors in the Presynaptic Regulation of Dopamine Release in Striosome-and Matrix-enriched Areas of the Rat Striatum
- Chapter 38: Inhibition of Synaptosomal Tyrosine Hydroxylase by Dopamine Autoreceptors: Role of Ca2+ and K+
- Chapter 39: Dopaminergic Modulation of Striatal Sensory Responses
- Chapter 40: Selective Presynaptic Dopamine Agonist Treatment of Schizophrenia with BHT-920
- Chapter 41: Effects of the Antiparkinsonian Drugs Amantadine and Memantine on Striatal Neurotransmitter Release in vitro
- Chapter 42: Transmitter Interactions in Striatum May Occur via Effects on High Affinity Transporters
- Chapter 43: A Comparison of the Effect of Baclofen on Radiolabelled GABA and Noradrenaline Release in Rat Cortical Slices
- Chapter 44: Effects of Chronic Treatment with Flunitrazepam on GABAA, Adenosine and Glutamate Receptor Plasticity in Rats
- Chapter 45: Modulation of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA)-stimulated Noradrenaline Release in Rat Brain Cortex by Presynaptic α2-adrenoceptors and Histamine H3 Receptors
- Chapter 46: Noradrenaline Release in the Pig Retina and Its Histamine H3 Receptor-mediated Inhibition
- Chapter 47: Structure and Function of the GABA Reuptake System
- Chapter 48: Energizing the Vacuolar System of Eukaryotic Cells
- Chapter 49: The Molecular Size of the Neuronal Noradrenaline Carrier
- Chapter 50: Identification and Regulation of High-affinity-choline Transporter
- Chapter 51: Ketanserin as a Ligand of the Vesicular Monoamine Transporter
- Chapter 52: Dopamine Transporter — Cocaine Receptor: Characterization and Purification
- Chapter 53: Characterization and Purification of the Serotonin Transporter Located at the Cytoplasmic Membrane of Human Platelets: A Three-step Strategy
- Chapter 54: Molecular Characterization of the Neuronal Sodium-ion Coupled 5-hydroxytryptamine Transporter
- Chapter 55: Kinetic Analyses of the Na+ and Cl−-Dependences of the Synaptosomal Specific Uptake of 3H Dopamine
- Chapter 56: Localization of Dopamine Uptake Complex by BTCP on Rat Brain Sections and Dopaminergic Neurons in vitro
- Chapter 57: In vivo Binding of [3H]GBR 12783 in Mouse Brain — Characteristics of the Labelling of Striatal Dopamine Uptake Sites
- Chapter 58: [3H]GBR12935 Binds to Membrane from the Human Platelet
- Chapter 59: Dopamine Transporter in Aging
- Chapter 60: Sodium Dependent, High Affinity Choline Transport Expressed in Oocytes
- Chapter 61: Comparison of the Effects of Vesamicol and of Cetiedil Analogues on Acetylcholine Release and Vesicular Acetylcholine Transport
- Chapter 62: Dopamine Modulates [3H]BTCP (a Phencyclidine Derivative) Binding to the Dopamine Uptake Complex
- Chapter 63: The Heterogeneous Labelling with 3H-noradrenaline of the Incubated Vas Deferens of the Rat
- Chapter 64: Alterations in Platelet [3H]-Imipramine Binding, 5HT Uptake and Plasma α1-acid Glycoprotein Concentrations in Patients with Major Depression
- Chapter 65: Ionic and Temperature Dependences of the 3H Dopamine Specific Uptake and 3H GBR 12783 or 3H Mazindol Specific Binding on the Dopamine Neuronal Carrier
- Chapter 66: Dynamic Properties of Monoamine Storage Vesicles: Pharmacological and Physiological Implications
- Chapter 67: GABA Uptake Inhibitors: Kinetics and Molecular Pharmacology
- Chapter 68: Coexistence of More Than One Neurotransmitter Uptake System on the Same Nerve Terminal in the Brain
- Chapter 69: Peptidergic Regulation of Striatal Dopamine Transporter Complex
- Chapter 70: Different Interactions of Citalopram with the Prejunctional Effects of Serotonin in Peripheral Tissues
- Chapter 71: Evolution of the Vesicular Monoamine Transporter During Ageing in the Rat Brain: a Quantitative Autoradiographic Study with 3H Dihydrotetrabenazine
- Chapter 72: Influence of the Oxygen Disponibility on the Efficiency of the Neuronal Dopamine Uptake Complex
- Chapter 73: Differences in Behavioural Responses Elicited by Dexamphetamine and the Pure Dopamine Uptake Inhibitor GBR 12783
- Chapter 74: Protection of the Synaptosomal 5-HT Uptake System by a Ginkgo Biloba Extract (GBE 761)
- Chapter 75: The Binding of Noradrenaline to the Substrate Recognition Site of the Neuronal Noradrenaline Carrier (Uptake1) Depends on Sodium and Chloride
- Chapter 76: In vivo Distribution of Radiolabelled Citalopram in Brain as a Marker of 5-HT Uptake Sites for PET
- Chapter 77: Relationship of [3H]Paroxetine Binding and 5-HT Recognition Sites on the Neuronal Serotonin Transporter
- Chapter 78: Effects of Repeated Administration of Antidepressants on Serotonin Uptake Sites Measured Using [3H]Cyanoimipramine Autoradiography
- Chapter 79: Rapid Changes in 3H-Imipramine Binding in Platelets of Depressed Patients After Amineptine Treatment
- Chapter 80: Brain 5-HT Uptake Sites, Labelled with [3H]Paroxetine, in Depressed Suicides
- Chapter 81: Pinoline, the Natural Ligand of Serotonin Transporter in Retina and Pineal Gland
- Chapter 82: Differential Interaction of Phencyclidine (PCP) with the Dopamine Uptake Complex and the PCP Receptor in vivo
- Chapter 83: The Uptake of the Amino Acid L-alanine on Its Inhibitory Presynaptic Effects in Rat Isolated Atria
- Chapter 84: Role of Omega (BZD) Sites of the GABAA Receptor Macromolecular Complex in the Modulation of Serotonin Release
- Chapter 85: Mechanisms of Inhibition of Transmitter Release by Adenosine Analogs
- Chapter 86: Dependence of the A1-adenosine Receptor-mediated Inhibition of [3H]Noradrenaline Release in Hippocampus on the Stimulation Conditions
- Chapter 87: Modulation of [3H]-serotonin Release in Rat Spinal Cord Synaptosomes via Dihydropyridine-sensitive Calcium Channels and Protein Kinase C
- Chapter 88: G-proteins and Prejunctional α-adrenoceptors
- Chapter 89: Opioid Inhibition of Oxytocin Release, but not Autoinhibition of Dopamine Release May Involve Activation of Potassium (K+) Channels
- Chapter 90: 3,4-diaminopyridine-evoked Noradrenaline Release in Hippocampal Slices: Further Properties and Involvement of Adenylate Cyclase
- Chapter 91: Interneuronal Cyclic GMP and ‘EDRF-like Substance’ Modulate Norepinephrine Release from Peripheral Sympathetic Nerves
- Chapter 92: Modulatory Role of Neuropeptide Y and Peptide YY at the NMDA Receptor Complex
- Chapter 93: Prejunctional Neuropeptide Y Receptors Are Linked to a G-protein: a Study with N-Ethylmaleimide and Pertussis Toxin
- Chapter 94: Protein Kinase C and Modulation of Neurotransmission: Studies With Protein Kinase Inhibitors
- Chapter 95: Intrasynaptosomal Protein Phosphorylation and Its Inhibition by Plasma Membrane Oxidoreductases
- Chapter 96: Functional and Regulatory Properties of Presynaptic Autoreceptors of the 5-HT1A Subtype on Dorsal Raphe Neurons in Brain Stem Slices
- Chapter 97: Do Schwann Cells Play a Role in ‘Upstream’ Regulation of the Release Probability in Sympathetic Nerve Varicosities?
- Chapter 98: Changes in α2 Presynaptic Receptor Sensitivity During Production of Dependence to Morphine in Conscious Rats
- Chapter 99: Role of Presynaptic α2 Heteroreceptors in Nonsynaptic Modulation of Transmitter Release
- Chapter 100: Autoregulation of Catecholamine Release at Central and Sympathetic Nerve Terminals: Common Features
- Chapter 101: Autoreceptor Mediated Changes in Dopaminergic Terminal Excitability in vivo
- Chapter 102: Prejunctional Autoreceptors in Mouse vas deferens
- Chapter 103: SK&F 104078 Identifies Subtypes of Prejunctional α2-adrenoceptors in the Rat vas deferens
- Chapter 104: Clonidine Inhibition of Norepinephrine Release from Normal and Morphine-Tolerant Guinea Pig Cortical Slices
- Chapter 105: Human Caki-1 Cells Are the First Clonal Cell Line Known to Possess the Extraneuronal Transport Mechanism for Noradrenaline (Uptake2)
- Chapter 106: Inhibition of NA Uptake by (+)-oxaprotiline Inhibits Sympathetic Nerve Activity
- Chapter 107: Autoregulation of Evoked Noradrenaline Release at the Surface of the Isolated Rat Tail Artery Studied by Electrochemistry
- Chapter 108: Autoregulation of Evoked Noradrenaline Release in the Rat Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Studied in vivo by Electrochemistry
- Chapter 109: Clonidine Early in Life: Effect on Brain Morphofunctional Disturbances Induced by Neonatal Malnutrition in the Rat
- Chapter 110: μ and κ Agonists Inhibit Carbachol-evoked Release of Catecholamines and [Met]enkephalin from ex situ Perfused Dog Adrenals
- Chapter 111: Electrophysiological Evidences for the Preferential Location of D2 Autoreceptors on Dendrites of DA Neurons in the Rat Substantia Nigra
- Chapter 112: Increase of Postsynaptic Dopaminergic Transmission by Presynaptic Actions of Cocaine
- Chapter 113: Autoregulation of Evoked Dopamine Release in the Rat at Central Terminal Sites Studied in vivo by Electrochemistry
- Chapter 114: Combined Effect of (–)-Vesamicol and (+)-Tubocurarine on Endplate Current Amplitude in Rat Skeletal Muscle at High Frequencies of Nerve Stimulation
- Chapter 115: Effect of (–)-Vesamicol on Miniature Endplate Current and Endplate Current Amplitudes in Rat Skeletal Muscle
- Subject Index