
- 566 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Neuroscience of Nicotine: Mechanisms and Treatment presents the fundamental information necessary for a thorough understanding of the neurobiological underpinnings of nicotine addiction and its effects on the brain. Offering thorough coverage of all aspects of nicotine research, treatment, policy and prevention, and containing contributions from internationally recognized experts, the book provides students, early-career researchers, and investigators at all levels with a fundamental introduction to all aspects of nicotine misuse.With an estimated one billion individuals worldwide classified as tobacco users—and tobacco use often being synonymous with nicotine addiction—nicotine is one of the world's most common addictive substances, and a frequent comorbidity of misuse of other common addictive substances. Nicotine alters a variety of neurological processes, from molecular biology, to cognition, and quitting is exceedingly difficult because of the number of withdrawal symptoms that accompany the process.- Integrates cutting-edge research on the pharmacological, cellular and molecular aspects of nicotine use, along with its effects on neurobiological function- Discusses nicotine use as a component of dual-use and poly addictions and outlines numerous screening and treatment strategies for misuse- Covers both the physical and psychological effects of nicotine use and withdrawal to provide a fully-formed view of nicotine dependency and its effects
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Understanding Tobacco Use in Different Countries
Abstract
Keywords
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Basic Concepts of Tobacco Epidemiology
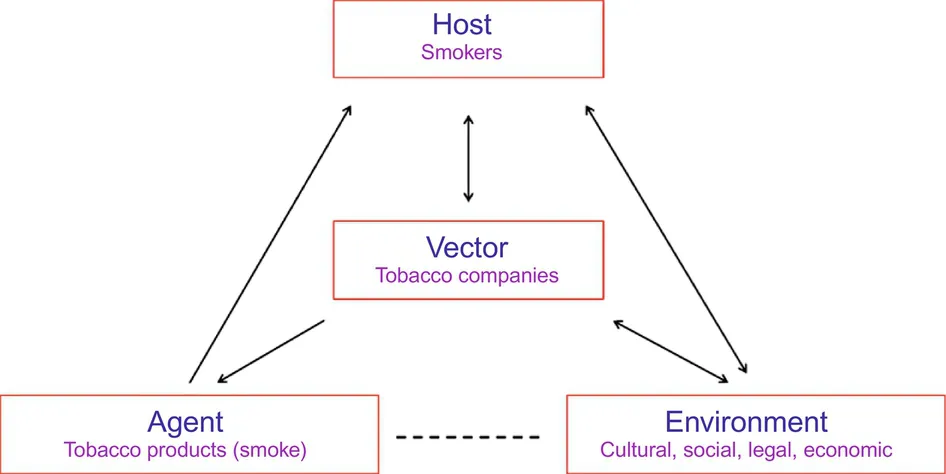
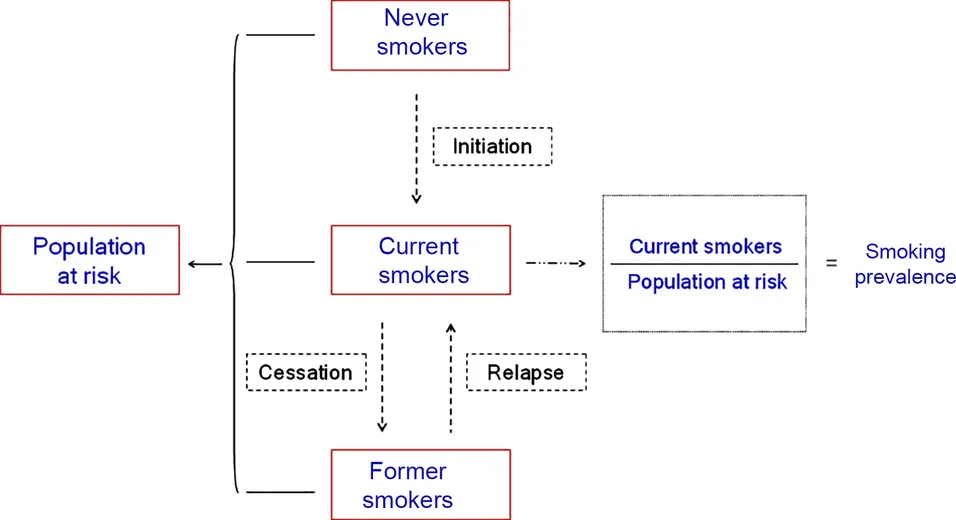
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Contributors
- Preface
- Editorial Advisors
- Chapter 1: Understanding Tobacco Use in Different Countries
- Chapter 2: Maternal Smoking and Fetal Brain Outcome: Mechanisms and Possible Solutions
- Chapter 3: Nicotine Effects in Adolescents
- Chapter 4: The Impact of Traditional Cigarettes and E-Cigarettes on the Brain
- Chapter 5: Reduction of Nicotine in Tobacco and Impact
- Chapter 6: Prenatal Nicotine Exposure and Neuronal Progenitor Cells
- Chapter 7: Synaptically Located Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunits in Neurons Involved in Dependency to Nicotine
- Chapter 8: Cotinine as a Possible Allosteric Modulator of Nicotine Effects in Various Models
- Chapter 9: Nicotine, Neural Plasticity, and Nicotine's Therapeutic Potential
- Chapter 10: Habenular Synapses and Nicotine
- Chapter 11: Nicotine Neuroprotection of Brain Neurons: The Other Side of Nicotine Addiction
- Chapter 12: Linking Nicotine, Menthol, and Brain Changes
- Chapter 13: Cigarette Smoking and Nicotine: Effects on Multiple Sclerosis
- Chapter 14: Tobacco and Positron-Emission Tomography (PET) of the Dopaminergic System: A Review of Human Studies
- Chapter 15: Resting-State Functional Connectivity Imaging and Nicotine Dependence
- Chapter 16: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Acute Nicotine Effects
- Chapter 17: Nicotine Dependence in Schizophrenia: Contributions of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Chapter 18: Attentional Bias and Smoking
- Chapter 19: Effects of Nicotine on Inhibitory Control in Humans
- Chapter 20: Nicotine, Corticotropin-Releasing Factor, and Anxiety-Like Behavior
- Chapter 21: 6-Hydroxy-l-Nicotine and Memory Impairment
- Chapter 22: Cotinine and Memory: Remembering to Forget
- Chapter 23: Nicotine in Aberrant Learning and Corticostriatal Plasticity
- Chapter 24: Prenatal Nicotine Exposure and Impact on the Behaviors of Offspring
- Chapter 25: Craving in Substance Use Disorders With a Focus on Cigarette Smoking
- Chapter 26: The Acute Effect of Exercise on Cravings and Withdrawal Symptoms
- Chapter 27: CRF2 Receptor Agonists and Nicotine Withdrawal
- Chapter 28: Delirium and Nicotine Withdrawal
- Chapter 29: Postoperative Nicotine Withdrawal
- Chapter 30: Nicotine and Alpha3beta2 Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Chapter 31: Nicotine Addiction and Alpha4beta2* Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Chapter 32: The Medial Habenula-Interpeduncular Nucleus Pathway in Nicotine Sensitization: The Role of α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors and Substance P
- Chapter 33: Targeting Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors for the Treatment of Pain
- Chapter 34: Pharmacology of Muscle-Type Nicotinic Receptors
- Chapter 35: Involvement of Opioid Receptors in Nicotine-Related Reinforcement and Pleasure
- Chapter 36: Nicotine-Induced Kindling: Influences of Age, Sex, and Prevention by Antioxidants
- Chapter 37: Nicotine Reward and Abstinence: Role of the CB1 Receptors
- Chapter 38: The Therapeutic Potential of the Cognitive-Enhancing Effects of Nicotine and Other Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists
- Chapter 39: Nicotine and Dopamine DA1 Receptor Pharmacology
- Chapter 40: Brain Gene Expression in the Context of Nicotine Rewards: A Focus on Cholinergic Genes
- Chapter 41: HIV-Infected Subjects and Tobacco Smoking: A Focus on Nicotine Effects in the Brain
- Chapter 42: Renin-Angiotensin System Genes and Nicotine Dependence
- Chapter 43: Nicotine Dependence and the CHRNA5/CHRNA3/CHRNB4 Nicotinic Receptor Regulome
- Chapter 44: Brain, Nrf2, and Tobacco: Mechanisms and Countermechanisms Underlying Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Cerebrovascular Effects of Cigarette Smoking
- Chapter 45: Effects of Nicotine and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on the Brain
- Chapter 46: L-Type Calcium Channels and Nicotine
- Chapter 47: The Co-occurrence of Nicotine With Other Substance Use and Addiction: Risks, Mechanisms, Consequences, and Implications for Practice, With a Focus on Youth
- Chapter 48: Comorbid Smoking and Gambling Disorder: Potential Underlying Mechanisms and Future Explorations
- Chapter 49: Neuroscience of Tobacco and Crack Cocaine Use: Metabolism, Effects, and Symptomatology
- Chapter 50: Salivary Cotinine Assays
- Chapter 51: Overview of Cotinine Cutoff Values for Smoking Status Classification
- Chapter 52: Smoking Abstinence Expectancies Questionnaire
- Chapter 53: Pharmacist-led Smoking Cessation Services: Current and Future Perspectives
- Chapter 54: Nicotine Use and Weight Control in Young People: Implications for Prevention and Early Intervention
- Chapter 55: Exercise as a Smoking Cessation Aid
- Chapter 56: Varenicline: Treating Smoking Addiction and Schizophrenia
- Chapter 57: Nicotine Vaccines: The Past, the Present, and the Future
- Chapter 58: Treating Nicotine Dependence in Psychiatric Hospitals
- Chapter 59: Oral 18-Methoxycoronaridine (18-MC) Decreases Nicotine Self-Administration in Rats
- Chapter 60: Pharmacogenetics and Smoking Cessation
- Chapter 61: The Orexin System and Nicotine Addiction: Preclinical Insights
- Chapter 62: Tobacco Control Policies and Smokers’ Responses
- Chapter 63: Resources for the Neuroscience of Nicotine
- Index