
- 162 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Example-Based Super Resolution
About this book
Example-Based Super Resolution provides a thorough introduction and overview of example-based super resolution, covering the most successful algorithmic approaches and theories behind them with implementation insights. It also describes current challenges and explores future trends.
Readers of this book will be able to understand the latest natural image patch statistical models and the performance limits of example-based super resolution algorithms, select the best state-of-the-art algorithmic alternative and tune it for specific use cases, and quickly put into practice implementations of the latest and most successful example-based super-resolution methods.
- Provides detailed coverage of techniques and implementation details that have been successfully introduced in diverse and demanding real-world applications
- Covers a wide variety of machine learning approaches, ranging from cross-scale self-similarity concepts and sparse coding, to the latest advances in deep learning
- Presents a statistical interpretation of the subspace of natural image patches that transcends super resolution and makes it a valuable source for any researcher on image processing or low-level vision
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Classic Multiframe Super Resolution
Abstract
This chapter introduces and discusses classic approaches in super resolution, which attempt to provide a finer sampling of a visual scene by combining several coarse and, possibly corrupted, captures of the same scene. The chapter starts by defining a suitable model to describe the problem and some available solutions, that is, frequency-domain reconstruction pipeline or Bayesian inference (Maximum Likelihood and Maximum A Posteriori). The chapter proceeds with a more detailed review of interpolation-based multiframe super resolution, involving the stages of registration, warping projection and restoration, and finishes with a discussion about the shortcomings and numerical limits of these approaches that lead to the need for example-based super-resolution approaches.
Keywords
Super resolution; Frequency-domain reconstruction; Bayesian inference; Registration; Warping projection; Restoration; Deblurring; Denoising
In contrast to the ideas presented throughout the rest of the book, this chapter introduces and discusses classic approaches in super resolution, which attempt to provide a finer sampling of a visual scene by combining several coarse and, possibly corrupted, captures. We shall start by defining a suitable model to describe the problem and the available solutions, and later discuss the shortcomings of these approaches.
1.1 Problem Statement
Let Y be a low-resolution (i.e., subsampled) and corrupted version of a desired image X for which we cannot directly obtain a capture with sufficient spatial resolution:
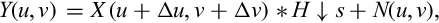
where u and v denote any pixel location in rows and columns, respectively, s is the subsampling factor of the observed image Y with respect to the desired image X, H is a certain low-pass function attempting to prevent aliasing from appearing in Y, Δu and Δv represent the optical flow (horizontal and vertical displacement, respectively) between X and Y, and N is additive, independent noise.
Let us now assume that we can obtain an arbitrarily large number NI of subsampled and corrupted images, each with a different displacement or optical flow with respect to the desired image:
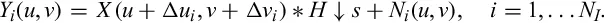
Note that we assume the same low-pass filter or blur function H for all observed images. Even though this notation cannot handle all the possible cases, it will be difficult (and costly) to determine the blur function in a frame-by-frame basis, so this formula does actually describe the most common scenario.
1.1.1 A Frequency-Domain Pipeline
Early efforts in super resolution from multiple images focused on frequency-domain approaches. The main idea is to enhance details by extrapolating the high-frequency information of the available images with a relatively low computational complexity through (the use of fast Fourier transforms) under the additional assumption of global translational motion, which further constrains target scenarios. The general idea in T. S. Huang and Tsai (1984), S. P. Kim, Bose, and Valenzuela (1990), Tom, Katsaggelos, and Galatsanos (1994), and Vandewalle, Süsstrunk, and Vetterli (2006), among others, is:
1. Transform the low-resolution images to frequency domain using the fast Fourier or wavelet transforms.
2. Combine the transformed images (including registration, blind deconvolution, and interpolation tasks) using Expectation-Maximization algorithms (Dempster, Laird, & Rubin, 1977; Gupta & Chen, 2011).
3. Invert the Fourier or wavelet transform to obtain the reconstructed high-resolution image.
The constraint of global translational motion is unaffordable for most app...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Dedication
- List of Figures
- Acknowledgment
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Classic Multiframe Super Resolution
- Chapter 2: A Taxonomy of Example-Based Super Resolution
- Chapter 3: High-Frequency Transfer
- Chapter 4: Neighbor Embedding
- Chapter 5: Sparse Coding
- Chapter 6: Anchored Regression
- Chapter 7: Trees and Forests
- Chapter 8: Deep Learning
- Chapter 9: Conclusions
- References
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Example-Based Super Resolution by Jordi Salvador in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Digital Media. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.