
Reaction Kinetics
Homogeneous Gas Reactions
- 242 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Reaction Kinetics
Homogeneous Gas Reactions
About this book
Reactions Kinetics: Volume I: Homogeneous Gas Reactions presents a general introduction to the subject of kinetics, including the basic laws of kinetics and the theoretical treatment of reaction rates. This four-chapter book deals mainly with homogeneous reactions in the gas phase. Chapter 1 presents the kinetic laws based on experimental results in terms of their simple concepts, with a special consideration of the way in which rates depend on concentration, while Chapter 2 deals with the interpretation of rates in terms of more fundamental theories. Chapter 3 covers the overall reactions that are believed to be elementary, such as the reaction between hydrogen and iodine, the reverse decomposition of hydrogen iodide, the corresponding reactions involving deuterium instead of hydrogen, and the dimerizations of butadiene and cyclopentadiene, as well as a few elementary termolecular reactions, all involving nitric oxide. This chapter also includes a general account of some of the elementary reactions that occur as steps in more complex mechanisms. Chapter 4 examines the reaction rates of numerous complex gas reactions. Undergraduate physical chemistry and chemical kinetics students, as well as advanced students in other fields, such as biology and physics, will find this book invaluable.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Basic Kinetic Laws
Publisher Summary
RATE OF REACTION
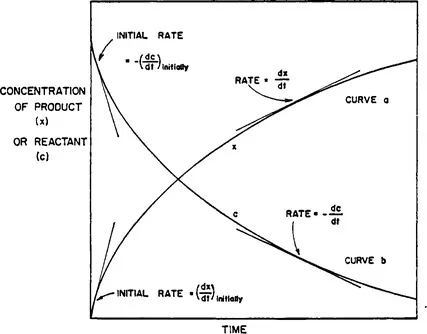

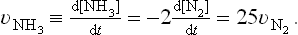
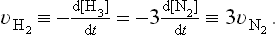
Order of Reaction
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Inside Front Cover
- Copyright
- Preface
- A Note to the Student
- Chapter 1: Basic Kinetic Laws
- Chapter 2: Molecular Kinetics
- Chapter 3: Elementary Gas Reactions
- Chapter 4: Complex Gas Reactions
- Correlation, and the Method of Least Squares
- Numerical Values
- Bibliography
- Name Index
- Subject Index