
- 234 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Hot-Dip Galvanizing of Steel Structures
About this book
Hot-Dip Galvanizing of Steel Structures contains practical information that is useful for both researchers in hot-dip galvanizing and engineers, designers, and inspectors. The book draws from the empirical experience and research of the authors, complementing the current state of knowledge of morphological variations of the coating and causes of coating delamination.
The book includes chapters devoted to qualitative tests of the coating, and to methods of making corrections. A section describing the principle of protecting steel against corrosion through zinc coating is also provided, along with an extensive chapter on the principles of good design for hot-dip galvanizing. The chapter related to the safety of hot-dip galvanized steel structures offers a new hypothesis about the mechanism of nucleation of LMAC cracks during hot-dip galvanizing, thus enriching the knowledge regarding this phenomenon.
- Provides practical information on hot-dip galvanizing from a scientific-disciplinary perspective, including coverage of design principles, reliability of galvanized structures, and legal aspects
- Features chapters devoted to qualitative assessments of the surface treatment and methods for correcting problems
- Includes discussion of hot-dip galvanizing with regard to environmental aspects and sustainable development
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Hot-Dip Galvanizing of Steel Structures by Vlastimil Kuklik,Jan Kudlacek in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Mining Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
List of selected zinc coating technologies
Abstract
The zinc coating could be on steel and iron components applied by various techniques. In regards with the purpose of use, environment in which the galvanized parts are exposed, their structural design and other aspects of rational can choose various plating technologies, such as electroplating, hot-dip galvanizing carried out by dipping into molten metal, or by spraying, sherardizing, or mechanical galvanizing.
Keywords
Zinc coating techniques; electrolytic deposition; galvanic deposition; electrolyte; zinc anode; electrochemical pre-treatment; thermal spraying; metallizing; hot-dip galvanizing; iron-zinc alloy phase; characteristics of zinc coatings; comparison of zinc coating types
With regard to its properties, zinc has proven its quality as a coating material to protect ferrous metals from corrosion and, over the course of time, a number of technologies for its application and use in surface finishing have been developed.
1.1 Electroplating of zinc
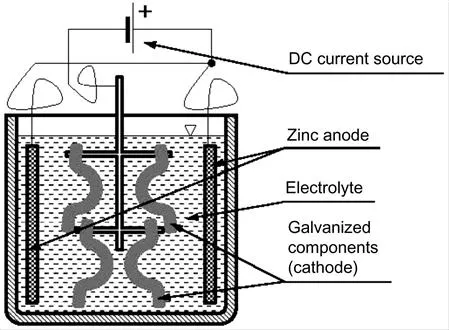
A very common zinc coating technology is electrolytic deposition of a zinc coating from an electrolyte [14]. In this system, a zinc electrode (anode) is connected to the positive pole of a source of direct electric current (Figure 1.1). Zinc ions contained in the electrolyte are deposited on the negative cathode represented by the steel product that zinc ions adhere to, forming a zinc layer. A precondition for successful deposition of the coating is chemical and electrochemical pre-treatment ensuring a perfectly pure metallic surface of the parts is achieved. The thickness of the deposited zinc layer is generally 10 to 20 μm and it can be controlled very exactly. Besides pure zinc coatings, alloy coatings are used as well (most commonly zinc-nickel).
1.2 Thermal spraying of zinc (metallizing)
Thermal spraying (Figure 1.2) is used to apply zinc that is melted by flame or electric arc and carried by a gas stream to the sand-blasted surface of the part to be coated. The coating adheres by mechanical adhesion [15]. Pure zinc may be used for thermal spraying for anti-corrosion, but for higher corrosion resistance, alloys of zinc with aluminum are also frequently used. The coating is applied as a layer with the thickness of 80 to 250 μm.

For reliable adhesion of a zinc coating applied by metallizing the surface requires pre-treatment by sand-blasting with the use of sharp-edged particles.
After the application of sprayed zinc it is necessary to apply an organic painting material on the deposited coating that will adhere very well in its profile. Combination of zinc coating with organic paint (referred to as a duplex system, see Section 8.3) offers a very good corrosion resistance with regard to efficient synergy of both the materials.
1.3 Hot-dip galvanizing (by immersion in molten zinc)
Parts designed to be zinc coated are first chemically pre-treated to achieve a clean steel surface. Then the surface is activated with flux and subsequently the parts are immersed in a bath of molten zinc. During immersion in the bath, a zinc coating consisting of a few alloy layers is formed on the steel surface. The coating is formed depending on the instantaneous conditions of diffusion of iron and zinc atoms and their mutual bond. In the bath, a spontaneous reaction between iron and zinc occurs, producing several iron-zinc alloy phases.
Batch hot-dip galvanizing (commercial) is carried out as a dry (see Section 2.2.1) or wet process (see Section 2.2.2) or as coating with centrifuging (see Section 2.2.3). Given the focus of this book, in the chapters below we will mainly concentrate on these technologies. A basic comparison of individual galvanized coating types by the method of their application is presented in Table 1.1. Besides these technologies there are methods for continuous zinc coating of strips, wires, or pipes.
Table 1.1
Comparison of hot-dip galvanized coatings applied by immersion in commercial zinc coating plants
| Application method | Characteristic | Application | |
| Batch | dry process | limited handling during coating application, high productivity | parts that can be suspended individually |
| wet process | good handling during coating application, limited weight | complex shapes requiring manual handling | |
| Centrifuged | low-temperature | the coating has the same characteristics as in the case of batch application, limited possibility to control the coating thickness | minor parts requiring a bigger coating thickness |
| high-temperature | the coating lacks the alloy phase ζ, good possibility to control the coating thickness | minor parts requiring exact control of the coating thi... | |
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- Introduction
- 1. List of selected zinc coating technologies
- 2. Hot-dip galvanizing
- 3. Chemical pre-treatment
- 4. Hot-dip galvanized coating formation
- 5. Morphology of hot-dip galvanized coatings
- 6. Phenomena on galvanized coatings
- 7. Tests of hot-dip galvanized coatings and assessment of their quality
- 8. Service life of hot-dip galvanized coatings
- 9. Proper design principles for hot-dip galvanizing
- 10. Maintaining the integrity of hot-dip galvanized steel structures
- 11. Standardization
- 12. Legislation
- 13. Hot-dip galvanizing and the environment
- 14. Sustainable development
- References
- Index