
- 746 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Intelligent Coatings for Corrosion Control
About this book
Intelligent Coatings for Corrosion Control covers the most current and comprehensive information on the emerging field of intelligent coatings. The book begins with a fundamental discussion of corrosion and corrosion protection through coatings, setting the stage for deeper discussion of the various types of smart coatings currently in use and in development, outlining their methods of synthesis and characterization, and their applications in a variety of corrosion settings. Further chapters provide insight into the ongoing research, current trends, and technical challenges in this rapidly progressing field.
- Reviews fundamentals of corrosion and coatings for corrosion control before delving into a discussion of intelligent coatings—useful for researchers and grad students new to the subject
- Covers the most current developments in intelligent coatings for corrosion control as presented by top researchers in the field
- Includes many examples of current and potential applications of smart coatings to a variety of corrosion problems
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Intelligent Coatings for Corrosion Control by Atul Tiwari,Lloyd Hihara,James Rawlins in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Industrial & Technical Chemistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Electrochemical Aspects of Corrosion-Control Coatings
L.H. Hihara Hawaii Corrosion Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA
Abstract
Corrosion of metals is an electrochemical process and is affected by moisture content, the chemical environment, and the electrochemical state of the metal. How the properties of a coating or coating system affect the above parameters governs the effectiveness of the coating in suppressing corrosion. Fundamental electrochemical aspects of corrosion are discussed, as well how coating properties (i.e., barrier characteristics and electrical resistivity, chemical and electrochemical) affect the corrosion behavior of the substrate metal. Barrier protection, corrosion inhibition, and cathodic protection as they relate to coatings are discussed.
Keywords
Corrosion protection
Coatings
Barrier
Corrosion inhibition
Cathodic protection
1.1 Introduction
In nature, almost all metals are found in their thermodynamically stable states which are ores that are comprised primarily of oxides, sulfides, and halides.1 Energy must be expended to extract the elemental metals from the ores. Hence, as soon as the elemental metals are extracted from their ores, they have a propensity to revert back to their thermodynamically stable compounds. In most cases, metals will form oxides when exposed to moisture. If the oxide is porous or does not have good adhesion to the substrate metal, the metal will actively corrode. If the oxide forms a compact impervious layer and has good adhesion, the metal will passivate, resulting in excellent corrosion resistance. In environments that contain aggressive ions, however, the passive film can breakdown, resulting in localized corrosion and very high corrosion rates. Hence, coatings are very frequently needed to suppress corrosion in metals that do not naturally form protective passive films or for aggressive environments that can break down passivity.
1.2 Corrosion
For a metal to corrode by aqueous corrosion, water molecules must be present. The metal, however, need not be fully immersed because water can condense on a surface due to temperature fluctuations, even if the relative humidity is lower than 100% (e.g., condensation on cold surface on a warm, humid day), or due to hygroscopic impurities such as airborne salts.2
1.2.1 Thermodynamics
Aqueous corrosion is an electrochemical process involving anodic (or oxidation) and cathodic (or reduction) reactions. Dissolution of a metal M, which is an anodic reaction, is represented by the half-cell reaction
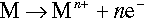
The electrons of the anodic reaction must be consumed by a cathodic reaction for corrosion to proceed. Two predominant cathodic reactions in aqueous corrosion are oxygen reduction (Equations 1.2 and 1.3) and hydrogen evolution (Equations 1.4 and 1.5), respectively. Their half-cell reactions are represented as follows:
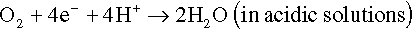
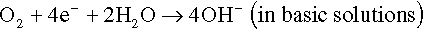
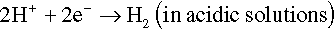
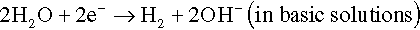
Oxygen reduction can only occur in aerated solutions, which contain dissolved oxygen molecules. Hydrogen evolution can occur ...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Contributors
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Electrochemical Aspects of Corrosion-Control Coatings
- Chapter 2: The Importance of Corrosion and the Necessity of Applying Intelligent Coatings for Its Control
- Chapter 3: Smart Inorganic and Organic Pretreatment Coatings for the Inhibition of Corrosion on Metals/Alloys
- Chapter 4: Low Temperature Coating Deriving from Metal-Organic Precursors: An Economical and Environmentally Benign Approach
- Chapter 5: Synthesis and Evaluation of Self-Healing Cerium-Doped Silane Hybrid Coatings on Steel Surfaces
- Chapter 6: Hybrid Zinc-Rich Paint Coatings: The Impact of Incorporation of Nano-Size Inhibitor and Electrical Conducting Particles
- Chapter 7: Innovative Luminescent Vitreous Enameled Coatings
- Chapter 8: Anticorrosion Coatings with Self-Recovering Ability Based on Damage-Triggered Micro- and Nanocontainers
- Chapter 9: Important Aspects Involved in Pilot Scale Production of Modern Paints and Coatings
- Chapter 10: Sol-Gel Route for the Development of Smart Green Conversion Coatings for Corrosion Protection of Metal Alloys
- Chapter 11: Conducting Polymers with Superhydrophobic Effects as Anticorrosion Coating
- Chapter 12: Smart Protection of Polymer-Inhibitor Doped Systems
- Chapter 13: Properties and Applications of Thermochromic Vanadium Dioxide Smart Coatings
- Chapter 14: One-Part Self-Healing Anticorrosive Coatings: Design Strategy and Examples
- Chapter 15: Intelligent Stannate-Based Coatings of Self-Healing Functionality for Magnesium Alloys
- Chapter 16: Electroactive Polymer-Based Anticorrosive Coatings
- Chapter 17: Corrosion Protective Coatings for Ti and Ti Alloys Used for Biomedical Implants
- Chapter 18: Optical Sensors for Corrosion Monitoring
- Chapter 19: Characterization of High Performance Protective Coatings for Use on Culturally Significant Works
- Chapter 20: Monitoring Corrosion Using Vibrational Spectroscopic Techniques
- Index