
Process Control in Textile Manufacturing
- 512 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Process Control in Textile Manufacturing
About this book
Complex raw materials and manufacturing processes mean the textile industry is particularly dependent on good process control to produce high and consistent product quality. Monitoring and controlling process variables during the textile manufacturing process also minimises waste, costs and environmental impact. Process control in textile manufacturing provides an important overview of the fundamentals and applications of process control methods.Part one introduces key issues associated with process control and principles of control systems in textile manufacturing. Testing and statistical quality control are also discussed before part two goes on to consider control in fibre production and yarn manufacture. Chapters review process and quality control in natural and synthetic textile fibre cultivation, blowroom, carding, drawing and combing. Process control in ring and rotor spinning and maintenance of yarn spinning machines are also discussed. Finally part three explores process control in the manufacture of knitted, woven, nonwoven textiles and colouration and finishing, with a final discussion of process control in apparel manufacturing.With its distinguished editors and international team of expert contributors, Process control in textile manufacturing is an essential guide for textile engineers and manufacturers involved in the processing of textiles, as well as academic researchers in this field.- Provides an important overview of the fundamentals and applications of process control methods- Discusses key issues associated with process control and principles of control systems in textile manufacturing, before addressing testing and statistical quality control- Explores process control in the manufacture of knitted, woven, nonwoven textiles and colouration and finishing, with a discussion on process control in apparel manufacturing
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Basics of process control in textile manufacturing
Abstract:
1.1 Introduction
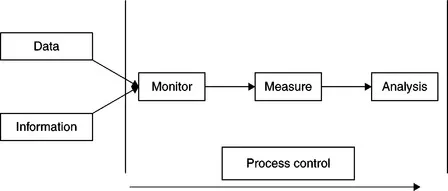
1.2 Process mapping, analysis and control
1.2.1 Process mapping
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Contributor contact details
- Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles
- Foreword
- Part I: General issues
- Part II: Process control in fibre production and yarn manufacture
- Part III: Process control in fabric manufacture, coloration and finishing
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app