
- 154 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
The Birnbaum-Saunders Distribution
About this book
The Birnbaum-Saunders Distribution presents the statistical theory, methodology, and applications of the Birnbaum-Saunders distribution, a very flexible distribution for modeling different types of data (mainly lifetime data).
The book describes the most recent theoretical developments of this model, including properties, transformations and related distributions, lifetime analysis, and shape analysis. It discusses methods of inference based on uncensored and censored data, goodness-of-fit tests, and random number generation algorithms for the Birnbaum-Saunders distribution, also presenting existing and future applications.
- Introduces inference in the Birnbaum-Saunders distribution
- Provides a comprehensive review of the statistical theory and methodology of the Birnbaum-Distribution
- Discusses different applications of the Birnbaum-Saunders distribution
- Explains characterization and the lifetime analysis
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Genesis of the Birnbaum–Saunders Distribution
Abstract
In this chapter, a background and the history of life distributions, as well as some of its indicators, such as the failure rate and reliability function, are provided. In addition, we detail how the fatigue processes are developed and the genesis and mathematical derivation of the Birnbaum–Saunders distribution. Furthermore, a connection between this distribution and the law of proportionate effects is discussed. Moreover, several real-world applications of the Birnbaum–Saunders distribution are mentioned.
Keywords
cumulative damage models
failure or hazard rate
fatigue
law of proportionate effects
life distributions
lifetime data
reliability or survival function.
1.1 Introduction
In general, the literature related to statistical methods and models for lifetime data recognizes the concept “lifetime” as a positive continuous random variable representing the time until the occurrence of some event of interest. However, in some occasions, the aging of items (e.g., components, systems, subsystems, specimens, structures, organs, units) is not measured in chronological terms. In such occasions, the lifetime is measured by means of other random variables. For example, the amount of kilometers traveled, strength of material specimens until its rupture, level of degradation, flexibility of an adhesive, and number of cycles until a material specimen fails caused by fatigue (fatigue-life). In addition, the terminology “lifetime random variable,” which we denote hereafter by T, is widely used for referring to any positive continuous random variable (e.g., amount of rain water or contaminant concentration). Any probabilistic model associated with a lifetime random variable is often called a life distribution. For more details about life distributions, the interested reader is referred to Marshall and Olkin (2007).
The reliability theory refers to probabilistic and statistical problems, which are related to life distributions of items subject to failure. The probabilistic methods of this theory describe the performance and degradation of items by means of lifetime random variables. Life distributions are used to determinate the reliability (or survival) function, failure (or hazard) rate, and average lifetime of these items. The statistical aspects of this theory solve estimation and inference aspects of the life distribution parameters.
Technically, the reliability of an item is defined as the probability that a lifetime random variable T > 0 surpasses a fixed time t. Thus, the reliability function of T over time t is given by
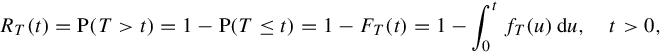
which, as noted, depends on the continuous life distribution when a parametric analysis is carried out. This life distribution for T can be characterized by its probability density function fT(⋅) or its cumulative distribution function FT(⋅), as viewed in Equation (1.1), or even by its failure or hazard rate given by
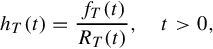
or its cumulative failure rate defined as
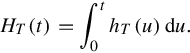
1.2 History
The most used probabilistic model is the normal (or Gaussian) distribution. However, often life distributions are two-parameter probabilistic models having asymmetry to the right (positive skewness), unimodality, and positive support (T > 0). Thus, the normal distribution is unsuitable for modeling lifetime data. In lifetime parametric analyses, the key distribution is the exponential model, also called the negative exponential distribution. Nevertheless, other probabilistic models have also been used as alternative distributions to the normal model upon asymmetry to the right and positive support. Next, the evolution of life distributions is presented.
Davis (1952) showed several examples of failure data, along with some goodness-of-fit tests for these data. This work provided a guideline toward the use of the exponential model as a life distribution. Later, the works by Epstein and Sobel (1953, 1954a,b, 1955) strengthened and helped to popularize the exponential l...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Dedication
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Genesis of the Birnbaum–Saunders Distribution
- Chapter 2: Characterizations of the Birnbaum–Saunders Distribution
- Chapter 3: Inference for the Birnbaum–Saunders Distribution
- Chapter 4: Modeling Based on the Birnbaum–Saunders Distribution
- Chapter 5: Goodness of Fit for the Birnbaum–Saunders Distribution
- Chapter 6: Data Analyses with the Birnbaum–Saunders Distribution
- Bibliography
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access The Birnbaum-Saunders Distribution by Victor Leiva in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Mathematics & Probability & Statistics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.