
- 792 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Corrosion Engineering: Principles and Solved Problems covers corrosion engineering through an extensive theoretical description of the principles of corrosion theory, passivity and corrosion prevention strategies and design of corrosion protection systems. The book is updated with results published in papers and reviews in the last twenty years. Solved corrosion case studies, corrosion analysis and solved corrosion problems in the book are presented to help the reader to understand the corrosion fundamental principles from thermodynamics and electrochemical kinetics, the mechanism that triggers the corrosion processes at the metal interface and how to control or inhibit the corrosion rates. The book covers the multidisciplinary nature of corrosion engineering through topics from electrochemistry, thermodynamics, mechanical, bioengineering and civil engineering.- Addresses the corrosion theory, passivity, material selections and designs- Covers extensively the corrosion engineering protection strategies- Contains over 500 solved problems, diagrams, case studies and end of chapter problems- Could be used as a text in advanced/graduate corrosion courses as well self-study reference for corrosion engineers
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Evaluation of Corrosion
Abstract
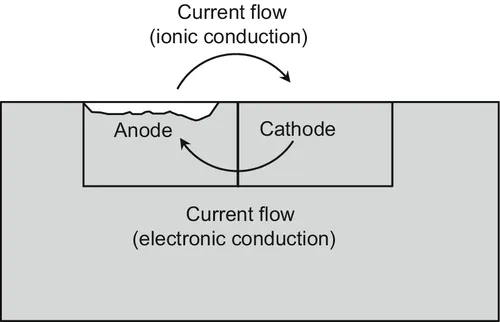
1.1 Significance and Cost of Corrosion
1.2 Definition
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Acknowledgment
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Evaluation of Corrosion
- Chapter 2: Thermodynamics in the Electrochemical Reactions of Corrosion
- Chapter 3: Electrochemical Kinetics of Corrosion
- Chapter 4: Passivity
- Chapter 5: Basics of Corrosion Measurements
- Chapter 6: Galvanic Corrosion
- Chapter 7: Pitting and Crevice Corrosion
- Chapter 8: Hydrogen Permeation and Hydrogen-Induced Cracking
- Chapter 9: Stress Corrosion Cracking
- Chapter 10: Atmospheric Corrosion
- Chapter 11: High-Temperature Corrosion
- Chapter 12: Corrosion of Structural Concrete
- Chapter 13: Organic Coatings
- Chapter 14: Corrosion Inhibitors
- Chapter 15: Cathodic Protection
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 2: Thermodynamics in the Electrochemical Reactions of Corrosion
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 3: Electrochemical Kinetics of Corrosion
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 4: Passivity
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 5: Basics of Corrosion Measurements
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 6: Galvanic Corrosion
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 7: Pitting and Crevice Corrosion
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 8: Hydrogen Permeation and Hydrogen-Induced Cracking
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 9: Stress Corrosion Cracking
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 11: High-Temperature Corrosion
- Solutions Guide: Chapter 15: Cathodic Protection
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app