
eBook - ePub
Controller Design for Industrial Robots and Machine Tools
Applications to Manufacturing Processes
- 260 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Controller Design for Industrial Robots and Machine Tools
Applications to Manufacturing Processes
About this book
Advanced manufacturing systems are vital to the manufacturing industry. It is well known that if a target work piece has a curved surface, then automation of the polishing process is difficult. Controller design for industrial robots and machine tools presents results where industrial robots have been successfully applied to such surfaces, presenting up to date information on these advanced manufacturing systems, including key technologies. Chapters cover topics such as velocity-based discrete-time control system for industrial robots; preliminary simulation of intelligent force control; CAM system for an articulated industrial robot; a robot sander for artistic furniture; a machining system for wooden paint rollers; a polishing robot for PET bottle blow moulds; and a desktop orthogonal-type robot for finishing process of LED lens cavity; and concludes with a summary. The book is aimed at professionals with experience in industrial manufacturing, and engineering students at undergraduate and postgraduate level.
- Presents results where industrial robots have been used successfully to polish difficult surfaces
- Presents the latest technology in the field
- Includes key technology such as customized several position and force controllers
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Controller Design for Industrial Robots and Machine Tools by F Nagata,K Watanabe in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Industrial Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
Velocity-based discrete-time control system with intelligent control concepts for openarchitecture industrial robots
Abstract:
A simulation technique of velocity-based discrete-time control system for open-architecture industrial robots is presented by giving and combining examples of intelligent controls such as genetic algorithms, fuzzy control and neural networks. In order to develop a novel control system for an open-architecture industrial robot, it is required with regard to safety, cost and simplicity to preliminarily examine and evaluate the characteristics and the performance. The proposed simulation technique has a high applicability.
Key words
servo system
dynamic simulation
PUMA560
gain tuning
genetic algorithms
force control
fuzzy control
neural network
1.1 Background
Industrial robots have drastically rationalized many kinds of manufacturing processes in industrial fields. The user interface provided by the robot manufacturer has been almost entirely limited to the so-called teaching pendant. The teaching pendant is a useful and safe tool to obtain positions and orientations at the tip of a robot along a desired trajectory, but the teaching task is very complicated and time-consuming. In particular, when the target trajectory is a free curved line, many through points must be given to acquire a smooth trajectory; the task is therefore not an easy one.
In the past decade, open-architecture industrial robots as shown in Fig. 1 have been produced from several industrial robot makers such as KAWASAKI Heavy Industries, Ltd., MITSUBISHI Heavy Industries, Ltd., YASKAWA Electric Corp., and so on. Open architecture, as described in this book, means that the servo system and kinematics of the robot are technically opened, so that various applications required in industrial fields can be planned and developed at the user side. For example, non-taught operation using a CAD/CAM system can be considered due to the opened accurate kinematics. Also, a force control strategy using a force sensor can easily be implemented due to the technically opened discrete-time servo system.
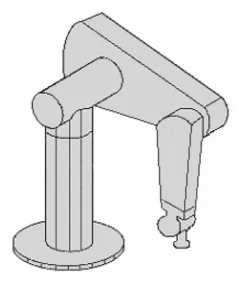
Figure 1.1 PUMA560 manipulator.
It is now possible to model and simulate many types of robots. For example, Chen et al. presented a new design of an environment for the simulation, animation, and visualization of sensor-driven robots. Conventional computer-graphics-based robot simulation and animation software packages lacked of capabilities for robot sensing simulation, so the system was designed to overcome the deficiency [1]. Benimeli et al. also addressed the implementation and comparison of indirect and direct identification procedures on an industrial robot provided with an open control architecture. The estimation of dynamic parameters in mechanical systems constituted an issue of crucial importance for dynamic simulation applications where high levels of accuracy were required [2].
In this chapter, we present a simulation technique of a velocity-based discrete-time control system for open-architecture industrial robots by giving and combining examples of intelligent control concepts such as genetic algorithms, fuzzy control and neural networks. In order to develop a novel velocity-based control system represented in discrete-time domain for an open-architecture industrial robot, it is required from the points of view of safety, cost and ease to preliminarily examine and evaluate the characteristics and performance. In such a case, the proposed simulation techniques will be useful. The validation and promise are evaluated through simulations, using a dynamic model of a PUMA560 manipulator as shown i...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- List of figures
- List of tables
- Preface
- About the authors
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Velocity-based discrete-time control system with intelligent control concepts for openarchitecture industrial robots
- Chapter 2: Preliminary simulation of intelligent force control
- Chapter 3: CAM system for articulated-type industrial robot
- Chapter 4: 3D robot sander for artistically designed furniture
- Chapter 5: 3D machining system for artistic wooden paint rollers
- Chapter 6: Polishing robot for pet bottle blow molds
- Chapter 7: Desktop orthogonal-type robot for LED lens cavities
- Chapter 8: Conclusion
- References
- Index