
Reactive Polymers Fundamentals and Applications
A Concise Guide to Industrial Polymers
- 576 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Reactive Polymers Fundamentals and Applications
A Concise Guide to Industrial Polymers
About this book
The use of reactive polymers enables manufacturers to make chemical changes at a late stage in the production process—these in turn cause changes in performance and properties. Material selection and control of the reaction are essential to acheive optimal performance.The second edition of Reactive Polymers Fundamentals and Applications introduces engineers and scientists to the range of reactive polymers available, explains the reactions that take place, and details applications and performance benefits.Basic principles and industrial processes are described for each class of reactive resin (thermoset), as well as additives, the curing process, and applications and uses. The initial chapters are devoted to individual resin types (e.g. epoxides, cyanacrylates, etc.); followed by more general chapters on topics such as reactive extrusion and dental applications. Material new to this edition includes the most recent developments, applications and commercial products for each chemical class of thermosets, as well as sections on fabrication methods, reactive biopolymers, recycling of reactive polymers, and case studies. Injection molding of reactive polymers, radiation curing, thermosetting elastomers, and reactive extrusion equipment are all covered as well.- Most comprehensive source of information about reactive polymers- Covers basics as well as most recent developments, including reactive biopolymers, recycling of reactive polymers, nanocomposites, and fluorosilicones- Indispensable guide for engineers and advanced students alike—providing extensive literature and patent review
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Unsaturated Polyester Resins
1.1 History
1.2 Monomers
1.2.1 Monomers for an Unsaturated Polyester
| Saturated Alcohols | Remarks |
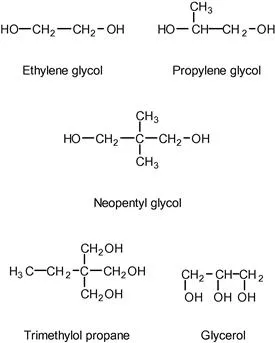
| 1,2-Propylene glycol | Most common glycol |
| Ethylene glycol | Less compatible with styrene than propylene glycol |
| Diethylene glycol | Good drying properties |
| Neopentyl glycol | Good hydrolysis resistance |
| Glycerol | Trifunctional alcohol, for branched polyesters. Danger of crosslinking during condensation |
| Flame retardant | |
| Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) | |
| Trimethylol propane | Trifunctional alcohol, cheaper than glycerol |
| Trimethylol propane mono allyl ether | Weather resistant for coatings [12,13] |
| Undecanol | Used as chain stopper |
| Saturated Acids and Anhydrides | Remarks |
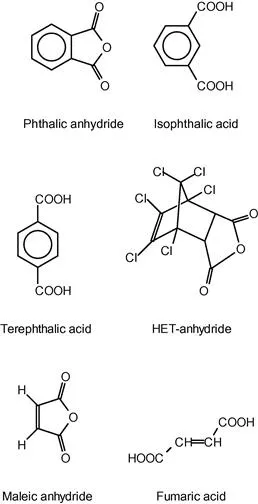
| Phthalic anhydride | Most common anhydride |
| Isophthalic acid | Good hydrolysis resistance |
| Terephthalic acid | Superior hydrolysis resistance |
| HET acid | Flame retardant systems. In fact, even when addressed as HET acid, the HET anhydride is used |
| Tetrabromophthalic anhydride | Flame retardant systems |
| Adipic acid | Soft resins |
| Sebacic acid | Soft resins |
| o-Carboxy phthalanilic acid | [14] |
| Unsaturated Acids and Anhydrides | Remarks |
| Maleic anhydride | Most common |
| Fumaric acid | Copolymerizes better with styrene than maleic anhydride |
| Itaconic acid |
1.2.1.1 Alcohol Components
1.2.1.2 Acid and Anhydride Components
Isomerization
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Plastics Design Library (PDL)
- Copyright
- PDL Series Editor’s Preface
- Preface
- Chapter 1. Unsaturated Polyester Resins
- Chapter 2. Poly(urethane)s
- Chapter 3. Epoxy Resins
- Chapter 4. Phenol/Formaldehyde Resins
- Chapter 5. Urea/Formaldehyde Resins
- Chapter 6. Melamine Resins
- Chapter 7. Furan Resins
- Chapter 8. Silicones
- Chapter 9. Acrylic Resins
- Chapter 10. Cyanate Ester Resins
- Chapter 11. Bismaleimide Resins
- Chapter 12. Terpene Resins
- Chapter 13. Cyanoacrylates
- Chapter 14. Benzocyclobutene Resins
- Chapter 15. Reactive Extrusion
- Chapter 16. Compatibilization
- Chapter 17. Rheology Control
- Chapter 18. Grafting
- Chapter 19. Acrylic Dental Fillers
- Chapter 20. Toners
- Index