
eBook - ePub
Internal Combustion Engines
Improving Performance, Fuel Economy and Emissions
- 288 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Internal Combustion Engines
Improving Performance, Fuel Economy and Emissions
About this book
This book contains the papers of the Internal Combustion Engines: Performance fuel economy and emissions conference, in the IMechE bi-annual series, held on the 29th and 30th November 2011. The internal combustion engine is produced in tens of millions per year for applications as the power unit of choice in transport and other sectors. It continues to meet both needs and challenges through improvements and innovations in technology and advances from the latest research. These papers set out to meet the challenges of internal combustion engines, which are greater than ever. How can engineers reduce both CO2 emissions and the dependence on oil-derivate fossil fuels? How will they meet the future, more stringent constraints on gaseous and particulate material emissions as set by EU, North American and Japanese regulations? How will technology developments enhance performance and shape the next generation of designs? This conference looks closely at developments for personal transport applications, though many of the drivers of change apply to light and heavy duty, on and off highway, transport and other sectors.
- Aimed at anyone with interests in the internal combustion engine and its challenges
- The papers consider key questions relating to the internal combustion engine
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Internal Combustion Engines by Institution of Mechanical Engineers in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Chemical & Biochemical Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Fuels and emissions
Research into requirements for worldwide sustainable biodiesel capability
T. Gardiner and J. Gaade, Jaguar Land Rover Advanced Powertrain Engineering, UK
B. Head, Shell Global Solutions, UK
C. Hygate, Green Fuels Ltd, UK
H.M. Xu and N.R. Abdullah, University of Birmingham, UK
ABSTRACT
Optimising engines for the potential use of Low Carbon alternative fuels is a key area of Sustainable Development for Jaguar Land Rover. Future legislated introduction of bio-diesel in worldwide markets will require Jaguar and Land Rover products to be robust to a wide-range of fuels.Alternative fuels are manufactured from a variety of feed stocks, which vary according to market, resulting in different fuel properties affecting combustion behaviour.Results generated will aid the understanding of effects on combustion and engine control strategies with a variety of bio-diesel fuels which may be found in future world markets.
1 INTRODUCTION
There is a growing requirement for the use of alternative and renewable fuels. An increase in the availability of biofuels in the UK as well as global markets has challenged industry to prepare a way forward for the use of these renewable fuels in place of conventional fossil fuels. This challenge has come about from the growing need for governments to develop sustainable transport solutions. Biodiesel is already blended into mineral fuels as a legislated minimum percentage of the total fuel requirement in most world markets.
The EU legislation – Renewable Energy Directive calls for 20 % renewable energy in each member state by 2020. This was set by EU commission leaders subject to ‘production being sustainable’ and to ‘advanced technology bio-fuels becoming commercially available’ (1).
In 2008, the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA) agreed that "– The majority of new gasoline vehicles can be operated on E10 and industry is working towards B7 compatibility. Pending completion of relevant fuel standards, the industry aims to complete its phase-in of 100% E10/B7 capability across all new models by 2010." (2). This is subject to the pending Fuel Quality Directive discussions within the European Institutions and the availability of quality biofuels and the blended fuels meeting the EN590 standard(3).
The blend of biodiesel may be as high as 5% at the pump with out the need for labelling. Any blend above 7% must be labelled to inform the customer of the percentage blend of biodiesel the fuel contains so that the customer is aware of what they are buying.
The Automotive Industry needs to be flexible to the large number of developing fuels. Some renewable fuels have been proven to be more successful than others during the research and development process. There are many different feedstocks that are being researched and utilised, the processes for the manufacture of these feedstocks into fuels also vary greatly and the fuel products vary greatly in their final properties even when made to a very high quality and the appropriate standards. Properties such as the energy content, density and viscosity to name a few can give the fuel unique combustion characteristics.
The technical approach of this research was to investigate the relationship between the fuel properties and engine emissions to understand the combustion characteristics of biodiesel fuels within diesel engines currently on the market.
Engine control strategy design will be required to be robust to a variety of fuel types.
Objectives for this research are:
• Identification of relevant detectable properties of a biodiesel blended fuel before combustion that can differentiate it from other fuels.
• The fuel properties identified should be directly related to a combustion characteristic of a diesel engine including emission levels and power output.
• Identify what engine actuators are available to be utilised within a emissions compensation control strategy.
• Investigation of a possible strategy with the use of existing engine actuators.
Other issues when operating on high concentrations of biodiesel, ie. engine lubrication, injector fouling, filter clogging, etc. are not part of this research paper.
2 WORLDWIDE BIODIESEL REVIEW
Issues surrounding the sustainable supply of feedstock materials are the single most critical factor affecting bio-fuels in Europe. The sale of bio-fuels will be linked to, and rewarded by, the carbon savings and levels of sustainability that are adhered to; through the Renewable Energy Directive and the Renewable Transport Fuels Obligation and further defined in the Fuel Quality Directive. The supply of bio-components for use in this research respond to the sustainability issues, where this does not compromise the technical imperative to test particular bio-components.
Feedstocks were sourced for the investigations based on the findings of a worldwide biodiesel fuels review conducted by Green Fuels Ltd and Shell Global Solutions aimed at providing an overview of current knowledge on alternative fuels for diesel and covers aspects including industry-adopted nomenclature, general properties, basics of feedstock processing and standard analytical techniques as well as identifying major producers and retailers, particularly in the UK.
Typically, alternative diesels can be classified as First and Second Generation bio-fuels. Biodiesel fuels produced using alkaline or acid transesterification processes are classified as first-generation. Those that use advanced processing technologies such as hydro-treating, gasification and Fischer-Tropsch reformation processes or non land based sources utilising any processing technology are classified as second-generation.
As 2nd generation products become more mature and new bio materials become of interest as automotive fuels, it would be unclear how to categorise these products.
An additional classification can be made by categorising the fuels into Research, Development and Commercial. The pyramid shown below illustrates each fuel’s level of cost and technical challenge versus the availability or applicability.
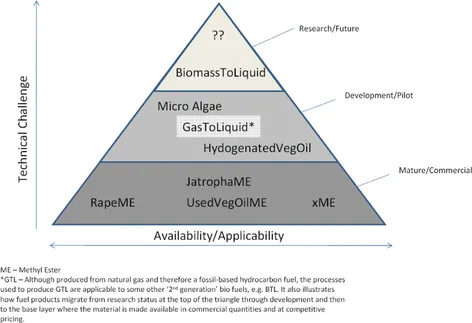
Figure 1 Developing fuels pyramid
Based on the review of worldwide bio-fuel feedstock availability and the sustainability of their bio-component production the following feedstocks were selected for the research:
• Tallow, which is animal fat.
• Rape seed oil of cookin...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- SI Engines and downsizing
- GDI Particulates and other emissions
- Diesel fuel injection
- Engine design
- Fuels and emissions
- Emissions after-treatment
- Author Index