
- 256 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Seismic Data Analysis Techniques in Hydrocarbon Exploration
About this book
Seismic Data Analysis Techniques in Hydrocarbon Exploration explains the fundamental concepts and skills used to acquire seismic data in the oil industry and the step-by-step techniques necessary to extract the sections that trap hydrocarbons as well as seismic data interpretation skills.It enhances the ability to interpret seismic data and use that data for basin evaluation, structural modeling of a fault, reservoir characterization, rock physics analysis, field development, and production studies.Understanding and interpreting seismic data is critical to oil and gas exploration companies. Arming young geoscientists with a reference that covers the key principles of seismic data analysis will enhance their job knowledge, skills and performance. A fundamental grasp of seismic data enhances employability and aids scientists in functioning effectively when working with seismic data in industry.- Edited by a team of petroleum geoscientists with more than 30 years of experience in hydrocarbon exploration and data analysis at O&G companies.- More than 200 figures, photographs, and illustrations aid in the understanding of the fundamental concepts and techniques used to acquire seismic data- Takes an easy-to-follow, step-by-step approach to presenting the techniques and skills used to extract the geologic sections from acquired seismic data.- Enhances the geoscientist's effectiveness when using seismic data for field development and other exploration and production studies
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Understanding the Detail Seismic Processing Techniques Used to Convert the Acquired Seismic Data into the Geologic Section of the Earth
Abstract
Keywords
What is Seismic Data Processing
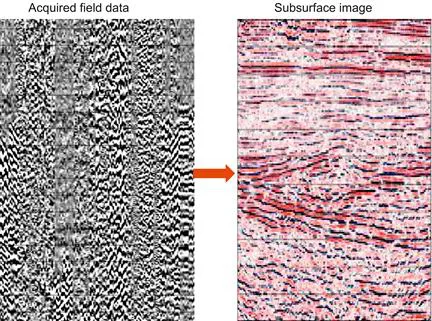
Note that wrong shot and geophone group coordinates will lead to mis-positioning and distortion of the final seismic image (migrated image).
Transcription
Observer Log
Spherical Divergence
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Acknowledgements
- Foreword
- Introduction
- I: Basic Sedimentology and Seismic Data Acquisition
- II: Detailed Seismic Data Processing Techniques
- III: Seismic Data Interpretation Methodology
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app