
eBook - ePub
Ecocatalysis
A New Integrated Approach to Scientific Ecology
- 100 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Ecocatalysis
A New Integrated Approach to Scientific Ecology
About this book
Reconquest of biodiversity; remediation of degraded and anthropic areas, prevention of environmental health risks; eco-innovation; Green industry ... The current French ambitions are closely related to an interdisciplinary approach to scientific ecology, all of which participate in the expected industrial renewal.Ecocatalysis explores the unusual combination of phytotechnologies adapted to pollution, ecological rehabilitation of polluted sites and enhancement of these processes through innovative green chemistry, all of which contribute to the development of scientific priorities; economic, ecological innovation and current environmental, of biomass conversion and transition from fossil fuels to renewable.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Ecocatalysis by Claude Grison,Vincent Escande,Jacques Biton in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Biological Sciences & Ecology. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
A New Approach to Multi-Site and Multi-Scale Rehabilitation by Phytoextraction
Abstract
The proposed ecological innovation is an integrated and interdisciplinary approach to phytoremediation, which is based on fundamental knowledge of plant and microbial ecology, in ecological and environmental chemistry.
Keywords
2-Keto-3-Deoxy-D-Gluconic acid (KDG)
Anthyllis vulneraria
Bacterial composition
Geissois pruinosa
Grevillea exul
Les Avinières
Metal pollution
Microbial diversity
Nitrogen-fixing symbioses
Sterile compacted soil (SS3)
The proposed ecological innovation is an integrated and interdisciplinary approach to phytoremediation, which is based on fundamental knowledge of plant and microbial ecology, in ecological and environmental chemistry.
The main objectives are to improve the environmental and ecological quality of sites and carefully manage the associated risks by providing means to control them over time.
The present results are the results of the collaboration between public research laboratories (Bio-inspired Chemistry and Ecological Innovations Laboratory at University of Montpellier), semi-public (New Caledonian Agronomic Institute) and private societies (Stratoz, Société Le Nickel) which have chosen to combine their own phytoremediation skills to develop a new program of chemical recycling of contaminated waste that can be adapted to the variability and multiplicity of soil and climatic conditions of degraded sites in mainland France and New Caledonia.
They are split into two study sites, each with very different origins of metallic waste and environmental and economic expectations of the populations concerned, but with common natural adaptation phenomena of certain plants and associated micro-organisms:
– the Languedoc-Roussillon region of mainland France, and more specifically the department Gard, where the tourist town of Saint-Laurent-Le-Minier is the representative pilot site of an old mining region where centuries of exploitation have contaminated large areas and adjacent rivers with zinc, cadmium and lead;
– a revegetation program largely using phytoextraction was set up with the collaboration of local representatives. The remarkable characteristics of two hyperaccumulator species of zinc and cadmium, Noccaea (Thlaspi) caerulescens (N. caerulescens) ecotype Ganges and the leguminous species, Anthyllis vulneraria (A. vulneraria), have been used in our applied ecological chemistry program;
– New Caledonia, a biodiversity hotspot, home to 3,350 plant species, 74% of which are endemic, and threatened by fires, invasive species such as deer, or increasing nickel mining. Moreover, due to the depletion of conventional garnierite deposits, new lateritic nickel ore deposits need to be exploited. This situation has become possible due to the development of new hydrometallurgical technologies that can profitably process previously untapped low-nickel content laterite ores. These deposits are more extensive at the surface and, therefore, potentially increase the negative impacts on the biodiversity of this area.
Besides the chemical nature of metal species hyperaccumulated by adapted plants, these two regions have a common feature: past mining activities have had a significant impact on the environment and new economic activities have struggled to take off. Our ecocatalysis program is aimed at their environmental reconstruction through a recovery project based on non-conventional and complementary processes. This mining past can become an opportunity to promote research and stimulate the development of new scientific and economic activities.
Plant communities that develop on mining land have adapted over a long period of time, and several species are capable of hyperaccumulating nickel, manganese and/or aluminum: a biodiversity with a mineral chemodiversity in terms of hyperaccumulation. This controlled recovery of such an environment using a sustainable green chemistry program is orientated toward local emerging markets in Caledonia and local populations.
1.1 Remedial phytoextraction on a highly contaminated former mining site: pilot site at “Les Avinières”
1.1.1 What are the characteristics of the site at “Les Avinières”?
The site of “Les Avinières” is located in the commune of Saint-Laurent-le-Minier, in Gard. The region is subject to strong contrasts: it has a low population density (<50 inhabitants per km2) and is situated between a national park (Cévennes National Park) and a conservation area of the Natura 2000 network. It also has significant liability in terms of mining activities: the district of les Malines, where millions tons of mineral were extracted between 1885 and 1991, is still the largest exploiter of zinc and lead that France has ever known [LEG 91]. The mine in “Les Avinières” is older – its activity begun in 1857 and continued until the early 1950s.
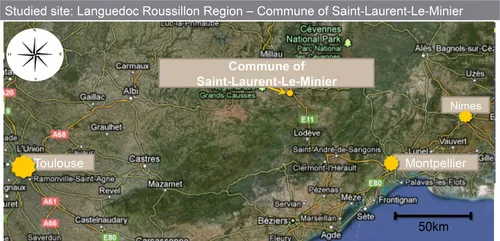
Figure 1.1 Geographical position of the experimental site of Saint-Laurent-le-Minier
The former mining activities at the “Les Avinières” site are responsible for significant modifications to the environment. The extraction of the ore has altered the landscape with the formation of a large heap with significant quantities of accumulated waste and high contents of “trace metals”. The purification stages, washing the ores that generated large amounts of waste with high contents of TEs, have formed a zone with highly contaminated soil at the site of storage. This zone includes all the former settling basins and has almost a complete lack of vegetation. This part of the site has become phytotoxic. The few plants th...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Introduction: Toward an Ecology of Industrial Pollution?
- 1. A New Approach to Multi-Site and Multi-Scale Rehabilitation by Phytoextraction
- 2. From Phytoextraction to Green Chemistry and Vice Versa via Ecocatalysis
- Conclusion
- Bibliography
- Index