![]()
none Part III
![]()
Chapter 9. Business Planning
Planning, of course is not a separate, recognizable act… Every managerial act, mental or physical is inexorably intertwined with planning. It is as much a part of every managerial act as breathing is to the living human.– C. George, The History of Management, 1972.
Introduction
Business forecasting involves the prediction of what could happen in the future and business planning involves the calculation of what is required to fulfil the forecast, that is, make the future happen as it is forecast. Thus a business plan uses a forecast as an initial point of departure and then adds the detail to reflect how the particular process or project is intended to proceed. Business plans are generally set in the future and involve making a series of assumptions about how the variables in the plan will behave in future periods.
Business plans are helpful with the decision-making process of an organisation. There are many types of business plans, which range from simple verbal or written descriptions of what is to be achieved, through diagrammatic representations such as Gantt charts to highly analytical numeric reports.
There are many definitions of planning, but perhaps one worth quoting is from Ackoff[1] who said: Planning is required when the future state that we desire involves a set of interdependent decisions; that is, a system of decisions… The principal complexity in planning derives from the interrelatedness of the decisions rather than from the decisions themselves…
1 R.L. Ackoff, A Concept of Corporate Planning , Wiley, New York, 1970.
In the context of this book, a business plan is a statement of quantifiable objectives, together with the resources required to achieve them. The objective may be profit, market share, return on investment or cash flow, to mention only a few, and the resources could be manpower, materials, capital, cash, etc.
There are many different ways of classifying business plans, including short-term plans, long-term plans, profit plans, marketing plans, production plans, personnel development plans, capital investment plans, merger and take-over plans, etc. The level of analysis in the plan reflects the ultimate use for which it is intended. For high-level strategic decisions, plans generally do not contain very much detail, whereas for operational planning a large amount of detail is required. The contents will reflect the nature of the project or process being planned, but it is not unusual for operational plans to involve dozens of line items. These types of plan often form the basis of a financial budget, which in some cases is no more than a plan divided into specific responsibility points and specific time periods.
An important aspect of business planning is what-if analysis. This is a process of changing one or more of the variables or assumptions on which a business plan has been based in order to see what effect such a change in circumstances would have on the results. This subject is covered in detail in Chapter 15.
Approaches to business planning
There are three generically different approaches to developing business plans, which are described as deterministic[2], stochastic[3] or probabilistic and optimising.
2 According to the American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language , Third Edition, deterministic refers to the fact that there is an inevitable consequence of antecedents.
3 According to the American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language , Third Edition, stochastic refers to involving a random variable or variables and the chance or probability of their occurrence.
Deterministic planning
Deterministic planning is the most frequently encountered planning. It is the basis on which virtually all corporate planning and budgeting is performed. A deterministic plan takes single values that are the best estimate for the variables in the plan and uses this value with a set of logic rules to produce the plan or budget. The single start value for a line item in a plan is referred to as a point estimate. This might be the result of a forecasting model, and although it is recognised by planners and budgeting officers, that accurate point estimates are almost impossible to obtain; it is usually possible to derive a value that is accurate enough to be useful.
The method of planning is called ‘deterministic’ because once the point estimates are derived, the outcome of the plan may be uniquely determined by the logic, that is, there will be only one answer. For example, consider the following:
- Sales volume 200
- Unit price 20
- Revenue 4000 (Sales volume *Unit price)
The only way a different result can be obtained in the above example is by changing one or both of the single point estimates, that is, the data for the sales volume and the unit price. Of course, one of the great advantages of the spreadsheet is that making changes to opening data, growth rates, cost factors, etc. causes all directly and indirectly affected cells to recalculate and thus different scenarios can be calculated. However, the basic principle is that the outcome is uniquely determined by the logic.
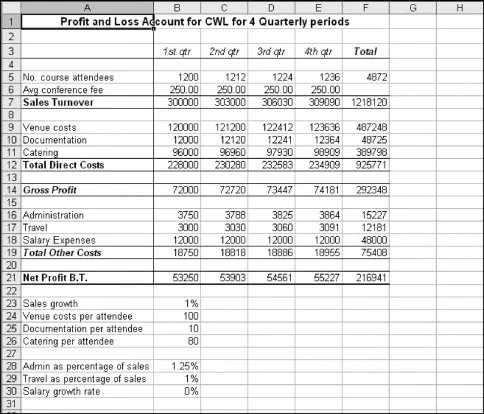
Figure 9.1 is a profit and loss account for CWL that has been developed as a deterministic plan. Figure 9.2 shows the formulae used for the plan.
Figure 9.1. A typical deterministic plan
Figure 9.2. Formulae for the ...