
- 214 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Neurology for Nurses
About this book
Neurology for Nurses is an attempt to make neurology as clear as possible, using the nursing model. The first portion of this book provides a diagram of the planes of the body that considers the nervous system anatomically, which is referenced throughout the book. The different orientations and planes of the body include the anterior (ventral) surface, posterior (dorsal) surface, lateral, medial, sagittal (median) section, Coronal (frontal) section, and transverse. Other than detailed descriptions of the anatomy and functions of nerves and the nervous system, this book provides diagnostic evaluation of diseases and clinical conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, cerebrovascular accidents, brain tumors, head injury, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and meningitis. This book includes as well discussions on neurological examinations, investigations, and observations. The topic on nursing care for unconscious patients is also provided. This text is aimed primarily at nursing students in training, but will also benefits those taking a post-basic nursing course in neurology.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
The planes of the body
| Anterior (ventral) surface | - towards or at the front |
| Posterior (dorsal) surface | - towards or at the back |
| Lateral | - away from the midline, on the side. |
| Medial | - towards the midline. |
| Sagittal (median) section | - dividing the body from top to bottom into a right and left part. |
| Coronal (frontal) section | - dividing the front from the back, i.e. vertically at right angles to the sagittal section. |
| Transverse | - dividing the upper part of the body from the lower. A horizontal section through the body. |
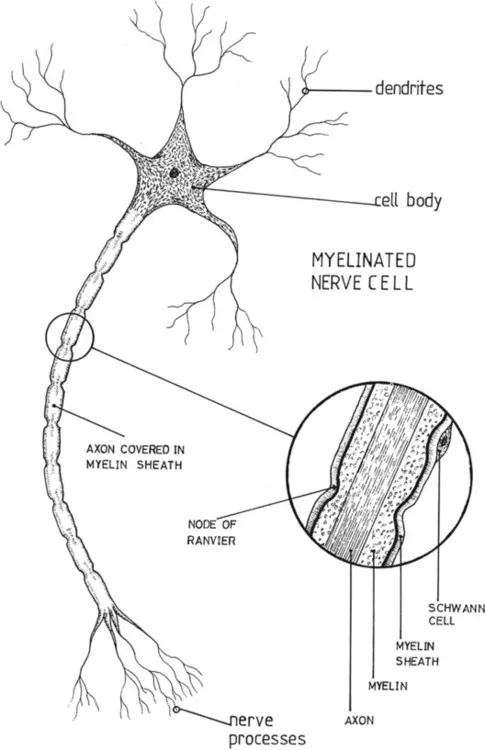
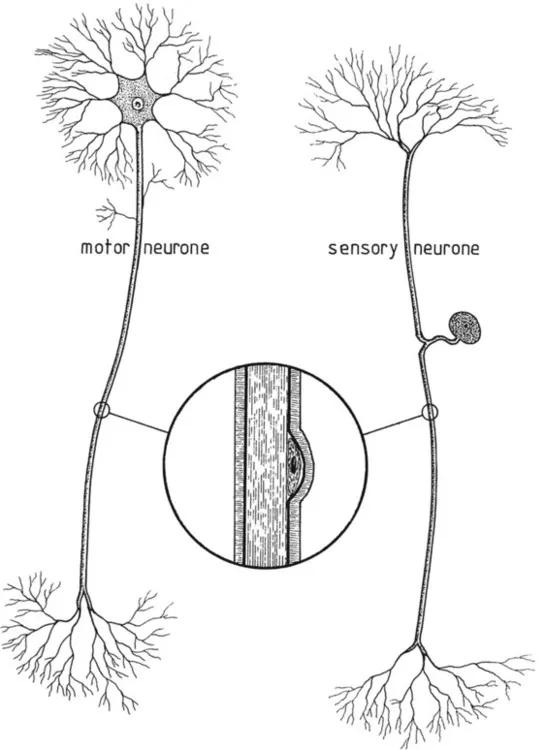
The neurone
Publisher Summary
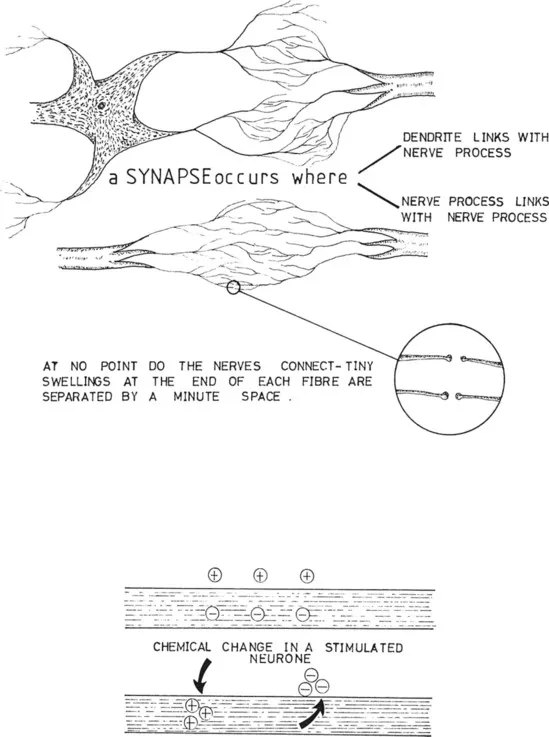
The synapse
The nerve impulse
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- PREFACE
- Inside Front Cover
- Chapter 1: The planes of the body
- Chapter 2: The neurone
- Chapter 3: Introduction to the central nervous system
- Chapter 4: The forebrain
- Chapter 5: The thalamus
- Chapter 6: The basal nuclei
- Chapter 7: The hypothalamus
- Chapter 8: The neuro-hypophysis (posterior pituitary)
- Chapter 9: The brain stem
- Chapter 10: The cerebellum
- Chapter 11: The meninges
- Chapter 12: The ventricles
- Chapter 13: Cerebrospinal fluid
- Chapter 14: Arterial supply of the brain
- Chapter 15: Venous drainage of the brain
- Chapter 16: The spinal cord
- Chapter 17: Ascending sensory tracts
- Chapter 18: Descending motor tracts
- Chapter 19: The reflex arc
- Chapter 20: An introduction to the peripheral nervous system
- Chapter 21: The spinal nerves
- Chapter 22: The cranial nerves
- Chapter 23: The nerves of the upper limb
- Chapter 24: The nerves of the lower limb
- Chapter 25: Sight
- Chapter 26: Hearing
- Chapter 27: Balance
- Chapter 28: Smell and taste
- Chapter 29: Touch
- Chapter 30: The autonomic nervous system
- Chapter 31: Neurological examination
- Chapter 32: Neurological investigations
- Chapter 33: Neurological observations
- Chapter 34: Nursing care of the unconscious patient
- Chapter 35: The paralysed patient
- Chapter 36: Multiple sclerosis
- Chapter 37: Cerebrovascular accident
- Chapter 38: Brain tumours
- Chapter 39: Head injury
- Chapter 40: Epilepsy
- Chapter 41: Parkinson’s disease
- Chapter 42: Meningitis
- Chapter 43: Encephalitis
- Chapter 44: Subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Chapter 45: Lesions of the spinal cord
- Chapter 46: Anterior poliomyelitis
- Chapter 47: Spina bifida
- Chapter 48: Hydrocephalus
- Chapter 49: Peripheral neuritis
- Chapter 50: The trigeminal and facial nerves
- Chapter 51: Menières disease
- Chapter 52: Headaches and migraine
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app