
Characterization of Porous Solids VII
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on the Characterization of Porous Solids (COPS-VII), Aix-en-Provence, France, 26-28 May 2005
- 748 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Characterization of Porous Solids VII
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on the Characterization of Porous Solids (COPS-VII), Aix-en-Provence, France, 26-28 May 2005
About this book
The 7th International Symposium on the Characterization of Porous Solids (COPS-VII) was held in the Congress Centre in Aix-en-Provence between the 25th-28th May 2005. The symposium covered recent results of fundamental and applied research on the characterization of porous solids. Papers relating to characterization methods such as gas adsorption and liquid porosimetry, X-ray techniques and microscopic measurements as well as the corresponding molecular modelling methods were given. These characterization methods were shown to be applied to all types of porous solids such as clays, carbons, ordered mesoporous materials, porous glasses, oxides, zeolites and metal organic frameworks.* 36 oral presentations and 166 posters and around 230 guests from 27 countries. * A large part of this symposium was devoted to the use computational methods to characterise porous solids
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Effect of pore morphology and topology on capillary condensation in nanopores: a theoretical and molecular simulation study
1. Abstract
2. Introduction
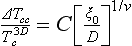
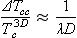
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Front Matter
- Copyright page
- Foreword
- Chapter 1: Effect of pore morphology and topology on capillary condensation in nanopores: a theoretical and molecular simulation study
- Chapter 2: Density functional theory model of adsorption on amorphous and microporous solids
- Chapter 3: Thickness of Adsorbed Nitrogen Films in SBA-15 Silica from Small-Angle Neutron Diffraction
- Chapter 4: Strong light scattering upon capillary condensation in silica aerogels
- Chapter 5: Characterisation of porous solids from nanometer to micrometer range by capillary condensation
- Chapter 6: Characterization of zeolite membrane quality by using permporosimtrey
- Chapter 7: Is the bet equation applicable to microporous adsorbents?
- Chapter 8: A new classification of pore sizes
- Chapter 9: Characterization of nanoporous carbons
- Chapter 10: Adsorption and neutron scattering studies: a reliable way to characterize both the mesoporous MCM-41 and the filling mode of the adsorbed species
- Chapter 11: Absolute assessment of adsorption-based microporous solid characterisation methods
- Chapter 12: Molecular modeling of mercury porosimetry
- Chapter 13: Predicting ambient temperature adsorption of gases in active carbons
- Chapter 14: Characterisation of periodic mesoporous silicas using molecular simulation
- Chapter 15: Structural characterization of porous carbonaceous materials using high-pressure adsorption measurements
- Chapter 16: Microcalorimetric Characterization of Hydrogen Adsorption on Nanoporous Carbon Materials
- Chapter 17: Effect of thermal treatments on the surface chemistry of oxidized activated carbons
- Chapter 18: Digital reconstruction of silica gels based on small angle neutron scattering data
- Chapter 19: The impact of mesoporosity on microporosity assessment by CO2 adsorption, revisited
- Chapter 20: A Monte Carlo study of capillary condensation of krypton within realistic models of templated mesoporous silica materials
- Chapter 21: Using molecular simulation to characterise metal-organic frameworks and judge their performance as adsorbents
- Chapter 22: Stability of porous carbon structures obtained from reverse monte carlo using tight binding and bond order hamiltonians
- Chapter 23: Simulation of mercury porosimetry using MRI images of porous media
- Chapter 24: Adsorption and microcalorimetric measurements on activated carbons prepared from Polyethylene Terephtalate
- Chapter 25: Compressing some sol-gel materials reduces their stiffness: a textural analysis
- Chapter 26: Characterisation of new Pd / hierarchical macro-mesoporous ZrO2, TiO2 and ZrO2-TiO2 catalysts for toluene total oxidation
- Chapter 27: Characterisation of palladium supported on exchanged BEA and FAU zeolites for VOCs catalytic oxidation
- Chapter 28: Comparison of transport characteristics and textural properties of porous material; the role of pore sizes and their distributions
- Chapter 29: Effect of noble metal deposition in zeolitic structures on their adsorption capacities
- Chapter 30: Influence of the Bentonite/Titania ratio on the textural characteristics of incorporated ceramics for photocatalytic destruction of volatile organic compounds
- Chapter 31: Simultaneous Determination of Intrinsic Adsorption and Diffusion of n-Butane in Activated Carbons by using the TAP Reactor
- Chapter 32: Porous carbon deposits in controlled fusion reactor: adsorption properties and structural characterization
- Chapter 33: Characterization of the porosity of a microporous model carbon
- Chapter 34: Qualitative assessment of the purity of multi-walled carbon nanotube samples using krypton adsorption
- Chapter 35: Study of the anomalous behaviour of MFI zeolites towards nitrogen adsorption
- Chapter 36: Characterization of alkaline post-treated ZSM-5 zeolites by low temperature nitrogen adsorption
- Chapter 37: Kureha activated carbon characterized by the adsorption of light hydrocarbons
- Chapter 38: Water adsorption/desorption isotherms for characterization of microporosity in sandstone and carbonate rocks
- Chapter 39: Determination of pore-size distributions of highly-connected networks with assisted-filling characteristics
- Chapter 40: Large-scale simulations of poly(propylene oxide)amine/Na+-montmorillonite and poly(propylene oxide) ammonium/Na+-montmorillonite using a molecular dynamics approach
- Chapter 41: A comparison of characterization methods based on N2 and CO2 adsorption for the assessment of the pore size distribution of carbons
- Chapter 42: Adsorption of nitrogen, hydrogen and carbon dioxide on alumina-pillared clays
- Chapter 43: CH4 adsorption in Faujasite systems: Microcalorimetry and Grand Canonical Monte Carlo simulations
- Chapter 44: Amino-functionalized low density silica xerogels seen by different characterization methods
- Chapter 45: CO2 adsorption in synthetic hard carbons
- Chapter 46: Characterisation of Nanoporous Aluminosilicate Monoliths Derivatised with Metal Cations for Selective Propene-Propane Adsorption
- Chapter 47: Comparison of nitrogen and carbon dioxide as molecular probes of low surface area carbonaceous materials
- Chapter 48: Water sorption in hydrophobic porous materials: isotherm shapes and their meanings for the mesoporous MCM-41 and the microporous ALPO4-5
- Chapter 49: Uncertainty in αS analyses and pore volumes propagated from uncertainty in gas adsorption data
- Chapter 50: Uncertainty in amount adsorbed and surface excess from uncertainty in high-pressure gas adsorption data
- Chapter 51: A new methodology to characterize the porosity of Y zeolites by liquid chromatography
- Chapter 52: Study of the microporous texture of active carbons by Small Angle Neutron Scattering
- Chapter 53: Characterisation of nanostructured materials by combination of neutron scattering and 3D stochastic reconstruction techniques
- Chapter 54: Hydrogen storage in nanoporous carbons
- Chapter 55: Migration of siloxane polymer in ordered mesoporous MCM-41 silica channels
- Chapter 56: The sorption dynamics of propane, i-butane and neopentane in carbon nanotubes
- Chapter 57: Adsorption and diffusion kinetics of alkanes (C3 & C5) on different CaA adsorbents
- Chapter 58: Transport properties of catalyst supports derived from a catalytic test reaction
- Chapter 59: Ellipsometric study of porosity distribution in hybrid silica-based sol-gel films
- Chapter 60: Positronium annihilation study of as-synthesized MCM-41 silica under pressure
- Chapter 61: Structure-adsorptive characteristics of template-based mesoporous silicas containing residues of some phosphorus acids derivatives in their surface layer
- Chapter 62: Melting of atomic layers in carbon nanotubes
- Chapter 63: Molecular simulation study on the structure of templated porous materials obtained from different inorganic precursors
- Chapter 64: The structure of high-pressure adsorbed fluids in slit-pores
- Chapter 65: Monte Carlo simulation of the isosteric heats – implications for the characterisation of porous materials
- Chapter 66: Pore size distribution in microporous carbons obtained from molecular modeling and density functional theory
- Chapter 67: Modeling Triblock Surfactant Templated Mesoporous Silicas (MCF and SBA-15): A Mimetic Simulation Study
- Chapter 68: Influence of temperature on water adsorption / desorption hysteresis loop in disordered mesoporous silica glass by Grand Canonical Monte Carlo simulation method
- Chapter 69: Determination of pore size distribution in microporous carbons based on CO2 and H2 sorption data
- Chapter 70: Assessment of the development of the pore size distribution during carbon activation: a population balance approach
- Chapter 71: Chemically modified nanoporous carbons obtained using template carbonization method
- Chapter 72: Influence of the synthesis conditions on the pore structure and stability of MCM-41 materials containing aluminium or titanium
- Chapter 73: Effect of oxidizing agent on activated carbon cloth porosity and surface chemistry
- Chapter 74: Study of the efficiency of monolithic activated carbon adsorption units
- Chapter 75: Amino functionalisation of microemulsion templated mesoporous silica foams
- Chapter 76: Effect Of Activation Process On Resin Based Activated Carbons
- Chapter 77: Highly microporous carbons prepared by activation of kraft lignin with KOH
- Chapter 78: Preparation and Characterization of Nanoporous Ternary Mixed Cerium Oxides
- Chapter 79: Preparation and dynamic adsorption properties of activated carbons with tailored micro- and mesoporosity
- Chapter 80: Preparation of functionally graded alumina ceramic materials with controlled porosity
- Chapter 81: Preparation of Mesoporous Ceria in the Presence of Non-Aqueous Phases
- Chapter 82: Preparation and Characterization of Nanoporous Solids With Composition CexMn1-xO2-y With x Values 0 to 1
- Chapter 83: Thermal stability of ion exchange and adsorption properties of titania gels prepared from titanous chloride and hydrogen peroxide
- Chapter 84: In-situ SAXS on Transformations of Mesoporous and Nanostructured Solids
- Chapter 85: Confinement effects on freezing of binary mixtures
- Chapter 86: New equipment for characterization of nanofiltration membranes
- Chapter 87: The porous structure of biodegradable scaffolds obtained with supercritical CO2 as foaming agent
- Chapter 88: Detection of specific electronic interactions at the interface aromatic hydrocarbon-graphite by immersion calorimetry
- Chapter 89: Characterization and modelling of argillaceous porous medium by compressional and shear acoustic waves
- Chapter 90: Modelisation and circulation of fluids in geological porous systems. Images analyzing and mercury porosimetry
- Chapter 91: Electrical behaviour of saturated and unsaturated geological carbonate porous systems
- Author Index
- Studies In Surface Science and Catalysis