
- 482 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Active Coatings for Smart Textiles
About this book
Active Coatings for Smart Textiles presents the latest information on active materials and their application to textiles in the form of coatings and finishes for the purpose of improving performance and creating active functional effects. This important book provides detailed coverage of smart coating types, processes, and applications.
After an introduction to the topic, Part One introduces various types of smart and active coatings, including memory polymer coatings, durable and self-cleaning coatings, and breathable coatings. Technologies and related processes for the application of coatings to textiles is the focus of Part Two, with chapters devoted to microencapsulation technology, plasma surface treatments, and nanotechnology-based treatments.
The book ends with a section on applications of smart textiles with responsive coatings, which are increasingly finding commercial niches in sportswear, protective clothing, medical textiles, and architecture.
- Introduces various types of smart and active coatings for textiles
- Covers technologies and application processes for the coating and finishing of textiles
- Reviews commercial applications of such coatings, including in sportswear, protective clothing, medical textiles and architecture
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Introduction to active coatings for smart textiles
J.L. Hu Institute of Textiles and Clothing, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Hong Kong
Abstract
This chapter begins by differentiating the definitions of finishing, coating, and laminating and then points out the unique features of coating in other textile-wetting technologies. Based on the fundamental definitions, the difference between common and active coating is introduced. This chapter also compares the functions and applications of common and active coated textiles and reviews materials and technologies. Finally, the chapter outlines the contents of the book.
Keywords
Active coating; Active coating applications; Active coating process technology; Active coating technology; Smart textiles1.1. Introduction
The coating, finishing, and lamination of textiles are old arts and traditional technologies and are used in almost every area of industry and our lives. Laminating combines a fabric and a prepared film by adhesive, heat, and mechanical bonding, which replaces or supplements sewing to obtain laminated fabrics with enhanced function and more consistent qualities. However, it is easy to confuse the definitions of coating and finishing. The term “finishing” is usually used in a broad sense to refer to operations for improving the appearance or usefulness of a textile after it leaves the loom or knitting machine (Tomasino, 1992). These operations include washing, bleaching, coloring, and all kinds of chemical and mechanical steps that may comprise coating. In this book, “finishing” is used in its narrow definition (Schindler and Hauser, 2004), which is the final step in the textile manufacturing process (Fig. 1.1), which distinguishes it from a coating according to film continuity or morphology in processing technologies. Under this definition, finishing and coating both create the characteristics of textiles and endow them with special performance such as the final hand feeling. The coating also can complete yarn preparation such as warp sizing. In coating, a thick liquid chemical or paste is used that forms a continuous film on the yarn or textile surface, formed in situ. Gaps between fibers and yarns may disappear or narrow to varying degrees. In finishing, the light liquid chemical paste is applied and penetrates into the fibers and yarns to make up the textile, after which the gaps cannot be altered between the yarns and fibers (Fung, 2002).
Traditional textile coatings are commonly passive protections or decorations for the substrate for which they are designed and are applied by providing a barrier on the surface. Some advanced coatings include functional materials that enable the textiles to exhibit increased functionalities such as wrinkle free, flame retardant, etc. Furthermore, an active coating is to be considered smart. It is able to sense a change in conditions and respond to it in a predictable and conspicuous manner. Generally speaking, an active coating gives textiles intelligent properties more than just functional performance (Smith, 2010). The active coating senses the environment changing, responds to it, and does something by itself.
Active coatings can be categorized in many different ways based on the smart ingredients, fabrication technologies, and applications. For intelligent textiles or systems, there are normally three parts: a sensor, a processor, and an actuator (Tao, 2001; Mattila, 2006). Therefore, besides response, active coatings can consciously trace performance, for instance by remotely monitoring.
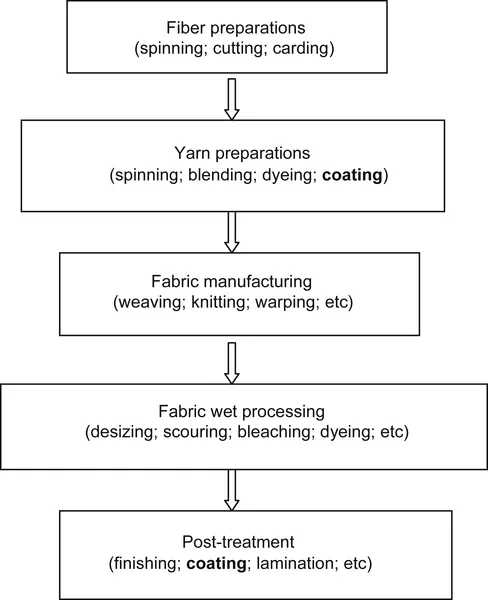
Figure 1.1 Coating positions in textile processing.
Intelligent materials contained in the coating layer can sense and respond to the environment, such as phase-change materials (Ghosh, 2006; Jyothi Sris et al., 2012), memory materials, and chromic materials. Active coatings by these intelligent materials acting as sensors can respond to changes in heat, light, chemicals, electronics, liquid, humidity, pressure, or bioactivity. Response may involve color change, shape adaptation, surface cleaning and healing, energy harvest and release, textile structure dimensional variance or drug release, and so on.
The smart ingredient within the active coating can be the polymer or resin itself, such as a memory polymer or a variety of additives consisting of nanoparticles for self-cleaning, pigments for color changing, microcapsules of phase-change materials for thermal regulation, microelectromechanical devices for wearable electronics, or antimicrobial agents for biomedical textiles. The successful combination of smart material science with advanced processing technology makes the active coating possible.
1.2. Functions and applications of active coating
Functions of textile coating are usually summarized according to their applied chemical properties, such as antibacterial, water resistance, etc. In this chapter, however, their functions are classified into three major categories; examples are listed in Table 1.1 based on the type of common or active coating.
Applications of textile coating are listed only partially based on industrial and civilian uses. This is a good place to begin understanding common coatings and discuss potential applications for active coatings, which also have occurred or been applied in these areas and products: for example, in breathable garments with a water-responsive, variable-sized opening fabric structure; in antibacterial bedding; and in impact-active protection (Table 1.2).
Table 1.1
Functions of common and active textile coating
| Categories | Common coating | Active coating |
| Aesthetic | Wrinkle free; flat appearance; dimensional stability; antistain; water or oil repellent; leather; color resistance | Color change; appearance retention; self-cleaning; |
| Comfort | Windproof; thermal resistance; water resistance; moisture management | Thermal adjustability; breathability |
| Protection | Humidity resistance; flame retardant; antiimpact; ultraviolet protection; antistatic; reflective; chemical resistance; blood resistance; anticorrosion; safety airbag; thermal insulating; aging resistance | Antibacterial; wearable electronics for biomedical use; self-healing; chemical odor absorbing and decomposing |
| Others | Filtration; stiffness |
Table 1.2
Applications of textile coatings
| Areas | Examples |
| Clothing | Garments; footwear; accessories |
| Home furnishings | Upholstery; bedding; carpet |
| Medicals | Implants; barrier materials; bandages; hygiene products; health monitor |
| Industrial | Belts; hoses; filtration; screens; covers; liners; barriers; tents; separation; building reinforcement layer |
1.3. Development of smart materials for active coating
Smart materials for active coating are mostly active materials which transport the sensing and responding properties to textiles by traditional coating technologies (Singha, 2012). Adaptive polymers can exhibit distinct and great changes when responding to a small stimulus. Accordingly, adaptive coating textiles have preprogrammed responses to small environmental changes. Different stimulations of active materials are listed; these have been applied in active coating textiles:
• heat and temperature
• pH value
• chemical and ionic strength
• electromagnetic radiation (ultraviolet, visible light)
• electrical and magnetic fields
• mechanical stress, strain, and pressure
• water and humidity
A number of active materials exist for textile coating, such as smart and polymeric hydrogels, mem...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- The Textile Institute and Woodhead Publishing
- Copyright
- List of contributors
- Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles
- 1. Introduction to active coatings for smart textiles
- Part One. Types of active coatings
- Part Two. Smart coating processes and technologies
- Part Three. Applications of smart textiles with responsive coatings
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Active Coatings for Smart Textiles by Jinlian Hu in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.