
- 272 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Used to clean the borehole, stabilize rock, control pressures, or enhance drilling rates, drilling fluids and their circulation systems are used in all phases of a drilling operation. These systems are highly dynamic and complicated to model until now. Written by an author with over 25 years of experience, Applied Drilling Circulation Systems: Hydraulics, Calculations and Models provide users with the necessary analytical/numerical models to handle problems associated with the design and optimization of cost-effective drilling circulation systems.The only book which combines system modeling, design, and equipment, Applied Drilling Circulation Systems: Hydraulics, Calculations and Models provides a clear and rigorous exposition of traditional and non-traditional circulation systems and equipment followed by self contained chapters concerning system modelling applications. Theories are illustrated by case studies based on the author's real life experience.The book is accompanied by a website which permits readers to construct, validate, and run models employing Newtonian fluids, Bingham Plastic fluids, Power Law fluids, and aerated fluids principles. This combination book and website arrangement will prove particularly useful to drilling and production engineers who need to plan operations including pipe-tripping, running-in casing, and cementing.- In-depth coverage of both on- and offshore drilling hydraulics.- Methods for optimizing both on- and offshore drilling hydraulics.- Contains problems and solutions based on years of experience.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Contents
1.1. Introduction
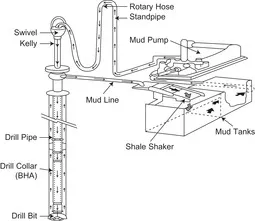 |
| Figure 1.1 A typical mud circulating system. |
1.2. Mud Pumps
 |
| Figure 1.2 A duplex pump. Courtesy of Great American. |
 |
| Figure 1.3 A triplex pump. Courtesy of TSC. |
 |
| Figure 1.4 Pump liners. Courtesy of TSC. |
1.3. Drill Strings
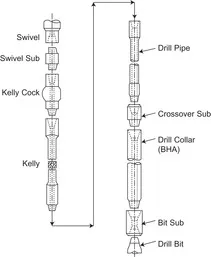 |
| Figure 1.5 A drill string used in the petroleum indus... |
Table of contents
- Cover Image
- Table of Contents
- Front Matter
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Preface
- Introduction
- Chapter One. Equipment in Mud Circulating Systems
- Chapter Two. Mud Hydraulics Fundamentals
- Chapter Three. Mud Pumps
- Chapter Four. Mud Hydraulics Optimization
- Introduction
- Chapter Five. Equipment in Gas Drilling Systems
- Chapter Six. Gas Compressors
- Chapter Seven. Gas Drilling Operations
- Introduction
- Chapter Eight. Equipment in Underbalanced Drilling Systems
- Chapter Nine. Gas and Liquid Injection Rates
- Chapter Ten. Underbalanced Drilling Operations
- Appendix A. Unit Conversion Factors
- Appendix B. Minimum Gas Flow Rates Required for Lifting Solids and Water in Air Drilling
- Appendix C. API Drill Collar Weight (lb/ft)
- Appendix D. API Drill Pipe Dimensional Data
- Appendix E. API Casing Dimensional Data
- Index