
Switchmode RF and Microwave Power Amplifiers
- 704 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Switchmode RF and Microwave Power Amplifiers
About this book
Combining solid theoretical discussions with practical design examples, this book is an essential reference on developing RF and microwave switchmode power amplifiers.With this book you will be able to: - Design high-efficiency RF and microwave power amplifiers on different types of bipolar and field-effect transistors using well-known and novel theoretical approaches, nonlinear simulation tools, and practical design techniques- Design any type of high-efficiency switchmode power amplifiers operating in Class D or E at lower frequencies and in Class E or F and their subclasses at microwave frequencies, with specified output power- Understand the theory and practical implementation of load-network design techniques based on lumped and transmission-line elements- Combine multi-stage Doherty architecture and switchmode power amplifiers to significantly increase efficiency of the entire radio transmitter- Learn the different types of predistortion linearization techniques required to improve the quality of signal transmission in a nonlinear amplifying system New to this edition: - Comprehensive overview of different Doherty architectures which are, and will be used in modern communication systems to save power consumption and reduce costs- A new chapter on analog and digital predistortion techniques- Coverage of broadband Class-F power amplifiers, high-power inverse Class-F power amplifiers for WCDMA systems, broadband Class-E techniques- Unique focus on switchmode RF and microwave power amplifiers that are widely used in cellular/wireless, satellite and radar communication systems and which offer major power consumption savings- Complete coverage of the new Doherty architecture which offers major efficiencies and savings on power consumption- Balances theory with practical implementatation, avoiding a cookbook approach, enabling engineers to develop better designs- Trusted content from leading figures in the field with a Foreword of endorsement by Zoya Popovic
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Power Amplifier Design Principles
Introduction
1.1 Spectral-domain analysis

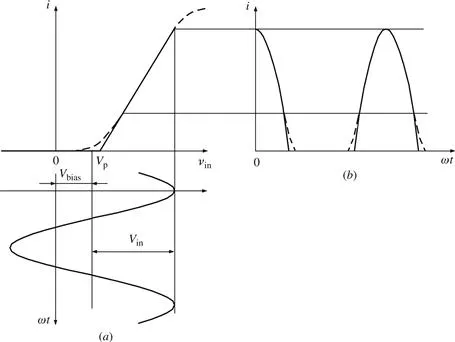
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- About the Authors
- Foreword
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Chapter 1. Power Amplifier Design Principles
- Chapter 2. Class-D Power Amplifiers
- Chapter 3. Class-F Power Amplifiers
- Chapter 4. Inverse Class-F
- Chapter 5. Class-E with Shunt Capacitance
- Chapter 6. Class-E with Finite DC-Feed Inductance
- Chapter 7. Class-E with Quarterwave Transmission Line
- Chapter 8. Broadband Class-E
- Chapter 9. Alternative and Mixed-Mode High-Efficiency Power Amplifiers
- Chapter 10. High-Efficiency Doherty Power Amplifiers
- Chapter 11. Predistortion Linearization Techniques
- Chapter 12. Computer-Aided Design of Switchmode Power Amplifiers
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app