
eBook - ePub
Internet of Things
- 352 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Internet of Things
About this book
This book outlines the background and overall vision for the Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications and services, including major standards. Key technologies are described, and include everything from physical instrumentation of devices to the cloud infrastructures used to collect data. Also included is how to derive information and knowledge, and how to integrate it into enterprise processes, as well as system architectures and regulatory requirements. Real-world service use case studies provide the hands-on knowledge needed to successfully develop and implement M2M and IoT technologies sustainably and profitably. Finally, the future vision for M2M technologies is described, including prospective changes in relevant standards. This book is written by experts in the technology and business aspects of Machine-to-Machine and Internet of Things, and who have experience in implementing solutions.
- Standards included: ETSI M2M, IEEE 802.15.4, 3GPP (GPRS, 3G, 4G), Bluetooth Low Energy/Smart, IETF 6LoWPAN, IETF CoAP, IETF RPL, Power Line Communication, Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Sensor Web Enablement (SWE), ZigBee, 802.11, Broadband Forum TR-069, Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) Device Management (DM), ISA100.11a, WirelessHART, M-BUS, Wireless M-BUS, KNX, RFID, Object Management Group (OMG) Business Process Modelling Notation (BPMN)
- Key technologies for M2M and IoT covered: Embedded systems hardware and software, devices and gateways, capillary and M2M area networks, local and wide area networking, M2M Service Enablement, IoT data management and data warehousing, data analytics and big data, complex event processing and stream analytics, knowledge discovery and management, business process and enterprise integration, Software as a Service and cloud computing
- Combines both technical explanations together with design features of M2M/IoT and use cases. Together, these descriptions will assist you to develop solutions that will work in the real world
- Detailed description of the network architectures and technologies that form the basis of M2M and IoT
- Clear guidelines and examples of M2M and IoT use cases from real-world implementations such as Smart Grid, Smart Buildings, Smart Cities, Participatory Sensing, and Industrial Automation
- A description of the vision for M2M and its evolution towards IoT
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Internet of Things by Jan Holler,Vlasios Tsiatsis,Catherine Mulligan,Stamatis Karnouskos,Stefan Avesand,David Boyle in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Part 1
The Vision for Moving from M2M to IoT
Outline
Part I. The Vision for Moving from M2M to IoT
Part I of this book provides an overview of the vision and market conditions for M2M and the move towards IoT. Here we discuss the global context within which M2M and IoT exist, and the business and technical drivers at work in both technology and industry. This part provides the basics of the M2M/IoT-Architecture and the principles behind them, preparing the reader for Part II, which outlines in detail the architecture for M2M and IoT.
Chapter 1
Introduction and Book Structure
This chapter provides an introduction to the book and overview of chapters, including the technical and market drivers from M2M towards IoT.
Keywords
chapter descriptions and structure of book; Market size
1.1 Introduction
This book provides a thorough and high-level analysis for anyone wishing to learn about how Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are being implemented and deployed in various industries, and also cities. This chapter provides a brief introduction to the topics covered and the structure of the book.
The number of “connected devices” (i.e. devices connected to the Internet) is growing and is expected to continue to grow exponentially as people increase the numbers of devices they purchase. Worldwide, mobile phone subscriptions have already exceeded 3 billion. End-users are also starting to use multiple devices (e.g. iPads, Kindles, mobile handsets, digital TVs, etc.). In addition, however, millions of new types of devices are emerging that allow machines to be connected to one another. These devices will communicate and offer services via the Internet, creating a new wave of innovation from both a technical and societal perspective. This explosive growth is unprecedented within not just the communications industries, but also the wider global economy.
This growth in the use of connected devices, M2M, and the IoT is expected to rapidly disrupt several business sectors in the next 5–10 years (Figure 1.1).
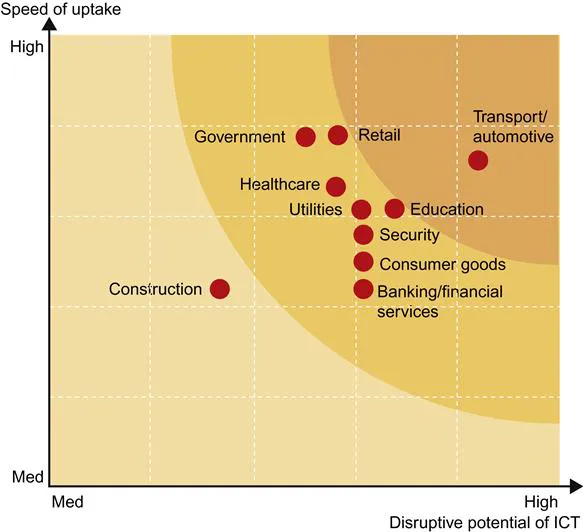
In addition, the traffic generated for M2M devices is predicted to grow 22-fold from 2011–2016.
In addition to all this, M2M solutions and services have a wider role to play in the future of our world. The year 2007 was a landmark year for the world: for the first time in history, more than 50% of the world’s population was living in cities rather than rural areas (UN-HABITAT, 2011). This trend sees no signs of reversing. The infrastructure of cities and nations must therefore adapt accordingly, from roads, lighting, metro/commuter trains, and pipelines, to name just a few (HM Treasury 2011). Much of this infrastructure will be instrumented with sensors and actuators for more efficient management, and all these devices associated with infrastructure will be connected to large-scale data analysis and management systems, the data of which needs effective capture, analysis, and visualization in order to be applied effectively in the development of smart, sustainable societies and cities. In the UK alone, this market represents a significant investment by both the government and private sector alike. The use of M2M and IoT in assisting the delivery of economic, social, and environmental outcomes for nations and regions is rapidly becoming an area of concern for professionals working in this space (Broadband Commission 2012).
The unprecedented numbers of devices foreseen, in combination with the vertical nature of many M2M applications, create an interesting set of barriers to success for anyone wishing to implement a solution based on these technologies. The deployment and operation costs of traditional telecom platforms adapted to handle the traffic load from tens of billions of additional connected devices would be a prohibitively high investment. Moreover, due to the specialized nature of the cases where M2M technologies will be applied, a fragmented ecosystem is emerging in each of the solution “silos.” Such industrial dynamics create barriers to entry for individuals and companies wanting to develop M2M applications or services, from supporting a mix of diverse devices and billing, to handling settlement and commission across the value chain.
Understanding how corporations and governments should respond to these changes is therefore a critical need for corporations, cities, and governments. The following section outlines the structure of the book as it covers these issues.
1.2 Structure of the book
Part I: The Internet of Things global context
Part I outlines the global context of M2M and the move towards IoT, including technology and business drivers.
Chapter 2: M2M to IoT – the vision
Chapter 2 provides an overview of how M2M solutions will move towards IoT, including the reasons that this is now occurring on the market.
Chapter 3: M2M to IoT – a market perspective
Chapter 3 provides an overview of the market drivers and industrial structures for the move from M2M to IoT.
Chapter 4: M2M to IoT – an architectural overview
Chapter 4 provides an overview of the architecture for IoT, including the overall design principles that sit behind the various architectures put forward by different standards bodies.
Part II: Nuts and bolts of M2M and IoT
In Part II, the technology building blocks of M2M and IoT solutions are presented, as well as the architecture.
Chapter 5: M2M and IoT technology fundamentals
This chapter provides an overview of relevant technologies for building M2M service solutions with a focus on the technologies that can be deployed widely, including: Devices and Device Gateways, Data Management, Business Process Engineering, and Cloud Technologies.
Chapters 6, 7 & 8: IoT architecture
These chapters together investigate how the different technologies introduced in Chapter 5 fit together in overall architectures, with reference to relevant system-level standards, including ETSI M2M and IoT-A.
Chapter 9: Real-world design constraints
Chapter 9 outlines design constraints that need to be taken into account when developing real-world technical solutions.
Part III: Implementation examples
Part III covers real-world implementation examples of M2M and IoT solutions.
Chapter 10: Asset management
Chapter 10 discusses Asset Monitoring, which enables the remote tracking and management of inventory in the field. Typically such functionality involves the collection of the exact location and state of assets at regular intervals for the purposes of improving the business (e.g. preventing stock-outs) or reducing risks (e.g. of getting lost).
Chapter 11: Industrial automation
Chapter 11 covers the emerging approach in industrial environments, which is to create system intelligence by a large population of intelligent, small, networked, embedded devices at a high level of granularity, as opposed to the traditional approach of focusing intelligence on a few large and monolithic applications within industrial solutions.
Chapter 12: The smart grid
Chapter 12 covers the Smart Grid, a revolution currently transforming the electricity system. Rapid advances in IT are increasingly being integrated in several infrastructure layers of the electricity grid and its associated operations. M2M interactions create new capabilities in the monitoring and management of the electricity grid, and the interaction between its stakeholders.
Chapter 13: Commercial building automation
Chapter 13 covers commercial buildings and the use of IoT. The purpose of a building automation systems is typically to reduce energy and maintenance costs, as well as to increase control, comfort, reliability, and ease of use for maintenance staff and tenants. M2M and IoT are starting to play an increasingly important role within Commercial Building Automation.
Chapter 14: Smart cities
Chapter 14 covers Smart Cities, an emerging and increasingly important field of application for IoT. This includes how sensors and associated IoT systems are being applied and linked to other paradigms (e.g. open data initiatives).
Chapter 15: Participatory sensing
Chapter 15 covers Participatory Sensing (PS), or Urban, Citizen, or People-Centric Sensing. This is a form of citizen engagement for the purposes of capturing the city surrounding environment and daily life. This chapter covers a few examples of such scenarios.
Chapter 16: Conclusion and looking ahead
Chapter 16 provides a brief overview of the future for IoT.
Part IV: Appendices
Part IV lists the abbreviations and references for the book.
Chapter 2
M2M to IoT – The Vision
The transition from M2M towards an IoT is mainly characterized by moving away from closed silo deployments to openness, multipurpose technologies, and innovation. This transition is triggered by a set of megatrends and global game changers that present new challenges and opportunities. The transition is characterized by the following: moving away from isolated solutions to an open environment; the use of IP and web technologies; the Internet; multimodal sensing and actuation; and knowledge-creation technologies. Together, these forces create capabilities and drivers that form the basis of the evolution from M2M to IoT.
Keywords
Evolution; Horizontal Development; Innovation; IoT Capabilities; Knowledge Creation; Megatrends; Silo; Transformation
2.1 Introduction
Our world is on the verge of an amazing transformation; one that will affect every person, town, company, and thing that forms the basis of our society and economy. In the same way that the Internet redefined how we communicate, work, and play, a new revolution is unfurling that will again challenge us to meet new business demands and embrace the opportunities of technical evolution. Old and new industries, cities, communities, and individuals alike will need to adapt, evolve, and help create the new patterns of engagement that our world desperately needs. In response to these issues, we are moving towards a new era of intelligence – one driven by rapidly growing technical capabilities.
M2M and the IoT are two of the technologies that form the basis of the new world that we will come to inhabit. Anything in the physical realm that is of interest to observe and control by people, businesses, or organizations will be connected and will offer services via the Internet. The physical entities can be of any nature...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Foreword
- Foreword
- Acknowledgements
- Author Biographies
- Part 1: The Vision for Moving from M2M to IoT
- Part 2: IoT Technologies and Architectures
- Part 3: IoT Use Cases
- Abbreviations
- References
- Index