
- 430 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Hormones
About this book
The 3rd edition of Hormones offers a comprehensive treatment of the hormones of humans all viewed from the context of current theories of their action in the framework of our current understanding their physiological actions as well as their molecular structures, and those of their receptors. This new edition of Hormones is intended to be used by advanced undergraduates and graduate students in the biological sciences. It will also provide useful background information for first year medical students as they engage in studies which are increasingly problem-based rather than discipline-focused. As the field of endocrinology itself has expanded so much in the past two decades, the up to date presentation of the basics presented in this book will be a solid foundation on which more specialized considerations can be based.New to this Edition: Hormones, 3rd Edition is organized with two introductory chapters followed by 15 chapters on selected topics of the molecular biology of the major endocrine systems operative in humans. Coverage, for the first time of the following hormones; ghrelin, oxyntomodulin, kisspeptin, adrenomedullin, FGF23, erythropoietin, VIP and extended coverage of NO. Coverage of the hypothalamus has been integrated with the anterior pituitary because of the intimate functional and relationship between the two. Consideration of the role of hormones in cancer has been integrated into the chapters on the relevant hormones. Each of these areas occupies a unique niche in our understanding of the biological world and is part of the universality of signaling systems and how they govern biological systems.- Organized with two introductory chapters, followed by 15 chapters on selected topics of the molecular biology of the major human endocrine systems- New full color format includes over 300 full color, completely redrawn images- Companion web site will host all images from the book as PPT slides and.jpeg files- All chapters have been completely updated and revitalized. Coverage of the hypothalamus has been integrated into the anterior pituitary chapter and coverage of the thymus has been eliminated and left to immunology textbooks- Provides essential basics for advanced undergraduates and graduate students in the biological sciences, as well as first year medical students as they engage in studies which are increasingly problem-based rather than discipline-focused
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Hormones
An Introduction
Keywords
I Overview of Hormones
A Introduction
B Review of Animal Cell Structure
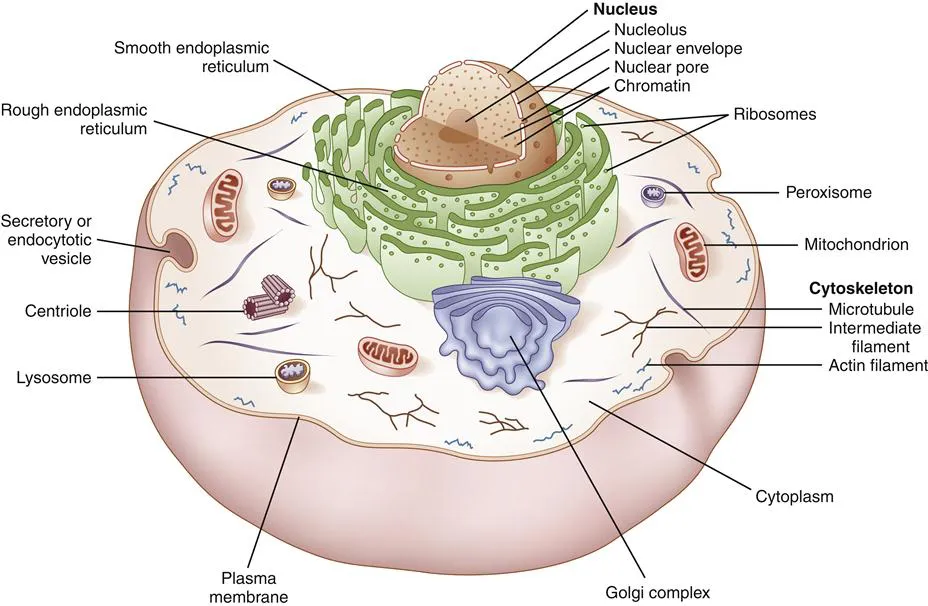
The major features shared by animal cells are shown. In eukaryotes the nuclear membrane separates the genetic material, the chromatin, from the cytoplasm. Molecules move between the two compartments through nuclear pores and a portion of the chromatin (see Figure 1-2), the nucleolus, is dedicated to the continual production of ribosomes. The cytoplasmic organelles depicted include the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (the microsomes of fractionated cells), which carries out metabolic conversions of carbohydrates and lipids, and the rough endoplasmic reticulum, associated with ribosomes that are synthesizing proteins to be secreted by the cell. These proteins are collected and processed in the Golgi apparatus. Mitochondria generate energy for the cell’s function from the products of the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Peroxisomes and lysosomes degrade molecules that are no longer needed or are potentially harmful. Elements of the cell’s cytoskeleton are shown, including the centriole, part of the organizing center for microtubules. The plasma membrane is described in Figure 1-3.
1 Nuclear Organization

A. Double helical DNA. The chemical nature of the DNA double helix is shown for a stretch of four base pairs. The negatively charged sugar-phosphate backbone is shown in yellow. Each purine, adenine (A, orange), or guanine (G, red) pairs with a pyrimidine, thymine (T, blue) or cytosine (C, green), respectively. The two DNA strands are complementary and anti-parallel to one another. The double helical structure of DNA is stabilized by the hydrogen bonds between the bases on each strand, two for each AT base pair and three for each GC base pair as well as by interactions between the stacked bases in the interior of the helix. B. Organization of DNA in chromosomes. The compaction of double helical DNA into a chromatid of a chromosome is shown. The first step is the coiling of the double helix of DNA around a core of histone proteins to form the core nucleosome. Histone H1 joins these “beads on a string,” 11 nm across, to promote their coiling upon themselves to form a 30 nm fiber. Further structural details are not completely understood, but include 300 nm loops and further coiling of these into the 700 nm chromatid.
2 The Plasma Membrane
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- About the Cover
- Chapter 1. Hormones: An Introduction
- Chapter 2. Steroid Hormones: Chemistry, Biosynthesis, and Metabolism
- Chapter 3. The Hypothalamus and Anterior Pituitary
- Chapter 4. Posterior Pituitary Hormones
- Chapter 5. Thyroid Hormones
- Chapter 6. Pancreatic Hormones: Insulin and Glucagon
- Chapter 7. Gastrointestinal Hormones
- Chapter 8. Eicosanoids
- Chapter 9. Calcium-Regulating Hormones: Vitamin D, Parathyroid Hormone, Calcitonin, and Fibroblast Growth Factor 23
- Chapter 10. Adrenal Corticoids
- Chapter 11. Hormones of the Adrenal Medulla
- Chapter 12. Androgens
- Chapter 13. Estrogens and Progestins
- Chapter 14. Hormones of Pregnancy, Parturition and Lactation
- Chapter 15. Hormones Related to the Kidney and Cardiovascular System
- Chapter 16. The Pineal Gland
- Chapter 17. Growth Factors
- Appendix A
- Appendix B
- Appendix C
- Appendix D
- Appendix E
- Appendix F
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app