
- 312 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Fatigue and Tribological Properties of Plastics and Elastomers
About this book
Part of a series of core databooks within the William Andrew Plastics Design Library, Fatigue and Tribological Properties of Plastics and Elastomers provides a comprehensive collection of graphical multipoint data and tabular data covering fatigue and tribology.The concept of fatigue is very straightforward: if an object is subjected to a stress or deformation, and it is repeated, the object becomes weaker. This weakening of plastic material is called fatigue. Tribology is the science and technology of surfaces in contact with each other and therefore covers friction, lubrication and wear. The reduction of wear and fatigue and the improvement of lubrication are key bottom-line issues for engineers and scientists involved in the plastics industry and product design with plastics.Fatigue and Tribological Properties of Plastics and Elastomers, Second Edition is an update of all that has changed in the world of plastics since the 1st edition appeared nearly 15 years ago, and has been reorganized from a polymer chemistry point of view.- A hard-working reference tool: part of the daily workflow of engineers and scientists involved in the plastics industry and product design with plastics- The reduction of wear and fatigue and the improvement of lubrication are key bottom-line issues- The data in this book provide engineers with the tools they need to design for low failure rates
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1.1. Introduction to Fatigue
1.2. Types of Stress
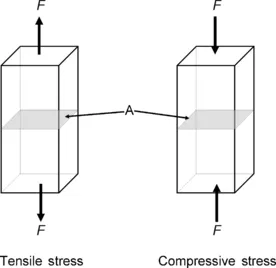 |
| Figure 1.1 Illustration of tensile stress and compressive stress. |
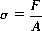
1.2.1. Tensile and Compressive Stress
1.2.2. Shear Stress
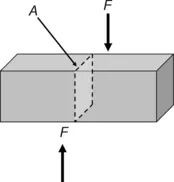 |
| Figure 1.2 Illustration of shear stress. |

1.2.3. Torsional Stress
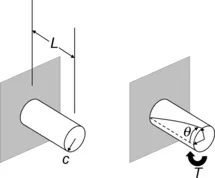 |
| Figure 1.3 Illustration of torsional stress. |
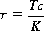
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- Chapter 1. Introduction to Fatigue and Tribology of Plastics and Elastomers
- Chapter 2. Introduction to the Tribology of Plastics and Elastomers
- Chapter 3. Introduction to Plastics and Polymers
- Chapter 4. Styrenic Plastics
- Chapter 5. Polyether Plastics
- Chapter 6. Polyesters
- Chapter 7. Polyimides
- Chapter 8. Polyamides (Nylons)
- Chapter 9. Polyolefins and Acrylics
- Chapter 10. Thermoplastic Elastomers
- Chapter 11. Fluoropolymers
- Chapter 12. High-Temperature Polymers
- Index