
- 600 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
PEM Fuel Cell Testing and Diagnosis
About this book
PEM Fuel Cell Testing and Diagnosis covers the recent advances in PEM (proton exchange membrane) fuel cell systems, focusing on instruments and techniques for testing and diagnosis, and the application of diagnostic techniques in practical tests and operation. This book is a unique source of electrochemical techniques for researchers, scientists and engineers working in the area of fuel cells.
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells are currently considered the most promising clean energy-converting devices for stationary, transportation, and micro-power applications due to their high energy density, high efficiency, and environmental friendliness. To advance research and development of this emerging technology, testing and diagnosis are an essential combined step. This book aids those efforts, addressing effects of humidity, temperature and pressure on fuel cells, degradation and failure analysis, and design and assembly of MEAs, single cells and stacks.
- Provides fundamental and theoretical principles for PEM fuel cell testing and diagnosis.
- Comprehensive source for selecting techniques, experimental designs and data analysis
- Analyzes PEM fuel cell degradation and failure mechanisms, and suggests failure mitigation strategies
- Provides principles for selecting PEM fuel cell key materials to improve durability
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access PEM Fuel Cell Testing and Diagnosis by Jiujun Zhang,Jifeng Wu,Huamin Zhang,Jiujun Zhang in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Materials Science. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
PEM Fuel Cell Fundamentals
Chapter Outline
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Electrochemical Reaction Thermodynamics in a H2/Air Fuel Cell
1.2.1. Thermodynamic Electrode Potential and Cell Voltage of a H2/Air Fuel Cell
1.2.2. Fuel Cell Electrical Work and Heat
1.2.3. Fuel Cell Electrical Energy Efficiency
1.3. Electrochemical Reaction Kinetics in a H2/Air Fuel Cell
1.3.1. Kinetics of the Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction
1.3.2. Kinetics of the Oxygen Reduction Reaction
1.4. PEM Fuel Cell Current–Voltage Expression
1.5. Fuel Cell Components
1.5.1. Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts
1.5.2. Catalyst Layers
1.5.3. Gas Diffusion Layer
1.5.4. Membrane (or Solid Electrolyte)
1.5.5. Membrane Electrode Assembly
1.5.6. Flow Field Plate/Bipolar Plate
1.5.7. Current Collectors
1.5.8. Other Components
1.6. Single Cell and Fuel Cell Stack Operation
1.7. Fuel Cell Performance
1.7.1. Fuel Cell Power Density
1.7.2. Fuel Crossover
1.7.3. Practical Electrical Energy Efficiency of Fuel Cells
1.8. Fuel Cell Operating Conditions
1.8.1. Operating Temperature
1.8.2. Operating Pressure
1.8.3. Relative Humidity
1.8.4. Gas Flow Rates and Stoichiometries
1.9. Chapter Summary
References
1.1 Introduction
Proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells, which directly convert chemical energy to electrical energy, have attracted great attention due to their numerous advantages, such as high power density, high energy conversion efficiency, fast startup, low sensitivity to orientation, and environmental friendliness. Figure 1.1 shows the schematic of a typical single PEM fuel cell [1], in which the anode and cathode compartments are separated by a piece of PEM such as Nafion®. This Nafion® membrane serves as the electrolyte and helps conduct protons from the anode to the cathode and also separates the anode and the cathode. During fuel cell operation, the fuel (e.g. H2) is oxidized electrochemically within the anode catalyst layer (CL), and this produces both protons and electrons. The protons then get transported across the membrane to the cathode side, while the electrons move through the outer circuit and thereby also reach the cathode side. These protons and electrons electrochemically react with the oxidant (i.e. oxygen in the feed air) within the cathode CL and produce both water and heat. The whole process of a H2/air PEM fuel cell produces electricity, water, and heat, without any polluting byproducts.
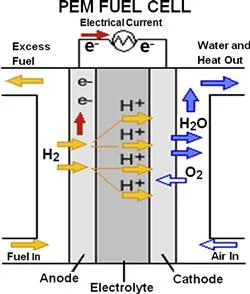
FIGURE 1.1 Schematic of a typical H2/air PEM fuel cell. (For color version of this figure, the reader is referred to the online version of this book.) [1]
To better understand how a PEM fuel cell works, it is necessary to grasp the fundamentals of PEM fuel cells, including their cell structure and the thermodynamics and kinetics of fuel cell electrochemical reactions. In the following sections of this chapter, the fundamentals of H2/air PEM fuel cells will be discussed in detail.
Several other types of fuel cells also belong to the PEM fuel cell family; these include the direct methanol fuel cell, direct ethanol fuel cell, and direct formic acid fuel cell. However, the scope of this book is such that we will only focus on the H2/air PEM fuel cell.
1.2 Electrochemical Reaction Thermodynamics in a H2/Air Fuel Cell
1.2.1 Thermodynamic Electrode Potential and Cell Voltage of a H2/Air Fuel Cell
A H2/air PEM fuel cell converts chemical energy stored in the fuel (hydrogen) into electrical energy through electrochemical reactions between H2 and O2. These electrochemical reactions can be written as follows:

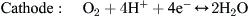
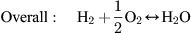
Note that the two-directional arrows in the...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- Biography
- Chapter 1. PEM Fuel Cell Fundamentals
- Chapter 2. Design and Fabrication of PEM Fuel Cell MEA, Single Cell, and Stack
- Chapter 3. Techniques for PEM Fuel Cell Testing and Diagnosis
- Chapter 4. The Effects of Temperature on PEM Fuel Cell Kinetics and Performance
- Chapter 5. Membrane/Ionomer Proton Conductivity Measurements
- Chapter 6. Hydrogen Crossover
- Chapter 7. Fuel Cell Open Circuit Voltage
- Chapter 8. Relative Humidity (RH) Effects on PEM Fuel Cells
- Chapter 9. Pressure Effects on PEM Fuel Cell Performance
- Chapter 10. High-Temperature PEM Fuel Cells
- Chapter 11. Fuel Cell Degradation and Failure Analysis
- Chapter 12. Electrochemical Half-Cells for Evaluating PEM Fuel Cell Catalysts and Catalyst Layers
- Acronyms and Abbreviations
- Index