
- 244 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Mechanics of Hydraulic Fracturing
About this book
Revised to include current components considered for today's unconventional and multi-fracture grids, Mechanics of Hydraulic Fracturing, Second Edition explains one of the most important features for fracture design — the ability to predict the geometry and characteristics of the hydraulically induced fracture. With two-thirds of the world's oil and natural gas reserves committed to unconventional resources, hydraulic fracturing is the best proven well stimulation method to extract these resources from their more remote and complex reservoirs. However, few hydraulic fracture models can properly simulate more complex fractures. Engineers and well designers must understand the underlying mechanics of how fractures are modeled in order to correctly predict and forecast a more advanced fracture network.Updated to accommodate today's fracturing jobs, Mechanics of Hydraulic Fracturing, Second Edition enables the engineer to: - Understand complex fracture networks to maximize completion strategies- Recognize and compute stress shadow, which can drastically affect fracture network patterns- Optimize completions by properly modeling and more accurately predicting for today's hydraulic fracturing completions- Discusses the underlying mechanics of creating a fracture from the wellbore- Enhanced to include newer modeling components such as stress shadow and interaction of hydraulic fracture with a natural fracture, which aids in more complex fracture networks- Updated experimental studies that apply to today's unconventional fracturing cases
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Fracturing of a wellbore and 2D fracture models
Abstract
Introduction
Fracturing of a wellbore
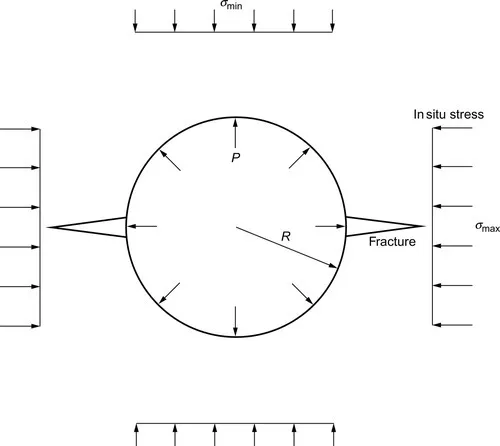
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface to the First Edition
- Preface to the Second Edition
- Chapter 1: Fracturing of a wellbore and 2D fracture models
- Chapter 2: Three-dimensional fracture modeling
- Chapter 3: Proppant transport in a 3D fracture
- Chapter 4: Deviated wellbores
- Chapter 5: Link-up of mini-fractures from perforated holes
- Chapter 6: Turning of fracture from a deviated wellbore
- Chapter 7: Fracture propagation in a naturally fractured formation
- Chapter 8: Stress shadow
- Chapter 9: Experimental studies
- Notations
- Author Index
- Subject Index