
Toxoplasma Gondii
The Model Apicomplexan. Perspectives and Methods
- 800 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Toxoplasmosis is caused by a one-celled protozoan parasite known as Toxoplasma gondii. In the United States, it is estimated that approximately 30% of cats, the primary carriers, have been infected by T. gondii. Most humans contract toxoplasmosis by eating cyst-contaminated raw or undercooked meat, vegetables, or milk products or when they come into contact with the T. gondii eggs from cat feaces while cleaning a cat's litterbox, gardening, or playing in a sandbox. Approx 1 in 4 (more than 60 million) people in the USA are infected with the parasite, and in the UK between 0.5 and 1% of individuals become infected each year. By the age of 50, 40% of people test positive for the parasite. The predilection of this parasite is for the central nervous system (CNS) causing behavioral and personality alterations as well as fatal necrotizing encephalitis, and is especially dangerous for HIV infected patients.Though there have been tremendous strides in our understanding of the biology of Toxoplasma gondii in the last decade, there has been no systemic review of all of the information that has accumulated. Toxoplasma gondii provides the first comprehensive summary of literature on this organism by leading experts in the field who were responsible for organising the 7th International Congress on Toxoplasmosis in May 2003. It offeres systematic reviews of the biology of this pathogen as well as descriptions of the methods and resources used. Within the next year the T. gondii genome will be completed making this an indispensable research resource for biologists, physicians, parasitologists, and for all those contemplating experiments using T. gondii.* Serves as a model for understanding invasion of host cells by parasites, immune response, motility, differentiation, phylogenetics, evolution and organelle acquisition* Discusses the protocols related to genetic manipulation, cell biology and animal models while also providing reference material on available resources for working with this organism
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
The History and Life Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii
Publisher Summary
1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 THE ETIOLOGICAL AGENT
1.3 PARASITE MORPHOLOGY AND LIFE CYCLE
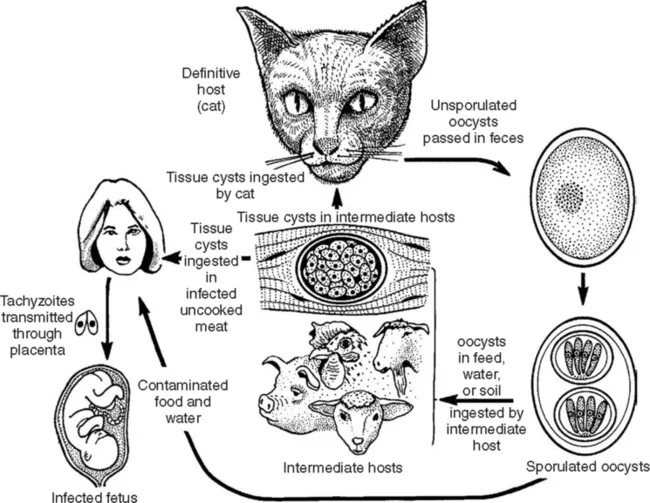
1.3.1 Tachyzoites
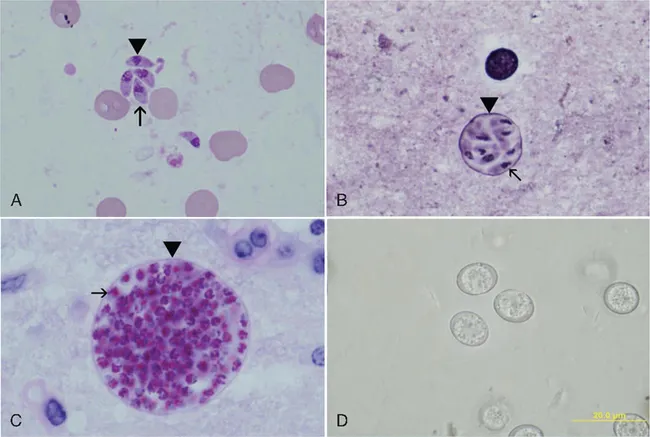
1.3.2 Bradyzoite and tissue cysts
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Chapter 1: The History and Life Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 2: The Ultrastructure of Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 3: Population Structure and Epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 4: Clinical Disease and Diagnostics
- Chapter 5: Ocular Disease Due to Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 6: Toxoplasmosis in Wild and Domestic Animals
- Chapter 7: Toxoplasma Animal Models and Therapeutics
- Chapter 8: Biochemistry and Metabolism of Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 9: The Apicoplast and Mitochondrion of Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 10: Calcium Storage and Homeostasis in Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 11: Toxoplasma Secretory Proteins and their Roles in Cell Invasion and Intracellular Survival
- Chapter 12: Alterations in Host-Cell Biology due to Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 13: Bradyzoite Development
- Chapter 14: Development and Application of Classical Genetics in Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 15: Genetic Manipulation of Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 16: Gene Regulation
- Chapter 17: The Secretory Protein Repertoire and Expanded Gene Families of Toxoplasma gondii and Other Apicomplexa
- Chapter 18: Comparative Aspects of Nucleotide and Amino-acid Metabolism in Toxoplasma gondii and other Apicomplexa
- Chapter 19: Toxoplasma as a Model System for Apicomplexan Drug Discovery
- Chapter 20: Proteomics of Toxoplasma gondii
- Chapter 21: Cerebral Toxoplasmosis: Pathogenesis and Host Resistance
- Chapter 22: Innate Immunity in Toxoplasma gondii Infection
- Chapter 23: Adaptive Immunity and Genetics of the Host Immune Response
- Chapter 24: Vaccination Against Toxoplasmosis: Current Status and Future Prospects
- Epilogue
- INDEX