
- 640 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Centrifugal Pumps: Design and Application, Second Edition focuses on the design of chemical pumps, composite materials, manufacturing techniques employed in nonmetallic pump applications, mechanical seals, and hydraulic design. The publication first offers information on the elements of pump design, specific speed and modeling laws, and impeller design. Discussions focus on shape of head capacity curve, pump speed, viscosity, specific gravity, correction for impeller trim, model law, and design suggestions. The book then takes a look at general pump design, volute design, and design of multi-stage casing. The manuscript examines double-suction pumps and side-suction design, net positive suction head, and vertical pumps. Topics include configurations, design features, pump vibration, effect of viscosity, suction piping, high speed pumps, and side suction and suction nozzle layout. The publication also ponders on high speed pumps, double-case pumps, hydraulic power recovery turbines, and shaft design and axial thrust. The book is a valuable source of data for pump designers, students, and rotating equipment engineers.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Centrifugal Pumps by Val S. Lobanoff,Robert R. Ross in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Fluid Mechanics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Part 1
Elements of Pump Design
1
Introduction
1. System Analysis for Pump Selection
Before a pump can be selected or a prototype designed, the application must be clearly defined. Whether a simple recirculation line or a complex pipeline is needed, the common requirement of all applications is to move liquid from one point to another. As pump requirements must match system characteristics, analysis of the overall system is necessary to establish pump conditions. This is the responsibility of the user and includes review of system configuration, changes in elevation, pressure supply to the pump, and pressure required at the terminal. Relevant information from this analysis is passed on to the pump manufacturer in the form of a pump data sheet and specification. From the information given, the following will ultimately determine pump selection.
• Capacity range of liquid to be moved
• Differential head required
• NPSHA
• Shape of head capacity curve
• Pump speed
• Liquid characteristics
• Construction
Differential Head Required
The head to be generated by the pump is determined from the system head curve. This is a graphical plot of the total static head and friction losses for various flow rates. For any desired flow rate, the head to be generated by the pump or pumps, can be read directly (Figures 1-1 and 1-2).
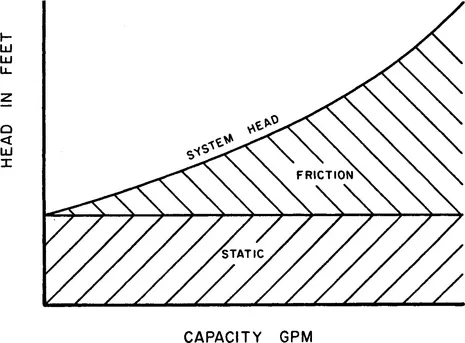
Figure 1-1 System head curve.
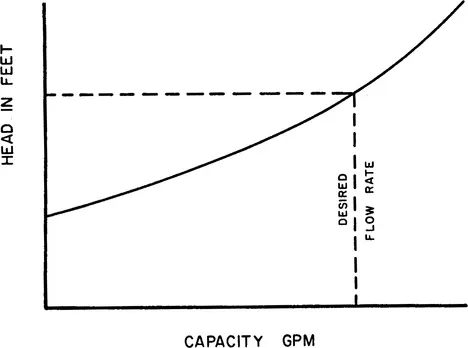
Figure 1-2 The system head curve establishes pump conditions.
NPSHA
Net positive suction head available (NPSHA) is of extreme importance for reliable pump operation. It is the total suction head in feet of liquid absolute, determined at the suction nozzle and referred to datum, less the vapor pressure of the liquid in feet absolute. This subject is discussed in detail in Chapter 9.
Shape of Head Capacity Curve
The desired shape of the head capacity (H-Q) curve is determined during analysis of the system. Most specifications call for a continuously rising curve (Figure 1-3) with the percentage rise from the best efficiency point (BEP) determined by system limits and mode of operation. Unstable or hooked curves (Figure 1-4) where the maximum developed head is at some flow greater than zero are undesirable in applications where multiple pumps operate in parallel. In such applications, zero flow head may be less than system head, making it impossible to bring a second pump on line. It is also possible for pumps to deliver unequal flow with the discharge pressure from one pump determining the flow rate from another. These legitimate reasons have resulted in many specifications forbidding the use of unstable curves for any application. This is most unfortunate as in many instances such curves are perfectly suitable. More importantly, pumps with unstable curves will develop more head and be more efficient than their continuously rising counterparts. It should be noted that this tendency of instability is normally confined to the lower range of specific speeds. As specific speed increases, the H-Q curve becomes more stable. Specific speed is defined in Chapter 2, and design parameters to correct instability in the low specific speed range will be discussed in Chapter 3.
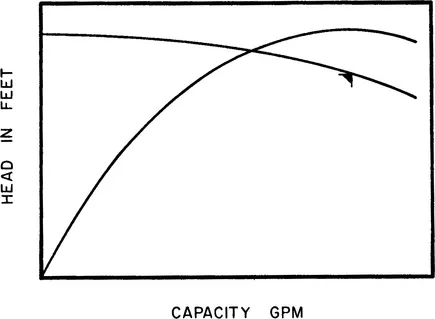
Figure 1-3 Continuously rising head capacity curve.
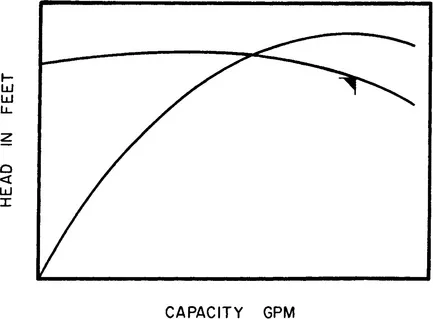
Figure 1-4 Unstable or hooked head capacity curve.
Pump Speed
Pump speed may be suggested by the user to match electric frequency or available driver speed. The pump manufacturer, however, has the ultimate responsibility and must confirm that the desired speed is compatible with NPSHA and satisfies optimum efficiency selection.
Liquid Characteristics
To have reasonable life expectancy, pump materials must be compatible with the liquid. Having intimate knowledge of the liquid to be pumped, the user will often specify materials to the pump manufacturer. When the pump manufacturer is required to spec...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- Part 1: Elements of Pump Design
- Part 2: Applications
- Part 3: Mechanical Design
- Part 4: Extending Pump Life
- Index