
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Transport Phenomena in Heat and Mass Transfer
About this book
Theoretical, numerical and experimental studies of transport phenomena in heat and mass transfer are reported in depth in this volume. Papers are presented which review and discuss the most recent developments in areas such as: Mass transfer; Cooling of electronic components; Phase change processes; Instrumentation techniques; Numerical methods; Heat transfer in rotating machinery; Hypersonic flows; and Industrial applications. Bringing together the experience of specialists in these fields, the volume will be of interest to researchers and practising engineers who wish to enhance their knowledge in these rapidly developing areas.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Transport Phenomena in Heat and Mass Transfer by J.A. Reizes in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Thermodynamics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
FORCED AND MIXED CONVECTION, HEAT EXCHANGERS
HEAT TRANSFER AND PRESSURE DROP IN AN ARTIFICIALLY ROUGHENED RECTANGULAR DUCT
L. Wu and P. Cooper, Ningxia Institute for the Application of New Technology, Yinchuan, Ningxia, P. R. China; Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, NSW 2500, Australia
ABSTRACT
Experimental results for friction factor and heat transfer coefficient are presented for a rectangular air duct with one duct-wall heated and the others adiabatic. Two sets of results are presented where the heat transfer surface is: a) nominally smooth and b) artificially roughened with regularly spaced spherical segments. The latter models a particular type of solar air heater and the purpose of this study is to further the development of an optimal collector design where the roughness element size and pitch are important parameters in that application. The pressure drop and heat transfer results are compared with previous data for roughness elements with configurations similar to the present case.
1 INTRODUCTION
Solar air collectors are characterised by relatively poor efficiencies when compared with collectors using water as the working fluid. The major cause of this is the poor heat transfer coefficient on the working fluid side, which leads to high absorber plate temperatures and, thus, high rates of heat loss to ambient air. Many methods have been suggested to enhance this heat transfer coefficient by increasing effective absorber area and increasing boundary layer disruption with artificial roughening elements. This paper describes work undertaken at the University of Wollongong to optimise the design of collectors utilising roughly hemispherical indentations on the working fluid side of the absorber plate. Such collectors are used in the People’s Republic of China for air heating in hospitals (Qiying and Laner, 1987). This method of heat transfer enhancement has been chosen for its ease of practical implementation given the fabrication methods available locally. The solar collector absorber and duct are made from sheet steel and the indentations are formed by simply pressing a large ball-bearing on to the plate which is backed by a suitable die. Qiying and Laner (1987) reported improvements of 10-15% in collector efficiency over similar air collectors without such indentations.
The present study sought to identify the most suitable size and pitch of such indentations with respect to pressure drop and heat transfer in the air collector duct. Previous literature on the topic indicated that a deal of work has been carried out for heat transfer from roughened surfaces in ducts but with no work immediately applicable to the geometry or working fluid in question. The first major theoretical contribution in the field of rough duct pressure drop was the Equivalent Sandgrain Roughness model proposed by Schlichting, 1936. This was based on experimental data by Nikuradse, 1933. Much work has been done by others since that time with Scaggs et al (1988) having recently presented detailed experimental and theoretical analyses of pressure drop in round ducts artificially roughened with elements including hemispheres and truncated cones with water as the working fluid.
FIGURE 2. Two sets of pressure drop experiments were conducted. One with nominally smooth duct walls and one with the upper surface artificially roughened with the heads of aluminium rivets as shown in Fig. 3. Initial tests were made to confirm that both pairs of pressure tappings gave identical results for both the smooth and rough duct cases. For the rough duct tests, static pressure drop along the duct was measured using the tappings in the upper face.
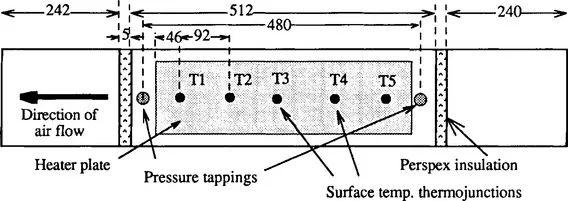
FIGURE 2 Location of pressure tappings and heat transfer surface temperature measurement points
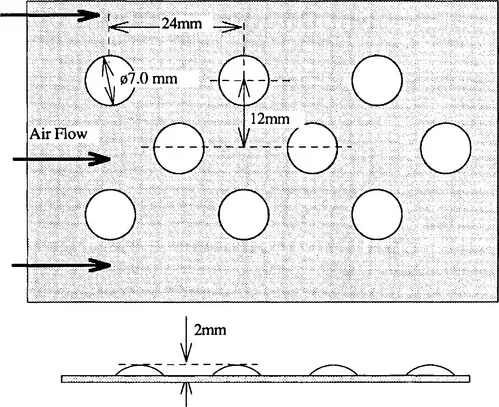
FIGURE 3 Illustration of roughness element geometry (not to scale).
FIGURE 3. Heat transfer tests were performed with the upper duct surfaces (smooth and rough) between the pressure tappings heated by means of a proprietary electrical heating mat. Power input to the latter was controlled by means of a variac transformer connected to a Research on heat transfer in roughened ducts has been less extensive. Dipprey and Sabersky (1963) who investigated round ducts roughened with a granular surface, water being the heat transfer medium. Their work allowed a comparison to be made between the original pressure drop data of Nikuradse and...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- PREFACE
- ISTP-IV ORGANISING COMMITTEE
- SCIENTIFIC ADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR THE SYMPOSIUM
- ADVISORY BOARD FOR INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIA ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA
- NATURAL AND FREE CONVECTION
- FORCED AND MIXED CONVECTION, HEAT EXCHANGERS
- PHASE CHANGE
- POROUS MEDIA