
- 327 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Working Guide to Reservoir Engineering
About this book
Working Guide to Reservoir Engineering provides an introduction to the fundamental concepts of reservoir engineering. The book begins by discussing basic concepts such as types of reservoir fluids, the properties of fluid containing rocks, and the properties of rocks containing multiple fluids. It then describes formation evaluation methods, including coring and core analysis, drill stem tests, logging, and initial estimation of reserves. The book explains the enhanced oil recovery process, which includes methods such as chemical flooding, gas injection, thermal recovery, technical screening, and laboratory design for enhanced recovery. Also included is a discussion of fluid movement in waterflooded reservoirs.
- Predict local variations within the reservoir
- Explain past reservoir performance
- Predict future reservoir performance of field
- Analyze economic optimization of each property
- Formulate a plan for the development of the field throughout its life
- Convert data from one discipline to another
- Extrapolate data from a few discrete points to the entire reservoir
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Basic Principles, Definitions, and Data
1.1 RESERVOIR FLUIDS
1.1.1 Oil and Gas
Reservoir oil may be saturated with gas, the degree of saturation being a function, among others, of reservoir pressure and temperature. If the reservoir oil has dissolved in it all the gas it is capable of holding under given conditions, it is referred to as saturated oil. The excess gas is then present in the form of a free gas cap. If there is less gas present in the reservoir than the amount that maybe dissolved in oil under conditions of reservoir pressure and temperature, the oil is then termed undersaturated. The pressure at which the gas begins to come out of solution is called the saturation pressure or the bubble-point pressure. In the case of saturated oil, the saturation pressure equals the reservoir pressure and the gas begins coming out of solution as soon as the reservoir pressure begins to decrease. In the case of undersaturated oil, the gas does not start coming out of solution until the reservoir pressure drops to the level of saturation pressure.
Apart from its function as one of the propulsive forces, causing the flow of oil through the reservoir, the dissolved gas has other important effects on recovery of oil. As the gas comes out of solution the viscosity of oil increases and its gravity decreases. This makes more difficult the flow of oil through the reservoir toward the wellbore. Thus the need is quite apparent for production practices tending to conserve the reservoir pressure and retard the evolution of the dissolved gas. Figure 1.1 shows the effect of the dissolved gas on viscosity and gravity of a typical crude oil.
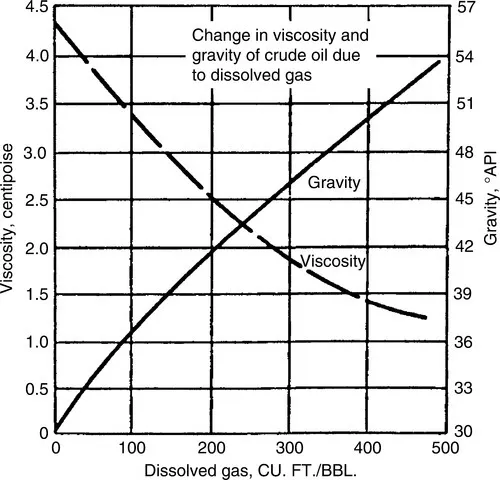
FIGURE 1.1 Change in viscosity and gravity of crude oil due to dissolved gas.
The dissolved gas also has an important effect on the volume of the produced oil. As the gas comes out of solution the oil shrinks so that the liquid oil at surface conditions will occupy less volume than the gas-saturated oil occupied in the reservoir. The number of barrels of reservoir oil at reservoir pressure and temperature which will yield one barrel of stock tank oil at 60 °F and atmospheric pressure is referred to as the formation volume factor or reservoir volume factor. Formation volume factors are described in a subsequent section. The solution gas–oil ratio is the number of standard cubic feet of gas per barrel of stock tank oil.
Physical properties of reservoir fluids are ...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright page
- Chapter 1: Basic Principles, Definitions, and Data
- Chapter 2: Formation Evaluation
- Chapter 3: Mechanisms & Recovery of Hydrocarbons by Natural Means
- Chapter 4: Fluid Movement in Waterflooded Reservoirs
- Chapter 5: Enhanced Oil Recovery Methods
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Working Guide to Reservoir Engineering by William Lyons in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Chemical & Biochemical Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.