
Trickle Bed Reactors
Reactor Engineering and Applications
- 284 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Trickle Bed Reactors
Reactor Engineering and Applications
About this book
This book provides a hybrid methodology for engineering of trickle bed reactors by integrating conventional reaction engineering models with state-of-the-art computational flow models. The content may be used in several ways and at various stages in the engineering process: it may be used as a basic resource for making appropriate reactor engineering decisions in practice; as study material for a course on reactor design, operation, or optimization of trickle bed reactors; or in solving practical reactor engineering problems. The authors assume some background knowledge of reactor engineering and numerical techniques.- Facilitates development of high fidelity models for industrial applications- Facilitates selection and application of appropriate models- Guides development and application of computational models to trickle beds
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
| Reaction Type | Process | Catalyst | Pressure (MPa) | Temperature (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidation reactions | Ethanol oxidation | Pd/Al | 2 | 343–373 |
| Wet oxidation of phenol | Pt/Al2O3 | 3–10 | 100–200 | |
| Oxidation of formic acid/oxidation of organic matter in waste water treatment/oxidation of phenol | Co/SiO2–AlO2, CuO | 0.1–1.5 | 300–403 | |
| Petroleum processing | Hydrodesulfurization Hydrodenitrification Hydrodemetallization | Mo–Ni | 20–80 | 593–653 |
| Hydrodemetallization | ||||
| Catalytic hydrocracking/catalytic hydrofinishing | ||||
| Catalytic dewaxing, dearomatization | ||||
| Hydrogenation reactions | Hydrogenation of various petroleum fractions, nitrocompounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids to alcohols (adipic acid to 1,6-hexanediol) | Pd, Pt, Ni, Cu | 3–10 | 323–423 |
| Selective hydrogenation of acetylene to separate compound from C4 fraction in the presence of butadiene | Au/Al, Pd/Al2O3 | 0.1–2.5 | 313–523 | |
| Hydrogenation of crotonaldehyde and α-methylstyrene to cumene | 0.05% Pd on Al2O3 | 0.1–5 | 373–773 | |
| Hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol | Ni | 10–30 | 350–450 | |
| Hydrogenation of caprolactone and adipic acid | Cu | 15–25 | 450–550 | |
| Hydrogenation of aniline to cyclohexylaniline | Pd/Al2O3 | 3–20 | 298–313 | |
| Hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol | Ru/C | 8 | 373–393 | |
| Hydrogenation of maleic anhydride | Raney nickel, Pt/C | 1–5 | 200–400 | |
| Hydrogenation of acid esters to alcohols | ||||
| Hydrogenation of coal liquefaction extracts | Ni–Mo/Al2O3 | 7 | 593–623 | |
| Esterification | Esterification of acetone and butanol | Strong acidic ion exchange resin | ||
| F–T synthesis | Fischer–Tropsch reaction | Co/TiO2 | 10–50 | 450–650 |
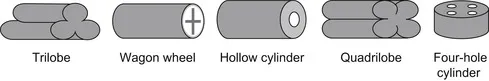 |
| FIGURE 1 Schematic shapes of catalyst particles used in practice (from Palmisano, Ramachandran, Balakrishnan, & Al-Dahhan, 2003). |
Table of contents
- Cover Image
- Table of Contents
- Front Matter
- Copyright
- Preface
- Chapter 1. Introduction
- Chapter 2. Hydrodynamics and Flow Regimes
- Chapter 3. Reaction Engineering of Trickle Bed Reactors
- Chapter 4. Flow Modeling of Trickle Beds
- Chapter 5. Reactor Performance and Scale-Up
- Chapter 6. Applications and Recent Developments
- Notations
- Author Index
- Subject Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app