1. Introduction
2. Solvent Extraction By Solvation
2.1. Solubility of Liquids
2.2. Mixtures of Solutions
2.2.1. Ideal Mixtures
2.2.2. Real Mixtures
2.3. Solute–Solvent Interactions (Extractability)
2.3.1. The Solubility Parameters
2.3.2. Thermodynamic Relations
3. Solvent Extraction with Chemical Reactions (By Complexation)
3.1. Thermodynamics of Extraction Systems
3.2. Solute–Solvent Interactions in Aqueous Phase
3.2.1. Dissociation
3.3. Solute–Solvent Interactions in Organic Phase
4. Driving Forces of Solvent Extraction
5. Influence of Kinetics Factors
5.1. Diffusion Transport Regime
5.1.1. Mathematical description of the diffusion transport
5.1.2. Determination of diffusion coefficients
5.2. Chemical Reaction Kinetics Regime Transport
5.2.1. Complexation–Decomplexation
5.2.2. Liquid–Liquid Interface
5.2.3. Mathematical Description of Kinetic Regime
5.2.4. Determination of Kinetic Parameters
5.3. Mixed Diffusional–Kinetic Transport Regime
5.3.1. Identification of the Rate-Controlling Transport Regimes
5.3.2. Basic Parameters of Transport Regime
5.3.3. Determination of Extraction Kinetic Parameters
6. Selectivity
7. Factors Affecting Extraction Process
7.1. Extractant Properties
7.1.1. Mixtures of Extractants (Ionic Additives)
7.1.2. Acidity–Basicity of the Extractant Influencing Extraction
7.1.3. Influence of Dissociation Constant and Distribution Coefficient of the Extractant
7.2. Aggregate Formation
7.3. Solvent (Diluent) Properties Influencing Extraction
7.4. Coupling Ions: Anion Type
7.5. Influence of Temperature
7.6. Influence of Complex Structure
7.6.1. Chelate Ring Size
7.6.2. Steric Hindrance Effect
7.6.3. Donor Ligand Effects
7.6.4. Inner and Outer Sphere Coordination Effect
7.7. Effects of the Aqueous Medium
8. Module Design Considerations
8.1. Calculation of Equilibrium Constants
8.2. Identification of Species
8.2.1. Job’s Method
8.2.2. Ligand Number Method
8.2.3. Graphic Slope Analysis
8.2.4. Linear Plots
8.2.5. Nonlinear Plots
8.2.6. Numerical Methods
9. Experimental Determination of Distribution Ratios
9.1. Stirred Cell Semicontinuous Techniques
9.2. Centrifugal Extraction–Separation Systems
10. Summarizing Remarks
References
1 Introduction
Solvent extraction (SX) is one of the favored separation techniques because of its simplicity, speed, and wide scope. By utilizing relatively simple equipment and requiring a few time to perform, extraction procedures offer much to the chemists and engineers. Frequently it appears to be the ideal method of separating trace constituents from large amounts of other substances.
Solution diffusion (with or without chemical reactions) is a commonly accepted mechanism for SX. The process is often very selective and the isolation of the solute of interest can usually be made as complete as desired by several repetitions of the extraction procedure.
Even at extraction without chemical reactions at partition of solute neutral molecules between two immiscible phases, there is a chemical change of the solute in its solvation environment. More drastic chemical changes of the solute species take place with the presence of extractant, when different chemical interactions (reversible or irreversible), formation of new coordination compound, dissociation or association, and aggregation are possible. This is facilitated, enhanced SX.
Kinetics of the SX is a function of the rates of chemical changes that occur in the system and the rates of diffusion of the various species that control the chemical reactions. At least one of the chemical or diffusion steps is slow enough to control the overall rate of the process. So, analysis of mechanisms and kinetics of the chemical and diffusion steps of the overall process are needed.
In chemical technology, the SX plays an important role in the purification of chemical reagents and semiconductor materials. This method is also widely used in nuclear chemistry and technology for the separation of various radioisotopes and for the reprocessing of nuclear fuels.
Using SX, important theoretical problems concerning the composition and stability of soluble as well as insoluble complexes can be solved. This quality is very useful especially for the case when it is not possible to obtain reliable results by other methods.
In this chapter, modern theoretical considerations in SX techniques are presented and are reviewed with a classification and grouping. Better understanding of the principles of SX allows the optimization of solute separations by SX technique. Factors that influence the effectiveness and selectivity of separation are analyzed.
2 Solvent Extraction By Solvation
2.1 Solubility of Liquids
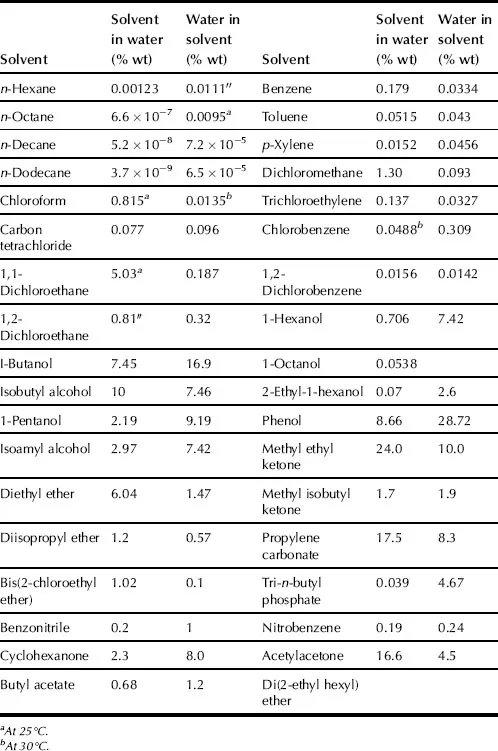
SX is the distribution of a solute or solutes between two immiscible liquids or phases. SX commonly takes place with aqueous and organic solutions. SX is generally carried out at ambient pressures and temperatures. Sometimes high pressures are used and liquid state can extend up to critical temperature. Organic phase usually consists of extractant dissolved in diluent. Normally, the organic phase contains a diluent, an extractant, but in some cases, a modifier, and a synergistic agent. The modifier is added to improve the physical properties of the system (e.g., to cause phase disengagement after mixing the two phases); synergistic agent is used for improvement and enhancement of extractant. The aqueous phase, or feed phase, consists of solute or mixture of solutes, contamination compounds, and acids dissolved in water. As an example, solubilities of water in some organic solvents and these solvents in water are presented in Table 1.1.
TABLE 1.1. Solubility of Water in Organic Solvents and These Solvents in Water at 25–30 °C
Liquids have some properties that are important in SX techniques. These are viscosity, surface tension, vapor pressure, density, polarity (electronegativity, dipole moment), and polarization ability.
Many liquids used in SX are polar. Polarity is determined by electric dipole in molecule, since their atoms have different electronegativities. The value of difference is characterized by dipole moment, δd, e.g., dipole moment of nitrobenzene, δd = 4.0 D (1 Debye unit = 3.34 ∗ 10−30 C ∗ m) and water, δd = 1.83 D.
Liquid compounds th...