
eBook - ePub
Electrical Load Forecasting
Modeling and Model Construction
- 440 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Succinct and understandable, this book is a step-by-step guide to the mathematics and construction of electrical load forecasting models. Written by one of the world's foremost experts on the subject, Electrical Load Forecasting provides a brief discussion of algorithms, their advantages and disadvantages and when they are best utilized. The book begins with a good description of the basic theory and models needed to truly understand how the models are prepared so that they are not just blindly plugging and chugging numbers. This is followed by a clear and rigorous exposition of the statistical techniques and algorithms such as regression, neural networks, fuzzy logic, and expert systems. The book is also supported by an online computer program that allows readers to construct, validate, and run short and long term models.
- Step-by-step guide to model construction
- Construct, verify, and run short and long term models
- Accurately evaluate load shape and pricing
- Creat regional specific electrical load models
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Mathematical Background and State of the Art
1.1 Objectives
The objectives of this chapter are
• Introducing a mathematical background to help the reader understand the problems formulated in this book.
• Studying matrices and their applications in estimation theory and showing that the use of matrix notation simplifies complex mathematical expressions. The simplifying matrix notation may not reduce the amount of work required to solve mathematical equations, but it usually makes the equations much easier to handle and manipulate.
• Explaining the vectors and the formulation of quadratic forms and, as we shall see, that most objective functions to be minimized (least error squares criteria) are quadratic in nature.
• Explaining some optimization techniques.
• Introducing the concept of a state space model, which is commonly used in dynamic state estimation.
• Reviewing the literature to introduce different techniques developed for short-term load forecasting.
• Explaining the merit of each technique used in the estimation of load forecasting and suitable places for implementation.
• In this chapter, we also try to compare different techniques used in electric load forecasting.
1.2 Matrices and Vectors
A matrix is an array of elements [1]. The elements of a matrix may be real or complex or functions of time. A matrix that has n rows and m columns is called an n × m (n by m) matrix. If n = m, the matrix is referred to as a square matrix. If A is an n × m matrix, then it can be written as

In shorthand,

Note that the determinant is also an array of elements with n rows and n columns (always square) and has a value. The matrix does not have a value but has a determinant.
Column Matrix: This type of matrix has only one column and more than one row; that is, an m × 1 matrix, m > 1. Quite often, a column matrix is referred to as a column vector or simply an m-vector. For example, the column vector X is written as

Row Matrix: This type of matrix has only one row and more than one column; that is, an 1 × n matrix, n > 1. Quite often, we call it a row vector. For example, the row vector Y is given by
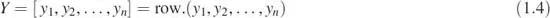
Diagonal Matrix: This is a square matrix with all elements equal to zero except for the diagonal element; that is, aij = 0 for all i ≠ j. For example,

or, in terms of a shortcut,

Symmetric Matrix: This type of matrix is a square matrix that satisfies the relation
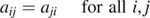
The following example indicates this matrix:
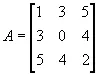
In terms of a shortcut:
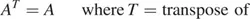
Transpose of a Matrix: The transpose of a matrix is defined as a matrix obtained by interchanging the corresponding rows and columns in A. If A is an n × m matrix, which is represented by
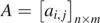
then the transpose of A, denoted by AT, is given by

Note that the order of A is n × m, while the order of AT is m × n. For example, if

then
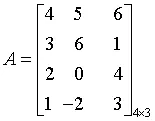
The following are some operations using the transpose of a matrix:




1.3 Matrix Algebra
1.3.1 Addition of Matrices
If A is an n × m matrix, and B is also an n × m matrix, then the sum of the two matrices is given by

where the elements of the matrix C are given by

For example, if
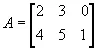
and
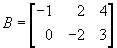
then
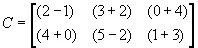
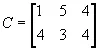
1.3.2 Matrix Subtraction (Difference)
The subtraction (difference) of matrices is similar to the addition of matrices if all the signs of the second matrix are changed from positive to negative and from negative to positive; that is,

where


or

The following rules hold true for addition and subtraction:

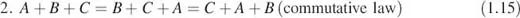
1.3.3 Matrix Multiplication
Let A be an n × m matrix and B be an m × p matrix. Then the product of A and B is defined as

Note that the number of columns in the first matrix, m, must be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix to carry out the multiplication.
The elements of the matrix C are given by

If, for example, the matrix A is given by
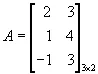
and
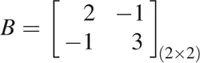
then
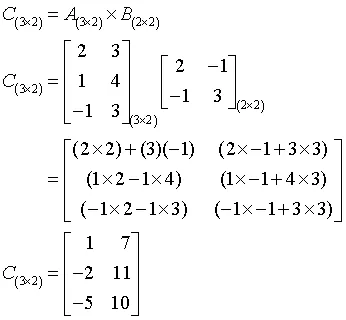
If the matrix A is given by
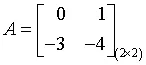
and the vector matrix X(t) is given by
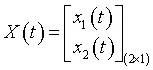
then
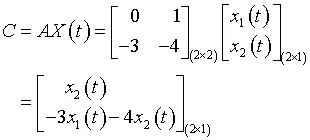
It is possible in some cases to obtain the two products AB and BA. This could happen if A is an r × n matrix, and B is an n × r matrix. In this case, AB is an r × r matrix, whereas BA is an n × n matrix. Obviously, AB ≠ BA, and we say that A and B do not commute, but if AB = BA, we say that...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Acknowledgments
- Introduction
- 1 Mathematical Background and State of the Art
- 2 Static State Estimation
- 3 Load Modeling for Short-Term Forecasting
- 4 Fuzzy Regression Systems and Fuzzy Linear Models
- 5 Dynamic State Estimation
- 6 Load-Forecasting Results Using Static State Estimation
- 7 Load-Forecasting Results Using Fuzzy Systems
- 8 Dynamic Electric Load Forecasting
- 9 Electric Load Modeling for Long-Term Forecasting
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Electrical Load Forecasting by S.A. Soliman,Ahmad Mohammad Al-Kandari in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Energy Industry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.