
- 608 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Gas Well Deliquification
About this book
Liquid loading can reduce production and shorten the lifecycle of a well costing a company millions in revenue. A handy guide on the latest techniques, equipment, and chemicals used in de-watering gas wells, Gas Well Deliquification, 2nd Edition continues to be the engineer's choice for recognizing and minimizing the effects of liquid loading. The 2nd Edition serves as a guide discussing the most frequently used methods and tools used to diagnose liquid loading problems and reduce the detrimental effects of liquid loading on gas production. With new extensive chapters on Coal Bed Methane and Production this is the essential reference for operating engineers, reservoir engineers, consulting engineers and service companies who supply gas well equipment. It provides managers with a comprehensive look into the methods of successful Production Automation as well as tools for the profitable use, production and supervision of coal bed gases.- Turnkey solutions for the problems of liquid loading interference- Based on decades of practical, easy to use methods of de-watering gas wells- Expands on the 1st edition's useful reference with new methods for utilizing Production Automation and managing Coal Bed Methane
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
INTRODUCTION
Publisher Summary
1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 MULTIPHASE FLOW IN A GAS WELL
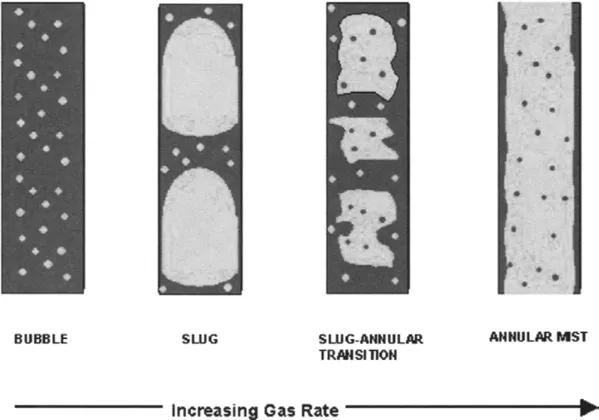
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION
- Chapter 2: RECOGNIZING SYMPTOMS OF LIQUID LOADING IN GAS WELLS
- Chapter 3: CRITICAL VELOCITY
- Chapter 4: SYSTEMS NODAL ANALYSIS
- Chapter 5: SIZING TUBING
- Chapter 6: COMPRESSION
- Chapter 7: PLUNGER LIFT
- Chapter 8: USE OF FOAM TO DELIQUIFY GAS WELLS
- Chapter 9: HYDRAULIC PUMPING
- Chapter 10: USE OF BEAM PUMPS TO DELIQUIFY GAS WELLS
- Chapter 11: GAS LIFT
- Chapter 12: ELECTRIC SUBMERSIBLE PUMPS
- Chapter 13: PROGRESSING CAVITY PUMPS
- Chapter 14: COAL BED METHANE
- Chapter 15: PRODUCTION AUTOMATION
- APPENDIX A: DEVELOPMENT OF CRITICAL VELOCITY EQUATIONS
- APPENDIX B: DEVELOPMENT OF PLUNGER LIFT EQUATIONS
- APPENDIX C: GAS FUNDAMENTALS
- Index