
Applied Intelligent Decision Making in Machine Learning
- 260 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Applied Intelligent Decision Making in Machine Learning
About this book
The objective of this edited book is to share the outcomes from various research domains to develop efficient, adaptive, and intelligent models to handle the challenges related to decision making. It incorporates the advances in machine intelligent techniques such as data streaming, classification, clustering, pattern matching, feature selection, and deep learning in the decision-making process for several diversified applications such as agriculture, character recognition, landslide susceptibility, recommendation systems, forecasting air quality, healthcare, exchange rate prediction, and image dehazing. It also provides a premier interdisciplinary platform for scientists, researchers, practitioners, and educators to share their thoughts in the context of recent innovations, trends, developments, practical challenges, and advancements in the field of data mining, machine learning, soft computing, and decision science. It also focuses on the usefulness of applied intelligent techniques in the decision-making process in several aspects.
To address these objectives, this edited book includes a dozen chapters contributed by authors from around the globe. The authors attempt to solve these complex problems using several intelligent machine-learning techniques. This allows researchers to understand the mechanism needed to harness the decision-making process using machine-learning techniques for their own respective endeavors.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Data Stream Mining for Big Data
Contents
1.1Introduction
- Unbounded size:
- Transient (lasts for only few seconds or minutes);
- Single-pass over data;
- Only summaries can be stored;
- Real-time processing (in-memory).
-
- Data streams are not static:
- Incremental/decremental updates;
- Concept drifts.
-
- Temporal order may be important.
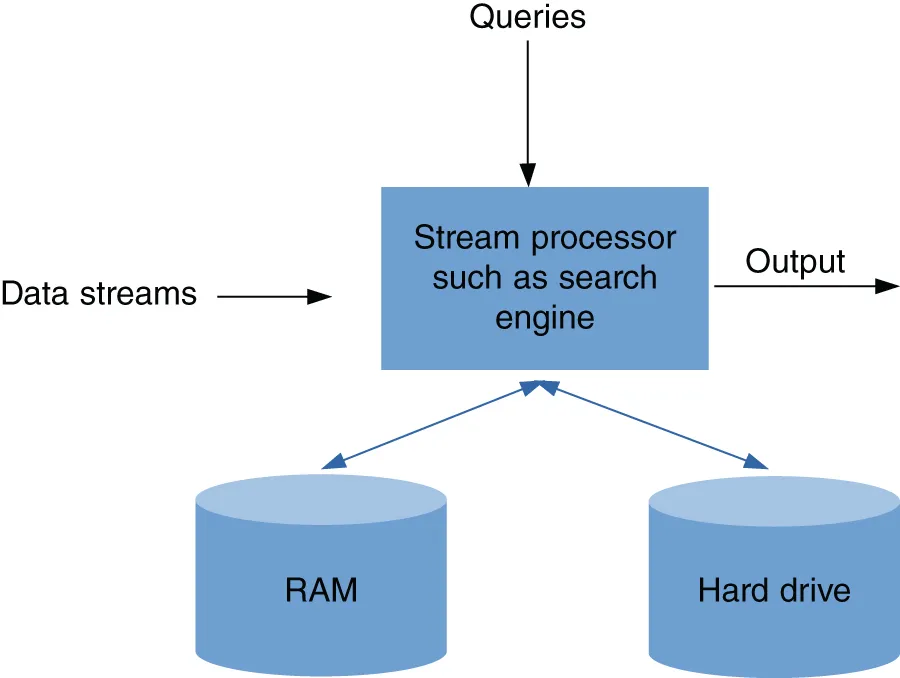
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Notes on the Editors and Contributors
- 1 Data Stream Mining for Big Data
- 2 Decoding Common Machine Learning Methods Agricultural Application Case Studies Using Open Source Software
- 3 A Multi-Stage Hybrid Model for Odia Compound Character Recognition
- 4 Development of Hybrid Computational Approaches for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Remotely Sensed Data in East Sikkim, India
- 5 Domain-Specific Journal Recommendation Using a Feed Forward Neural Network
- 6 Forecasting Air Quality in India through an Ensemble Clustering Technique
- 7 An Intelligence-Based Health Biomarker Identification System Using Microarray Analysis
- 8 Extraction of Medical Entities Using a Matrix-Based Pattern-Matching Method
- 9 Supporting Environmental Decision Making Application of Machine Learning Techniques to Australia’s Emissions
- 10 Prediction Analysis of Exchange Rate Forecasting Using Deep Learning-Based Neural Network Models
- 11 Optimal Selection of Features Using Teaching-Learning-Based Optimization Algorithm for Classification
- 12 An Enhanced Image Dehazing Procedure Using CLAHE and a Guided Filter
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app