
Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem Blockset
- 27 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem Blockset
About this book
Matlab SimPowerSystems is a modern design tool that allows scientists and engineers to rapidly and easily build models that simulate power systems. Not only can you draw the circuit topology rapidly, but your analysis of the circuit can include interactions with mechanical, thermal, control, and other disciplines. The paper covers some case studies that provide detailed, realistic examples of how to use SimPowerSystems in power system analysis. The following types of studies are covered on the paper: 1. Thyristor-Based Static Var Compensator: Study the steady-state and dynamic performance of a static var compensator (SVC) on a transmission system.2. Transient Stability of a Power System with SVC and PSS: Study of the application of static var compensator (SVC) and power system stabilizers (PSS) to improve transient stability and power oscillation damping of the system. 3. GTO-Based STATCOM: Study the steady-state and dynamic performance of a static synchronous compensator (STATCOM) on a transmission system. 4. Control of load flow using UPFC: Study the steady-state and dynamic performance of a unified power flow controller (UPFC).5. Variable-frequency Induction Motor Drive: Study of a PWM inverter is used as a variable-voltage, variable-frequency source to drive an induction motor in variable-speed operation.6. Chopper-Fed DC Motor Drive: Study of a DC motor drive with armature voltage controlled by a GTO thyristor chopper.7. VSC-Based HVDC Link: Modeling of a forced-commutated voltage-sourced converter high-voltage direct current (VSC-HVDC) transmission link.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Introduction
1. THYRISTOR-BASED STATIC VAR COMPENSATOR
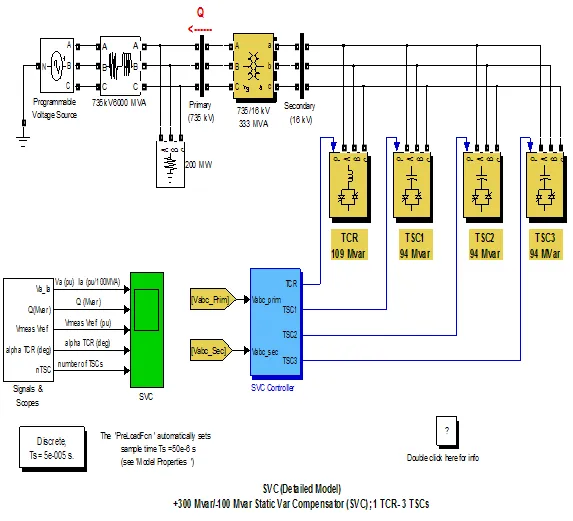
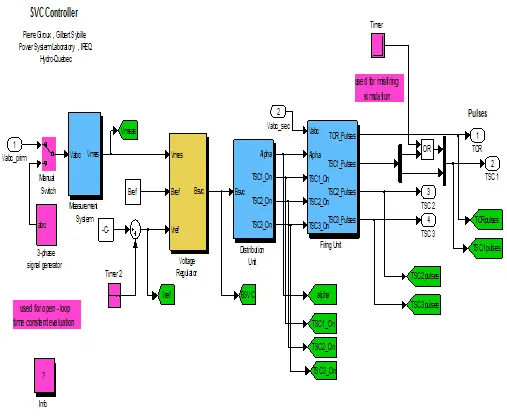
Table of contents
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem Blockset
- Abstract
- Introduction
- 1. THYRISTOR-BASED STATIC VAR COMPENSATOR
- 2. TRANSIENT STABILITY OF A POWER SYSTEM
- 3. GTO-BASED STATCOM
- 4. CONTROL OF LOAD FLOW USING UPFC
- 5. CONTROL OF AC MOTOR
- 6. CONTROL OF DC MOTOR
- 7. VSC-Based HVDC Link
- 8. CONCLUSION
- 9. REFERENCES