
- 200 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This book covers the complete gamut of neuroradiology cases, including normal anatomy, pitfalls, and artifacts across the brain and spine in a single volume, enriched with high-resolution images that support the interpretation of CT and MRI images of the brain, spine, head, and neck. It includes case studies commonly encountered in clinical practice, in addition to normal anatomy, that prepare the reader for the challenges in the clinical setting. Each case study discusses the clinical history, relevant imaging findings, differential diagnosis, and management, serving as a helpful read for trainee radiologists, neurophysicians, neurosurgeons, and CT/MRI technicians, along with physicians interested in medical imaging.
Key Features
- Provides a succinct overview of normal variants with case studies structured into thematic chapters
- Serves as a basic accompaniment for radiology residents, fellows, practicing radiologists, neurophysicians, neurosurgeons, emergency medicine practitioners, trainee and practicing radiographers, and those studying for Board exams
- Highlights the relevance of artificial intelligence in clinical practice
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Normal Brain Development and Congenital Malformations
- 1) Dorsal induction involves the process of neurulation or neural tube formation.
- The appearance of the neural plate (at around 4.5–5 weeks of gestation), followed by its invagination, leads to the formation of a neural groove. Thickening and proliferation of the lateral portion of the groove form neural folds. The apposition of the neural folds in the midline forms the neural tube.
- Malformations at dorsal induction include anencephaly, cephalocele, and Chiari 2 malformation.
- Secondary neurulation involves the formation of the distal spine, including the skull, dura, pia, and vertebrae, at 4–5 weeks. Abnormalities at this phase result in spinal dysraphic disorders like spina bifida occulta, meningocele, lipomeningocele, neurenteric cysts, dermal sinus, caudal regression syndrome, etc., which will be discussed in the next section.
- 2) Ventral induction involves formation of primary brain vesicles by rostral expansion of the neural tube. The proximal two-thirds of the neural tube develops into the future brain, with the caudal one-third developing into the future spinal cord. The lumen of the tube develops into the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord.
- Abnormal development at this time results in anomalies such as holoprosencephaly, hydrocephalus, aqueductal stenosis, corpus callosum agenesis, and posterior fossa malformations such as the Dandy-Walker malformation, cerebellar hypoplasia, and rhombencephalosynapsis.
- 3) Neuronal proliferation, differentiation, migration, and histogenesis occur at around 8–22 weeks of gestation. At this time, neurons migrate peripherally from the germinal matrix (that lines the ventricular surface) to the pia mater/cortex. Brain insults during this time result in abnormalities like lissencephaly (smooth brain) to schizencephaly (split brain), polymicrogyria, laminar/focal heterotopia, microcephaly, megalencephaly, focal cortical dysplasia, hemimegalencephaly, schizencephaly, vascular anomalies, and phakomatoses.
- 4) Myelination will be discussed in Chapter 6.
Case Studies
Chiari Malformations
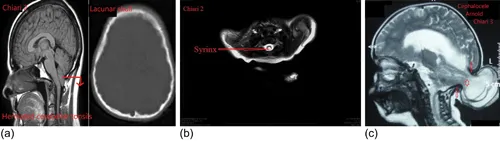
Clinical
IMAGING
Chiari 0 Malformation
Chiari 1 Malformation
- Syringohydromyelia (syrinx) – CSF accumulation within the spinal cord
- Hydrocephalus
- Osseous anomalies like basilar invagination, atlanto-occipital assimilation, platybasia, and Klippel-Feil syndrome
Chiari 1.5 Malformation
Chiari 2 Malformation
- Hydrocephalus
- Lateral ventricles – colpocephaly
- 3rd ventricle – large massa intermedia
- 4th ventricle – tube-like, elongated, and inferiorly displaced
- Brain...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half-Title
- Title
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- About the Author
- Abbreviations
- PART I THE BRAIN
- PART II: THE SPINE
- PART III: THE HEAD AND NECK
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app