
- 70 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Learn Python Programming the Easy and Fun Way
About this book
This book is written with the intention to let readers understand and learn Python programming in a fun and easy way. Basically everybody finds it hard to understand programming language. However with the right techniques and programming logics, anyone can learn Python programming easily.In today's industry, Python programming is widely used for Big Data, Internet of Things, Geographical information, basic mathematical functions in school, university projects and etc. This book caters for all level of users who wants to explorer Python programming language. This book also covers important programming logics like bubble sorting, timer program, queen card program, running numbers, displaying prime numbers and etc to help to build up the programming skills.All the programming steps and screenshots are clearly demonstrated in this book. Anyone completes reading and practicing sample codes of this book should be ready to take up good Python projects to further enhance their programming skills. All the programming logics has been utilized in many Python trainings and workshops.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
b = 2
- Boolean - The simplest data type is boolean, it represents the truth values which are False and True.
- Integer - Normal integers or numbers. Eg. 4321
- Long - these numbers are of unlimited size. Eg.42000000000000000000L
- Float - Floating-point numbers for example: 42.11, 3.1415e-10
- String - A string type object is a sequence of characters from left to right order.
- List - A list is a container which holds comma-separated values. Eg. [1,4,6,7]
- Object - Objects get their variables and functions from classes. Eg. class MySampleClass: variable = "Hello World"
- None - This type has a single value. There is a single object with this value.
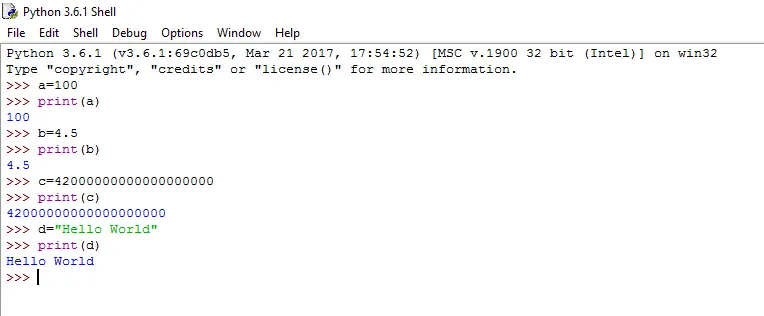
Table of contents
- Learn Python Programming the Easy and Fun Way
- Contents
- Foreword
- About the Author
- Introduction : What is Python Programming?
- Common Usage of Python Programming
- Installation Steps For Python Compiler
- Chapter 1 : Values and Variables
- 1.1 What is a variable?
- 1.2 Python's Identifiers
- 1.3 Integers and Strings
- 1.4 Floating Numbers
- 1.5 String Manipulation
- Chapter 2 : Conditions and Iterations
- 2.1 Conditional Statements
- 2.1.1 The Guessing Number Coding Program
- 2.1.2 The Queen Card Coding Program
- 2.2 Looping
- 2.2.1 Running Numbers Coding Program
- 2.2.2 Simple Timer Coding Program
- 2.2.3 Bubble Sorting of Numbers
- 2.3 Control Statements
- 2.3.1 Sample Break Statement
- 2.3.2 Sample Continue Statement
- 2.3.3 Sample Pass Statement
- Chapter 3 : List,Tuples and Dictionaries
- 3.1 Lists
- 3.2 Tuple
- 3.3 Dictionaries
- Chapter 4 : Functions,Modules and Exception Handling
- 4.1 Functions
- 4.2 Modules
- 4.3 Exception Handling
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app