
Digital Finance
Security Tokens and Unlocking the Real Potential of Blockchain
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Explores how the financial industry will be affected by developments in blockchain and cryptocurrencies at the dawn of a new digital age in finance?
Our financial system is in the midst ofa digital revolution. Blockchain, viewed by many experts as "the most important invention since the Internet, " haschangedthe way we exchange value and information. Although most people are aware of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, fewunderstandhowsecurity tokens—digitized forms of traditional ownership certificates—candriveblockchainto reach its fullestpotentialbyofferinginvestors features and innovations that are simply not possible with paper certificates.
Digital Finance: Security Tokens and Unlocking the Real Potential of Blockchain explainshowthe integration of blockchain and security token technology willtransform the current financial infrastructure and radically improve efficiency, transparency, and security. Using clear language and an easy-to-follow framework, author Baxter Hines draws upon his decades' experience in the financial industry toaddresshowthedigitizationof assetswilldrive cost reductions, enhance flexibility, andpave the way fornew business models and revenue streamsfor years to come. Filled with real-world case studies and expert insights on the latestopportunities andtrends, such as the COVID-19 pandemic'srole inacceleratingthe adoption of blockchain, this must-have resource:
- Shows how blockchainanddistributed ledger technology are disrupting the financial industry
- Explains what security tokensareandwhythey are the next major breakthrough for investing
- Highlightshowblockchain technology has created newand moreefficient ways of fund raising and investing
- Identifiesthewayscompanieslike IBM, Fidelity Investments, and AXA are deploying blockchain and tokenized solutions
- Describes howassets only available to institutional investors could become marketed to the mainstream
- Discussesthe impact that security tokens will have on real assets such as stocks, real estate, bonds, and derivatives
- Provides insight into how centralbanksaround the worldare embracingblockchain and beginning to issue digital currencies
Digital Finance: Security Tokens and Unlocking the Real Potential of Blockchain is essential reading for financial professionals, general investors, finance and technology students, regulators, legal professionals, and users of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
PART I
THE MAGIC LEDGER
CHAPTER 1
BLOCKCHAIN BASICS
- Blockchain provides a highly effective means for exchanging value.
- Blockchain technology is made up of three main elements: accounting, computer science, and governance systems.
- Distributed ledger technology is the mechanism by which transactions are recorded and relayed to all participants on a blockchain.
- By design, blockchains are trustworthy, secure, transparent, efficient, and innovative.
What Is Blockchain?
Foundational Elements of Blockchain
Accounting
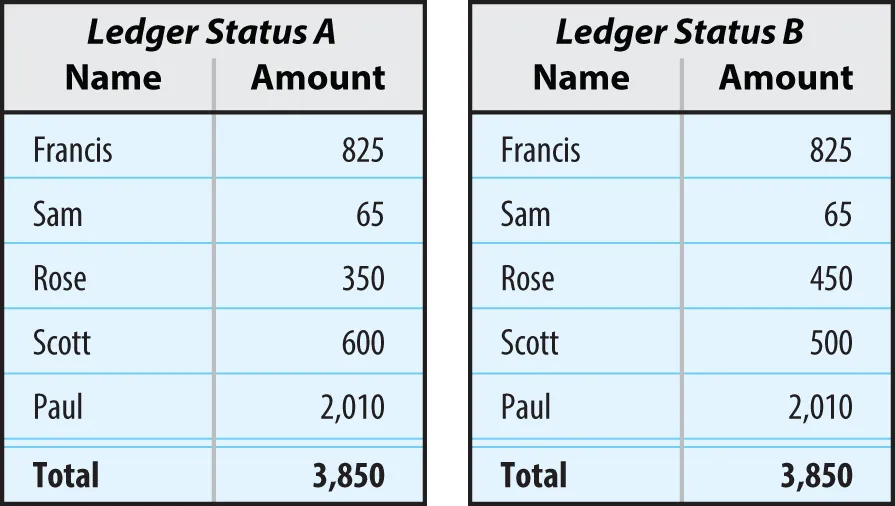

- Identifying the parties involved and the provisioning of significant proofs of identities
- Acknowledging that the parties involved are of proper capacity to engage in what is intended
- Witnessing the state of a document
- Attesting to the seals and signatures contained in that document
- Recording the signatures along with the timing
- Delivering copies of the document to all relevant parties
Computer Science
- Public blockchain networks have no restrictions whatsoever as to who can access them. If you can find an internet connection, you can participate in and validate the activities on the blockchain. Ethereum and Bitcoin are two well‐known blockchain platforms that use public networks.
- Private blockchain networks require permission to join. Typically, a network administrator has rights to grant this access.
- Hybrid blockchain networks have a combination of characteristics from both public and private networks. Various factors determine the information on the blockchain that is made available to the public or held back for permissioned use. Dragonchain operates on a hybrid network.
- Consortium blockchain networks could be described as semi‐d...
Table of contents
- COVER
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
- TITLE PAGE
- COPYRIGHT
- DEDICATION
- DISCLAIMER NOTICE:
- ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- PREFACE
- INTRODUCTION
- PART I: THE MAGIC LEDGER
- PART II: CREATING THE DIGITAL WRAPPER
- PART III: REALIZING THE POTENTIAL OF SECURITY TOKENS
- CONCLUDING THOUGHTS
- ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
- ABOUT THE AUTHOR
- INDEX
- END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT